Provide ICAO a mandatory information for cosmic ray radiation protection management of aircrews
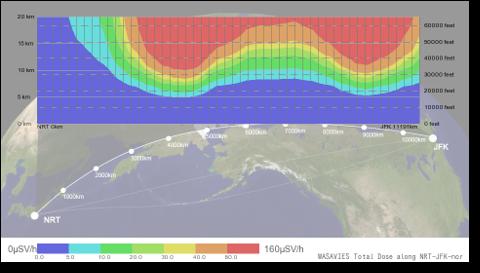
Credit: National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, National Institute of Polar Research, Hiroshima University, National Institute of Technology, Ibaraki College, Nagoya University
Highlights
- Develop a system to estimate radiation dose due to solar energetic particles in real-time
- Possible dose estimation up to 100 km above a ground at anywhere in the Earth
- Provide ICAO a mandatory information for cosmic ray radiation protection management of aircrews
Abstract
A research group led by the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), and the National Institute of Polar Research (NIPR) succeeded to develop a WArning System for AVIation Exposure to Solar energetic particles (WASAVIES), which can estimate radiation dose due to solar energetic particles in real-time just after the solar flare occurrence.
This system can estimate radiation dose up to 100 km above a ground at anywhere in the Earth and monitor aircrew radiation dose in real-time. This system enables to give information on the aircrew radiation dose as a space weather information used for aviation operation management.
NICT starts to provide information on HF communications, GNSS positioning, and radiation exposure as the only Asian center for the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) space weather centers. The system will have been used as the mandatory information to operate the ICAO center.
Background
Recently, needs of space weather information are getting higher in various fields. Especially, the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) decided to use space weather information for civil aviation flight operation in 2011. NICT was elected as the only Asian center for the ICAO space weather center, and starts a service on November 7, 2019.
ICAO concerns an increasing radiation exposure by cosmic rays as well as a disruption of HF communication and increasing an error of GNSS measurement caused mainly by solar activities, therefore, ICAO requires information on radiation dose by cosmic rays as space weather information. Since cosmic ray exposure is recognized as occupational radiation exposure, radiation dose management of aircrews is required for the civil aviation companies. (Almost no increase of radiation dose is expected on the ground.)
In this situation, the research group has developed a warning system for aviation exposure to solar energetic particles aiming to offer information on radiation dose by cosmic rays.
The main components of radiations from space are galactic cosmic rays (GCR) which come from outside the solar system and solar energetic particles (SEP) which sporadically come from the Sun when large solar flares occur. Estimation of radiation dose by GCR is relatively easy because it is almost constant in the short time scale. So, the system to estimate GCR dose is already practical and has been used for radiation exposure management in the several civil aviation companies.
On the other hand, the real-time estimation of radiation dose by SEP had been difficult so far because SEP suddenly increases when a large solar flare occurs and quickly decrease during several hours.
Achievements
We developed real-time SEP radiation dose estimation system, named WASAVIES, which can estimate SEP radiation dose at anywhere in the Earth just after solar flare occasion triggered by real-time detection of a sudden increase of SEP.
Although SEP radiation dose estimation systems have developed in the other countries, these ones used each of only ground-based or satellite-based observation data. On the other hand, our system has achieved high estimation performance by using both ground- and satellite-based observations simultaneously, just after detecting a sudden increase of SEP.
Also, various physical processes can be reproduced by integrating several models developed by researchers with different background field, and high estimation accuracy of SEP radiation dose has been achieved.
This system enables real-time monitoring of SEP radiation dose, and it is expected that the system is used for a civil aviation operation such as rerouting or change of flight altitude as a mandatory information.
This study is a successful example of interdisciplinary research that has been achieved through collaboration among researchers in various fields such as space weather, solar physics, upper atmosphere, nuclear physics, and radiation protection.
Information on WASAVIES is available at https:/
Future Perspective
WASAVIES will further evolve not only for real-time estimation but also to improve the accuracy of prediction of radiation dose up to end of the event. We will push forward the development of the system to apply radiation exposure management for astronauts of manned space missions such as the moon and planet explorations, which will be prosperous in the near future.
NICT strives to contribute to the safer air operation as to providing state-of-the-arts knowledges on space weather to ICAO.
###
Media Contact
Sachiko Hirota
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




