In recent news, there has been a case where a patient experienced pain due to a surgical procedure involving sutures, resulting in the unintended presence of gauze within the patient’s body. Gauze is typically employed to control bleeding during medical interventions, aiding in hemostasis. However, when inadvertently left in the body, it can lead to inflammation and infection. Addressing this issue, recent research has been published by researchers focusing on a hemostatic agent derived from mussels and silkworm cocoons. This hemostatic agent has garnered attention in the academic community due to its efficacy in clotting blood and its safety within the body.
Credit: POSTECH
In recent news, there has been a case where a patient experienced pain due to a surgical procedure involving sutures, resulting in the unintended presence of gauze within the patient’s body. Gauze is typically employed to control bleeding during medical interventions, aiding in hemostasis. However, when inadvertently left in the body, it can lead to inflammation and infection. Addressing this issue, recent research has been published by researchers focusing on a hemostatic agent derived from mussels and silkworm cocoons. This hemostatic agent has garnered attention in the academic community due to its efficacy in clotting blood and its safety within the body.
A collaborative team, led by Professor Hyung Joon Cha (Department of Chemical Engineering and the School of Convergence Science and Technology) and Dr. Jaeyun Lee (Department of Chemical Engineering) at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Professor Kye Il Joo (Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science) at Ewha Womans University, and Dr. Jong Won Rhie (Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery) at Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital of the College of Medicine at the Catholic University of Korea, has developed a bilayer nanofiber membrane hemostat using natural proteins derived from mussels and silkworm cocoons. The findings of this research have been recently published online in the latest issue of Small, an international journal specializing in nanoengineering.
Conventional hemostatic agents such as gauze or medical bands are limited to application on the surface of the skin. Although there are certain materials that naturally degrade within the body like fibrin glue and collagen sponges, they necessitate proteins sourced from humans or animals, making them considerably expensive. Moreover, existing hemostatic materials lack consistent adherence to bleeding sites and are prone to infection from external contaminants.
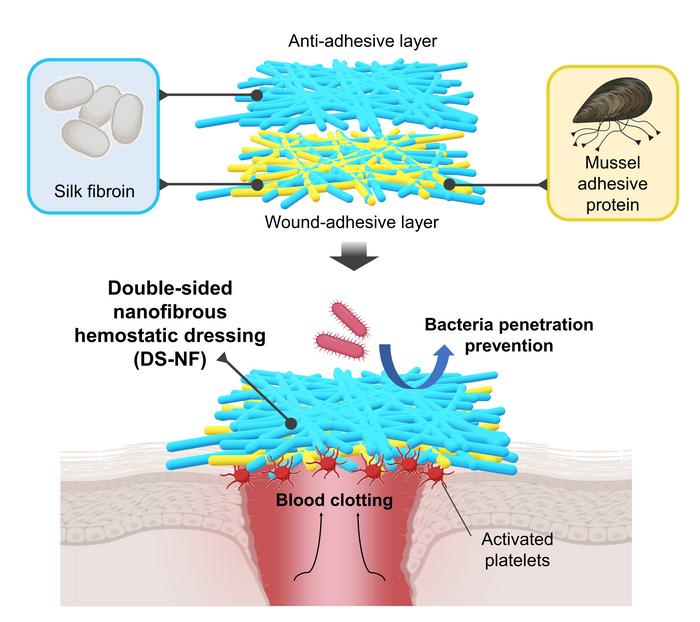
In response, the researchers developed a bilayer adhesive hemostat utilizing mussel adhesive proteins that exhibit strong tissue adhesion underwater and silk fibroin extracted from silkworm cocoons. In the research, mussel adhesive proteins demonstrated excellent hemostatic effects including platelet activation. The researchers employed methanol vapor to modify the secondary structure of silkworm silk proteins, resulting in a nanofiber membrane with a hydrophobic outer surface.
In light of this, the team engineered a hemostatic agent featuring an inner layer with mussel adhesion proteins for wound adhesion and an outer protective layer entirely composed of silkworm silk proteins. Through animal experiments, the hemostatic agent demonstrated rapid acceleration of tissue adhesion and hemostasis in bleeding wounds, effectively preventing the infiltration of water containing infectious agents such as bacteria. Using two proteins that are both highly biocompatible and biodegradable, the researchers have introduced a novel hemostatic agent capable of clotting blood and providing defense against infection.
Professor Hyung Joon Cha of the POSTECH who led the study remarked, “We have validated the exceptional hemostatic performance of a multifunctional topical adhesive hemostatic agent that is derived from nature and is based on degradable proteins in the human body.” He added, “We will continue further research to assess its applicability in real-world patient care or surgical settings.”
The research was conducted with support from the Marine BioMaterials Research Center Program of the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries and the Mid-Career Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Journal
Small
DOI
10.1002/smll.202308833
Article Title
Protective Topical Dual-Sided Nanofibrous Hemostatic Dressing Using Mussel and Silk Proteins with Multifunctionality of Hemostasis and Anti-Bacterial Infiltration
Article Publication Date
7-Jan-2024




