Temperature is a critical parameter in determining cleansing efficiency during a root canal
Credit: Hanhui Jin
WASHINGTON, August 11, 2020 — Scientists used computational fluid dynamics to determine the effect of temperature on root canal cleaning efficiency. Higher temperatures can, to a point, improve cleansing, but this benefit falls off if the temperature gets too high.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, scientists from China and the U.S. report calculations with a model of the conical-shaped root canal inside a tooth. This cavity is usually filled with pulp. When the pulp becomes inflamed or infected, an endodontist removes the infected pulp, and then cleans, shapes and fills the canal. The apex is then sealed.
A crucial step in this common dental procedure is irrigation, or rinsing, of the root canal cavity with an antibacterial solution, such as sodium hypochlorite. Efficient cleaning and successful destruction of any bacteria or other microbes in the cavity depend on the penetration and cleaning ability of the irrigation fluid.
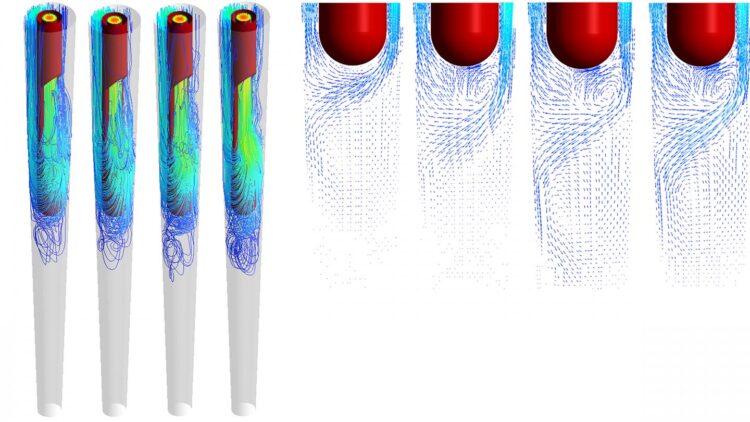
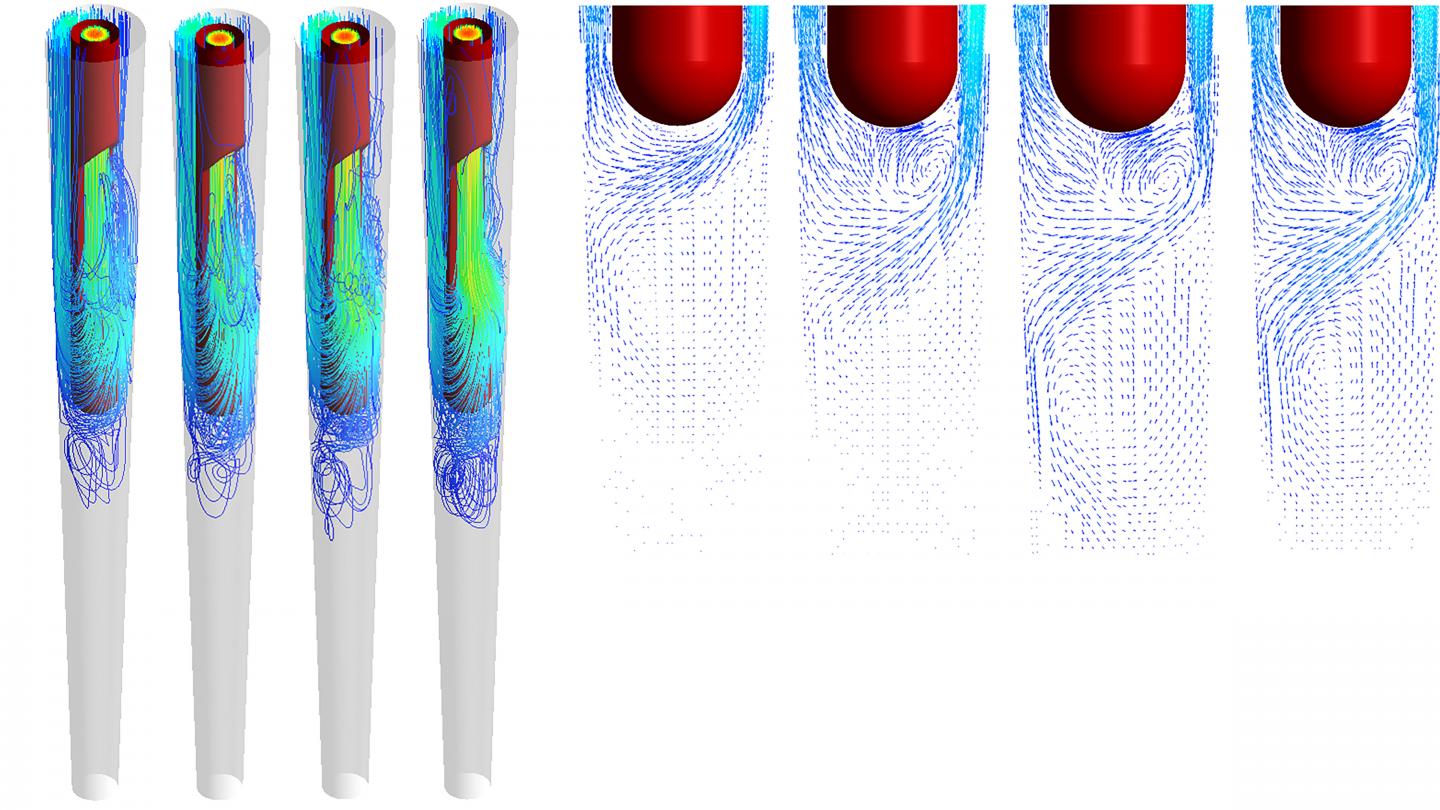
The computational investigation used a structured mesh as a model of the conical root canal cavity. More than 1 million cells in the mesh completely and accurately described both the root canal and the side-vented needle through which the hypochlorite solution is injected. Fluid dynamics equations were used to model flow of the hypochlorite solution.
The scientists varied the fluid velocity, temperature and input power to determine the most efficient cleansing technique. As expected, higher fluid velocities lead to better cleansing. Perhaps counterintuitively, cleansing efficiency is higher on the wall behind the needle vent.
“The effective area on the root canal wall, in which the shear stress exceeds the critical value to clean the wall, is usually larger behind the needle outlet than in front of it,” said author Hanhui Jin.
The maximum shear stress also usually occurs on the wall behind the needle outlet, Jin explained.
The investigators also looked at the effect of temperature on cleansing. They considered four different temperatures: 22 Celsius, which is room temperature; 37 C, which is body temperature; and two higher temperatures of 45 C and 60 C. Temperatures above 60 C are painful for the patient and tend to cause root canal damage.
Increasing the temperature to 45 C, while holding the fluid velocity fixed, improved the depth of cleansing and the cleansing span across the canal’s width, but further increases in temperature beyond 45 C actually decreased the cleansing efficiency.
The investigators considered the effect of power consumption by the irrigation device. If the power consumption is held at a fixed value, the effect of temperature on cleansing efficiency is much more pronounced.
“The fluid circulation within the canal is clearly enlarged when the temperature is increased,” said Jin. Therefore, careful control of both power consumption and temperature leads to increased cleaning efficiency.
###
The article, “Effect of inflow temperature on root canal irrigation: A computational fluid dynamics study,” is authored by Mingzhou Yu, Zhengqiu Huang, Na Zhou, Zihan Xu, Shuli Deng and Hanhui Jin. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on Aug. 11, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0014737). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.