Post-mortem changes may shed light on important brain studies
Credit: Dr. Jeffrey Loeb/UIC
In the hours after we die, certain cells in the human brain are still active. Some cells even increase their activity and grow to gargantuan proportions, according to new research from the University of Illinois Chicago.
In a newly published study in the journal Scientific Reports, the UIC researchers analyzed gene expression in fresh brain tissue — which was collected during routine brain surgery — at multiple times after removal to simulate the post-mortem interval and death. They found that gene expression in some cells actually increased after death.
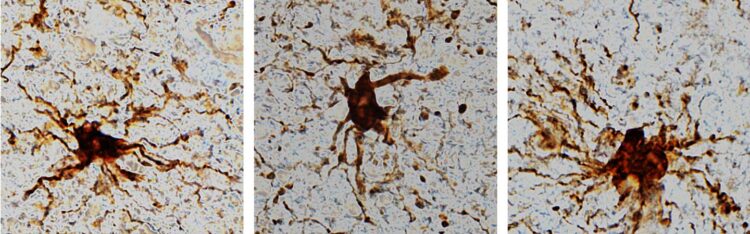
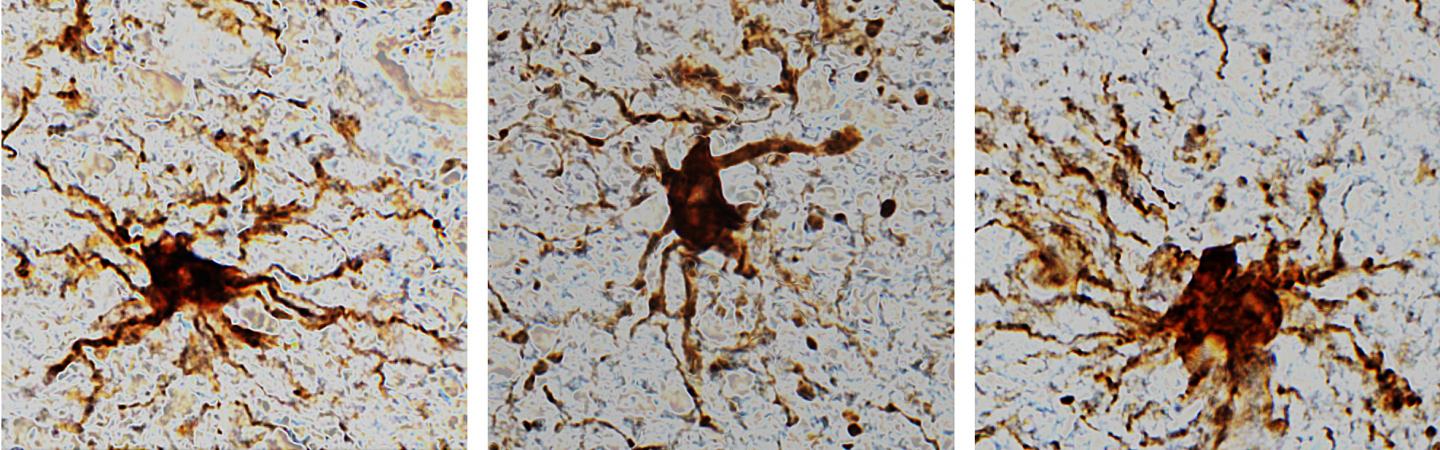
These ‘zombie genes’ — those that increased expression after the post-mortem interval — were specific to one type of cell: inflammatory cells called glial cells. The researchers observed that glial cells grow and sprout long arm-like appendages for many hours after death.
“That glial cells enlarge after death isn’t too surprising given that they are inflammatory and their job is to clean things up after brain injuries like oxygen deprivation or stroke,” said Dr. Jeffrey Loeb, the John S. Garvin Professor and head of neurology and rehabilitation at the UIC College of Medicine and corresponding author on the paper.
What’s significant, Loeb said, is the implications of this discovery — most research studies that use postmortem human brain tissues to find treatments and potential cures for disorders such as autism, schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease, do not account for the post-mortem gene expression or cell activity.
“Most studies assume that everything in the brain stops when the heart stops beating, but this is not so,” Loeb said. “Our findings will be needed to interpret research on human brain tissues. We just haven’t quantified these changes until now.”
Loeb and his team noticed that the global pattern of gene expression in fresh human brain tissue didn’t match any of the published reports of postmortem brain gene expression from people without neurological disorders or from people with a wide variety of neurological disorders, ranging from autism to Alzheimer’s.
“We decided to run a simulated death experiment by looking at the expression of all human genes, at time points from 0 to 24 hours, from a large block of recently collected brain tissues, which were allowed to sit at room temperature to replicate the postmortem interval,” Loeb said.
Loeb and colleagues are at a particular advantage when it comes to studying brain tissue. Loeb is director of the UI NeuroRepository, a bank of human brain tissues from patients with neurological disorders who have consented to having tissue collected and stored for research either after they die, or during standard of care surgery to treat disorders such as epilepsy. For example, during certain surgeries to treat epilepsy, epileptic brain tissue is removed to help eliminate seizures. Not all of the tissue is needed for pathological diagnosis, so some can be used for research. This is the tissue that Loeb and colleagues analyzed in their research.
They found that about 80% of the genes analyzed remained relatively stable for 24 hours — their expression didn’t change much. These included genes often referred to as housekeeping genes that provide basic cellular functions and are commonly used in research studies to show the quality of the tissue. Another group of genes, known to be present in neurons and shown to be intricately involved in human brain activity such as memory, thinking and seizure activity, rapidly degraded in the hours after death. These genes are important to researchers studying disorders like schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease, Loeb said.
A third group of genes — the ‘zombie genes’ — increased their activity at the same time the neuronal genes were ramping down. The pattern of post-mortem changes peaked at about 12 hours.
“Our findings don’t mean that we should throw away human tissue research programs, it just means that researchers need to take into account these genetic and cellular changes, and reduce the post-mortem interval as much as possible to reduce the magnitude of these changes,” Loeb said. “The good news from our findings is that we now know which genes and cell types are stable, which degrade, and which increase over time so that results from postmortem brain studies can be better understood.”
###
Fabien Dachet, Tibor Valyi-Nagy, Kunwar Narayan, Anna Serafini and Gayatry Mohapatra of UIC; James Brown and Susan Celniker of Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory; Nathan Boley of the University of California, Berkeley; and Thomas Gingeras of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory are co-authors on the paper.
This research was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01NS109515, R56NS083527, and UL1TR002003).
Media Contact
Jackie Carey
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.