By illuminating a sample surface with short laser beam pulses, it is possible to film sequences of various chemical and physical reactions. A research team that included researchers from the University of Gothenburg has now developed the world’s fastest single-shot laser camera, which is at least a thousand times faster than today’s most modern equipment for combustion diagnostics. The discovery has enormous significance for studying the lightning-fast combustion of hydrocarbons.
Credit: Yogeshwar Nath Mishra and Peng Wang
By illuminating a sample surface with short laser beam pulses, it is possible to film sequences of various chemical and physical reactions. A research team that included researchers from the University of Gothenburg has now developed the world’s fastest single-shot laser camera, which is at least a thousand times faster than today’s most modern equipment for combustion diagnostics. The discovery has enormous significance for studying the lightning-fast combustion of hydrocarbons.
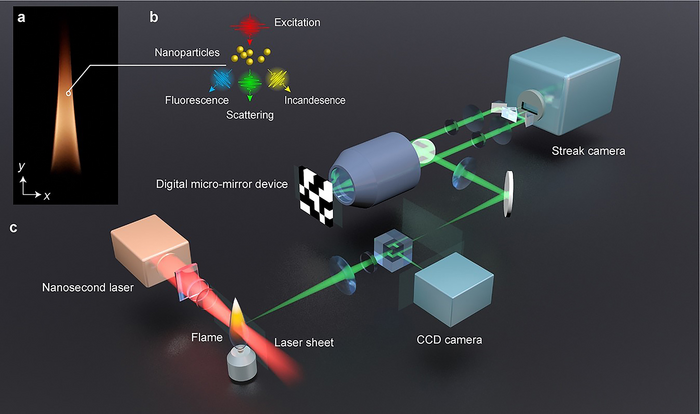
What happens to a material that is burned in different conditions? To investigate this question, researchers use a laser camera that photographs the material in a two-dimensional layer, known as LS CUP (single-shot laser sheet compressed ultrafast photography). By observing the sample from the side, it is possible to see what reactions and emissions occur over time and space. Researchers have used LS-CUP to study the combustion of various hydrocarbons.
12.5 billion images per second
Physicists from the University of Gothenburg, together with colleagues in the US and Germany, have developed an ultrafast laser camera that can create videos with a record-fast speed of 12.5 billion images per second, which is at least a thousand times faster than today’s best laser equipment. This has enabled researchers to illustrate combustion with a time resolution that has never been achieved before.
“The more pictures taken, the more precisely we can follow the course of events. Hydrocarbon fuel combustion produces nano-sized soot particles, various light phenomena and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, PAH, which are hazardous to the environment,” says Yogeshwar Nath Mishra, who was one of the researchers at the University of Gothenburg and who is now presenting the results in a scientific article in the journal Light: Science & Applications.
Short-lived soot particles
Soot particles from hydrocarbons constitute 70% of the material in interstellar space and are also interesting nanomaterial with applications in electronics and energy. Soot particles and aromatic hydrocarbons are extremely short-lived, with a lifespan measured in nanoseconds when they burn up. Combustion is characterised by extremely fast reactions that are not repeated. Studying combustion requires ultrafast methods to capture images, which researchers have now achieved with this new laser camera.
“Before, problems arose when the camera was limited to a few million images per second. Producing two-dimensional pictures of different types of combustion has required repeated laser pulses, which impacts the combustion temperature when the laser adds energy,” says Yogeshwar Nath Mishra.
Application in many research fields
The new laser camera takes a unique picture with a single laser pulse. The image speed is up to 10 billion pictures per second and can easily be adapted to observe all types of laser-induced signals throughout the particle’s lifespan. Applications extend far beyond combustion research and can be used broadly in physics, chemistry, biology and medicine, energy and environmental research.
DOI
10.1038/s41377-023-01095-5
Method of Research
Randomized controlled/clinical trial
Article Title
Single-pulse real-time billion-frames-per-second planar imaging of ultrafast nanoparticle-laser dynamics and temperature in flames
Article Publication Date
21-Feb-2023




