Credit: Image by the research groups
In a study published online in Nature on June 26, research teams led by Dr. YANG Weiwei at the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and Dr. LI Guohui from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of CAS reported a new function of uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose), a metabolic intermediate in the uronic acid pathway: It impairs lung cancer metastasis by accelerating SNAI1 mRNA decay.
This discovery is important because lung cancer is the leading cancer killer in both China and the world, and cancer metastasis is estimated to be responsible for 95% of cancer deaths. Lung cancer alone kills more than 600,000 people each year in China.
Primary malignant tumors can often be effectively treated by traditional therapies such as surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. However, in most cases, traditional therapies have limited effect on metastatic tumors. Therefore, understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying tumor metastasis helps to provide a biomarker for the early detection of tumor metastasis and a new strategy for intervening in metastasis, thus offering patients a better prognosis.
Deregulated metabolism is the hallmark of cancer. Mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes cause alterations to multiple intracellular signaling pathways that affect tumor cell metabolism and re-engineer it to allow enhanced survival and growth. The unique biochemical microenvironment further influences the metabolic phenotype of tumor cells, and thus affects tumor progression, response to therapy and patient outcome.
This study reveals a unique function of UDP-glucose in impairing tumor metastasis, presents a new model of metabolite-regulated protein function, and establishes a new connection between metabolism and RNA stability.
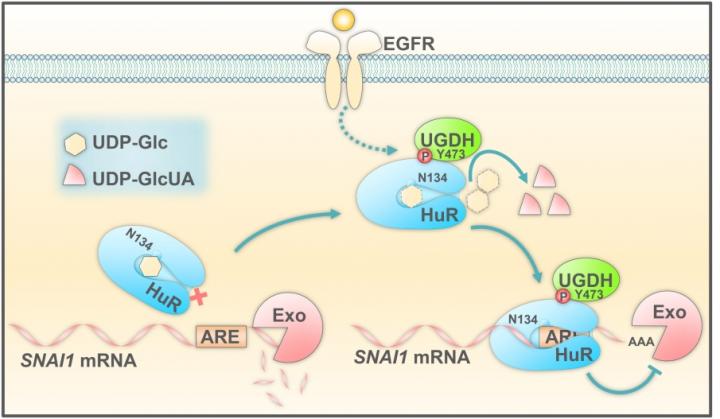
Specifically, the researchers demonstrated that upon epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation, UDP-glucose dehydrogenase (UGDH) is phosphorylated at tyrosine (Y) 473. UGDH is the rate-limiting enzyme in the uronic acid pathway. It catalyzes UDP-glucose to produce UDP-glucuronic acid and participates in the biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycan.
Phosphorylated UGDH binds to HuR and converts UDP-glucose into UDP-glucuronic acid, which attenuates UDP-glucose-mediated inhibition on HuR association with SNAI1 mRNA, thereby enhancing SNAI1 mRNA stability. Increased Snail (encoded by SNAI1) expression in turn initiates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tumor cells, thus promoting tumor cell migration and lung cancer metastasis.
In addition, the scientists found that lower UDP-glucose levels are closely related to the metastasis and recurrence of lung cancer. They observed that UDP-glucose levels in metastatic tumors were much lower than in primary tumors. Patients with distant metastasis had much lower UDP-glucose levels than those without distant metastasis, and patients with high UGDH Y473 phosphorylation in tumor tissues had a higher rate of metastasis and worse prognosis.
###
Media Contact
YANG Weiwei
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




