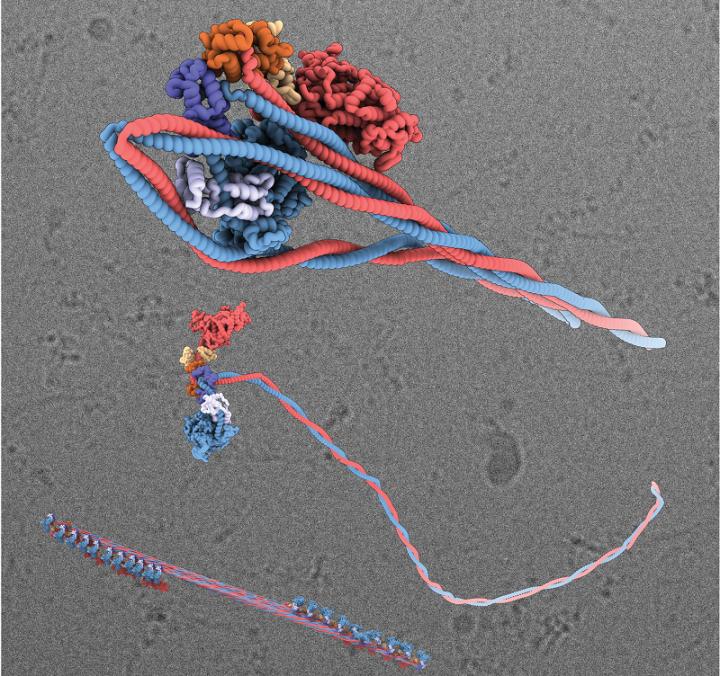
Credit: University of Leeds
A visualisation made from nearly 100,000 electron microscope images has revealed the ingenious way a protein involved in muscle activity shuts itself down to conserve energy.
The protein is called myosin and it is known as a molecular motor because of the way it interacts with other proteins and energy molecules to generate force and movement. It is found inside muscle fibres where it forms long myosin filaments made up of hundreds of individual myosin molecules.
When muscle activity ceases, the process of forming the myosin filaments goes into reverse: the filaments decouple and return to the individual myosin molecule state.
The visualisation – developed by scientists from the University of Leeds in the UK and East Carolina University in the US – has revealed how the structure of the molecule changes. It folds up and becomes more compact, meaning it can be moved more easily to where it is next needed in the cell.
Their findings – Structure of the shutdown state of myosin-2 – are published today (Wednesday, 2 December) in the journal Nature.
When the embargo lifts, the paper can be accessed at: https:/
Structure of myosin
An individual molecule of myosin is large – and is made up of a ‘head’ and a ‘tail’. When in an active state, the tails of the molecules come together to form fibrous myosin filaments. The heads within the filament bind with another protein called actin to produce muscle contraction.
By combing 96,000 electron microscope images, the scientists were able to see how the molecule adopts an inactive form in unprecedented detail. The tail of each molecule wraps itself around the head and is locked in place by key molecular interactions. That process shuts down its activity and makes it easier for the molecule to be recruited to where it is next needed.
Professor Michelle Peckham, from the Astbury Centre for Structural Molecular Biology at Leeds who supervised the research, said: “The analogy here is that the folded myosin is like a Brompton bicycle, kept in a folded state when not needed, and able to be quickly unfolded when it is, by releasing a simple catch.
“The compact folded myosin is also more easily transported through a crowd to where it’s needed.”
Scientists have been aware of the role of myosin in muscle activity for decades. But until now, they were unclear about how this inactive state was formed or how its formation was so highly controlled.
What does the research mean for understanding disease?
There are genetic mutations of myosin linked with certain diseases.
Professor Peckham explained: “Mutations in muscle myosin cause a wide range of muscle diseases. Our research into the structure of myosin and the way it functions help explain how mutations or defects in the protein may be causing disease. That opens the door to the possibility that scientists can develop therapeutic approaches to ensure myosin functions normally.”
The Astbury Centre for Structural Molecular Biology at the University of Leeds is an interdisciplinary research group involving biologists, physicists and chemists to investigate the molecular basis of life. One of the major research themes is to understand the process of protein folding.
The research was funded by the Medical Research Council and Wellcome Trust.
Note to Editors
The image shows, top, a 3D visualisation of the shutdown state of the myosin molecule, where the tail has wrapped around the head; below that is a myosin molecule in its active state and at the bottom, a myosin filament. Picture credit: University of Leeds.
University of Leeds
The University of Leeds is one of the largest higher education institutions in the UK, with more than 38,000 students from more than 150 different countries, and a member of the Russell Group of research-intensive universities. The University plays a significant role in the Turing, Rosalind Franklin and Royce Institutes.??
We are a top ten university for research and impact power in the UK, according to the 2014 Research Excellence Framework, and are in the top 100 of the QS World University Rankings 2020.??
The University was awarded a Gold rating by the Government’s Teaching Excellence Framework in 2017 recognising its ‘consistently outstanding’ teaching and learning provision. Twenty-six of our academics have been awarded National Teaching Fellowships – more than any other institution in England, Northern Ireland and Wales – reflecting the excellence of our teaching. http://www.
###
Media Contact
David Lewis
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




