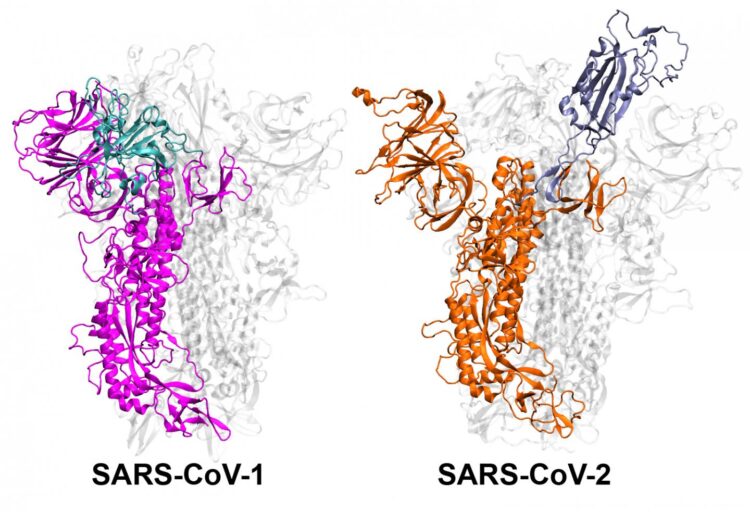
The coronaviruses that cause SARS and COVID-19 have spike proteins that move into ‘active’ and ‘inactive’ positions, and new research indicates how those molecular movements may make the COVID-19 virus more infectious compared to the SARS virus
Credit: Image courtesy of Mahmoud Moradi.
ROCKVILLE, MD – Coronavirus outbreaks have occurred periodically, but none have been as devastating as the COVID-19 pandemic. Vivek Govind Kumar, a graduate student, and colleagues in the lab of Mahmoud Moradi at the University of Arkansas, have discovered one reason that likely makes SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, so much more infectious than SARS-CoV-1, which caused the 2003 SARS outbreak. Moradi will present the research on Thursday, February 25 at the 65th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society
The first step in coronavirus infection is for the virus to enter cells. For this entry, the spike proteins on the outside of the SARS-CoV virus must reposition. Scientists know the position of the “inactive” and “active” states of the spike proteins of both the SARS-CoV-1 and -2 viruses, but Moradi and colleagues wanted to study how the spikes moved from one position to another and the dynamics of those movements. They turned to molecular simulations, performed at the Texas Advanced Computing Center and the Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center.
“We discovered in these simulations that SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 have completely different ways of changing their shape, and on different time scales,” Moradi says. “SARS-CoV-1 moves faster, it activates and deactivates, which doesn’t give it as much time to stick to the human cell because it’s not as stable. SARS-CoV-2, on the other hand, is stable and ready to attack,” he added.
There is a region at the tail end of the spike protein that has largely been ignored in research, Moradi says, but that piece is important in the stability of the protein. Mutations in that region could affect the transmissibility, he says, and are worth paying attention to. The other implication for their research is “we could design therapeutics that alter the dynamics and make the inactive state more stable, thereby promoting the deactivation of SARS-CoV-2. That is a strategy that hasn’t yet been adopted,” Moradi explained.
It is valuable to be able to do these kinds of simulations, Moradi says, in the event a new coronavirus emerges, or SARS-CoV-2 mutates so that they can predict if the new virus or variant could be higher in transmissibility and infection. They have now begun studying the new SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 variant in the lab to detect differences in its movements.
###
Media Contact
Leann Fox
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/