Credit: Met Office
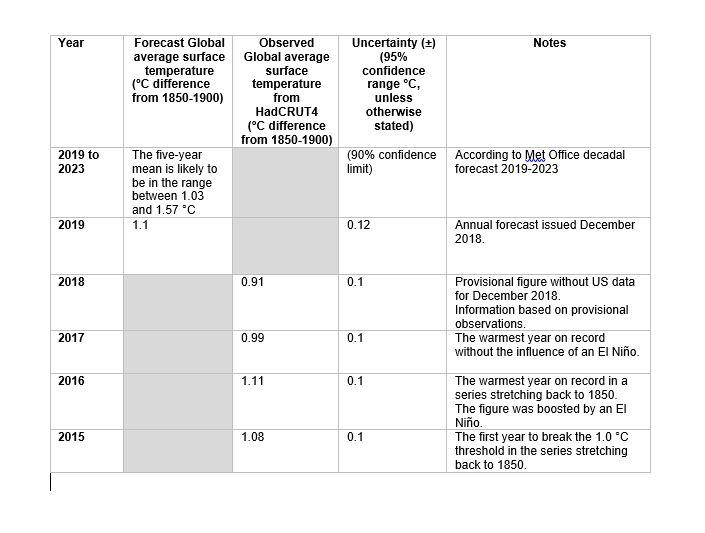
The forecast for the global average surface temperature for the five-year period to 2023 is predicted to be near or above 1.0 °C above pre-industrial levels, says the Met Office. If the observations for the next five years track the forecast that would make the decade from 2014 to 2023 the warmest run of years since records began.
Today’s figures released by the Met Office include data from a number of sources including the latest publication of provisional figures for 2018 and the publication of the latest Met Office decadal forecast to 2023.
Records for annual global average temperature extend back to 1850.
Professor Adam Scaife, Head of Long-Range Prediction at the Met Office said: “2015 was the first year that global annual average surface temperatures reached 1.0 °C above pre-industrial levels and the following three years have all remained close to this level. The global average temperature between now and 2023 is predicted to remain high, potentially making the decade from 2014 the warmest in more than 150 years of records.”
Averaged over the five-year period 2019-2023, forecast patterns suggest enhanced warming is likely over much of the globe, especially over land and at high northern latitudes, particularly the Arctic region.
Dr Doug Smith, Met Office Research Fellow said, “A run of temperatures of 1.0 °C or above would increase the risk of a temporary excursion above the threshold of 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels. Predictions now suggest around a 10 per cent chance of at least one year between 2019 and 2023 temporarily exceeding 1.5 °C.”
Alongside this forecast, 2018 is today cited to be nominally the fourth warmest year on record globally in data released by the Met Office, at 0.91±0.1°C above the long-term pre-industrial average. It follows 2015, 2016 and 2017, which are the three warmest years in the 169-year record of the HadCRUT4 dataset.
Professor Tim Osborn, director of the University of East Anglia’s Climatic Research Unit, which co-produces the HadCRUT4 global temperature figures with the Met Office Hadley Centre, said: “The warmth of 2018 is in line with the long-term warming trend driven by the world’s emissions of greenhouse gases.”
The effects of climate change are not limited to surface temperature. Warming of the climate system is seen across a range of climate indicators that build a picture of global changes occurring across the land, atmosphere, oceans and ice.
The Met Office decadal forecast show that global average surface temperatures may be close to reaching 1.5 °C, but this would be a temporary exceedance rather than the climatological level of warming in the Paris 1.5 °C threshold.
###
Media Contact
Cat Bartman
[email protected]
44-016-035-93007




