A University of Hawaiʻi-led discovery of an immense bubble 820 million light years from Earth is believed to be a fossil-like remnant of the birth of the universe. Astronomer Brent Tully from the UH Institute for Astronomy and his team unexpectedly found the bubble within a web of galaxies. The entity has been given the name Hoʻoleilana, a term drawn from the Kumulipo, a Hawaiian creation chant evoking the origin of structure.
Credit: Frédéric Durillon, Animea Studio; Daniel Pomarède, IRFU, CEA University Paris-Saclay. This work benefited from a government funding by France 2030 (P2I – Graduate School of Physics) under reference ANR-11-IDEX-0003.
A University of Hawaiʻi-led discovery of an immense bubble 820 million light years from Earth is believed to be a fossil-like remnant of the birth of the universe. Astronomer Brent Tully from the UH Institute for Astronomy and his team unexpectedly found the bubble within a web of galaxies. The entity has been given the name Hoʻoleilana, a term drawn from the Kumulipo, a Hawaiian creation chant evoking the origin of structure.
The new findings published in The Astrophysical Journal, mention these massive structures are predicted by the Big Bang theory, as the result of 3D ripples found in the material of the early universe, known as Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO).
“We were not looking for it. It is so huge that it spills to the edges of the sector of the sky that we were analyzing,” explained Tully. “As an enhancement in the density of galaxies it is a much stronger feature than expected. The very large diameter of one billion light years is beyond theoretical expectations. If its formation and evolution are in accordance with theory, this BAO is closer than anticipated, implying a high value for the expansion rate of the universe.”
Astronomers located the bubble using data from Cosmicflows-4, which is to date, the largest compilation of precise distances to galaxies. Tully co-published the exceptional catalog in fall 2022. His team of researchers believe this may be the first time astronomers identified an individual structure associated with a BAO. The discovery could help bolster scientists’ knowledge of the effects of galaxy evolution.
Related UH News story: UH astronomers map distances to 56,000 galaxies, largest-ever catalog, September 26, 2022
Enormous bubbles of matter
In the well-established Big Bang theory, during the first 400,000 years, the universe is a cauldron of hot plasma similar to the interior of the Sun. Within a plasma, electrons were separated from the atomic nuclei. During this period, regions with slightly higher density began to collapse under gravity, even as the intense bath of radiation attempted to push matter apart. This struggle between gravity and radiation made the plasma oscillate or ripple and spread outward.
The largest ripples in the early universe depended on the distance a sound wave could travel. Set by the speed of sound in the plasma, this distance was almost 500 million light years, and was fixed once the universe cooled and stopped being a plasma, leaving vast three-dimensional ripples. Throughout the eons, galaxies formed at the density peaks, in enormous bubble-like structures. Patterns in the distribution of galaxies, properly discerned, could reveal the properties of these ancient messengers.
“I am the cartographer of the group, and mapping Hoʻoleilana in three dimensions helps us understand its content and relationship with its surroundings,” said researcher Daniel Pomarede of CEA Paris-Saclay University in France. “It was an amazing process to construct this map and see how the giant shell structure of Hoʻoleilana is composed of elements that were identified in the past as being themselves some of the largest structures of the universe.”
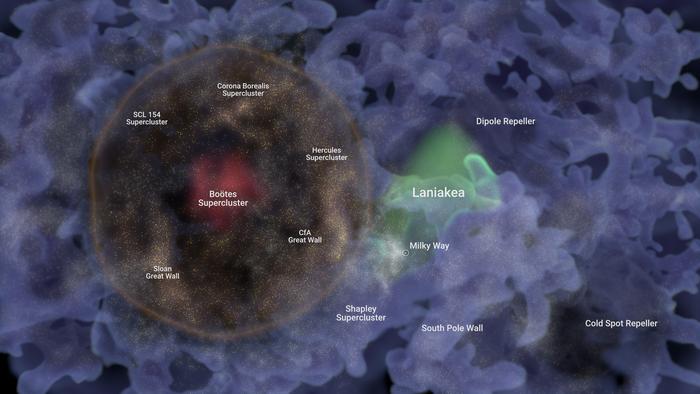
This same team of researchers also identified the Laniākea Supercluster in 2014. That structure, which includes the Milky Way, is small in comparison. Stretching at a diameter of about 500 million light years, Laniākea extends to the near edge of this much larger bubble.
Uncovering a single BAO
Tully’s team discovered that Hoʻoleilana had been noted in a 2016 research paper as the most prominent of several shell-like structures seen in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. However, the earlier work did not reveal the full extent of the structure, and that team did not conclude they had found a BAO.
Using the Cosmicflows-4 catalog, the researchers were able to see a full spherical shell of galaxies, identify its center, and show that there is a statistical enhancement in the density of galaxies in all directions from that center. Hoʻoleilana encompasses many well-known structures previously found by astronomers, such as the Harvard/Smithsonian Great Wall containing the Coma Cluster, the Hercules Cluster and the Sloan Great Wall. The Boötes Supercluster resides at its center. The historic Boötes Void, a massive empty spherical region, lies inside Hoʻoleilana.
The implications of Hoʻoleilana
Tests with simulations have demonstrated that the shell structure identified as Hoʻoleilana has less than 1% probability of being a statistical accident. Hoʻoleilana has the properties of a theoretically anticipated baryon acoustic oscillation, including the prominence at its center of a rich supercluster, however it stands out stronger than expected. In detail, Hoʻoleilana is slightly larger than anticipated from the theory of the standard model of cosmology, and what has been found from prior statistical pair-wise studies of galaxy separations. The size is in accord with observations of the local expansion rate of the universe and of galaxy flows on large scales that also hint at subtle problems with the standard model.
Journal
The Astrophysical Journal
DOI
10.3847/1538-4357/aceaf3
Article Title
Ho’oleilana: An Individual Baryon Acoustic Oscillation?
Article Publication Date
5-Sep-2023




