PNNL researchers discover a new route to forming complex crystals
Credit: (Composite image by Mike Perkins | Pacific Northwest National Laboratory)
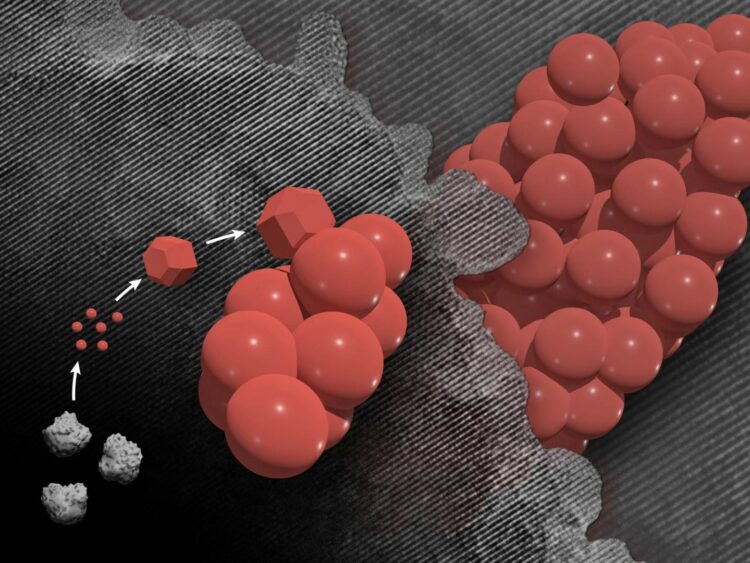
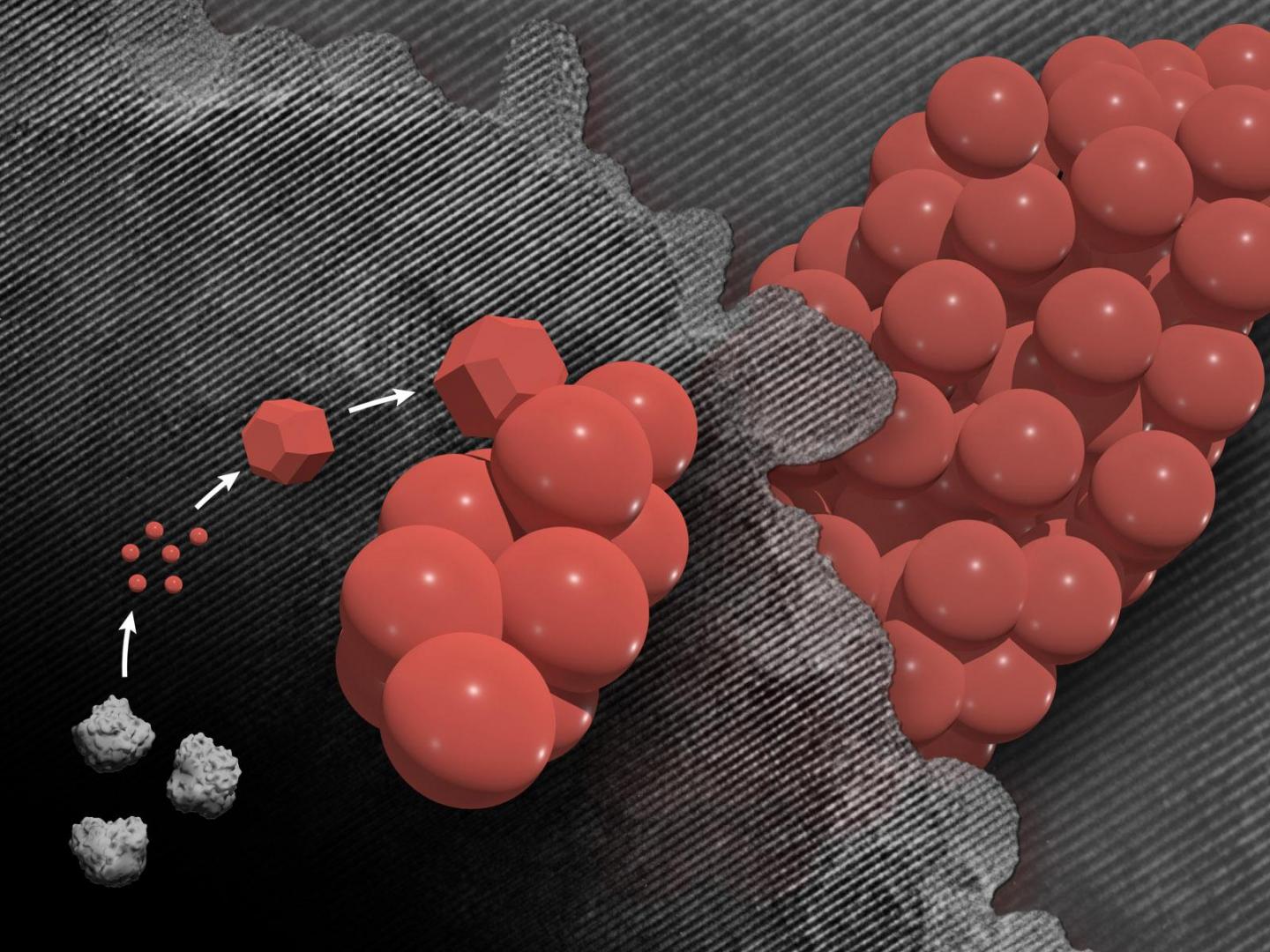
When materials reach extremely small size scales, strange things begin to happen. One of those phenomena is the formation of mesocrystals.
Despite being composed of separate individual crystals, mesocrystals come together to form a larger, fused structure that behaves as a pure, single crystal. However, these processes happen at scales far too small for the human eye to see and their creation is extremely challenging to observe.
Because of these challenges, scientists had not been able to confirm exactly how mesocrystals form.
Now new research by a Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL)-led team used advanced transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques to see mesocrystals form in solution in real time. What they saw runs contrary to conventional wisdom and their insights could one day help scientists design materials for energy storage and understand how minerals in soil form.
Rather than individual crystals nucleating, the step that begins crystal formation, and then randomly aggregating into mesocrystals in two unrelated steps, the researchers observed that nucleation and attachment were closely coupled in forming these highly uniform structures. The researchers reported their work in the February 18, 2021 issue of Nature.
“Our findings identify an important new pathway of crystallization by particle attachment and resolve key questions about mesocrystal formation,” said PNNL and University of Washington materials scientist Guomin Zhu. He was part of the research team led by Jim De Yoreo, PNNL materials scientist and co-director of the Northwest Institute for Materials Physics, Chemistry, and Technology. “We suspect this is a widespread phenomenon with significant implications both for the synthesis of designed nanomaterials and for understanding natural mineralization,” Zhu added.
Seeing crystallization in real-time
The project took years to execute and required significant problem solving. For the microscopy experiments, the scientific team chose a model system that included hematite, an iron compound commonly found in the Earth’s crust, and oxalate, a naturally abundant compound in soil.
They visualized the process using in situ TEM, which gives researchers the ability to see crystallization at the nanometer scale as it happens. They combined this real-time method with “freeze-and-look” TEM that enabled them to follow an individual crystal at different points during growth. Theoretical calculations helped complete the picture, allowing the PNNL team to piece together how the mesocrystals grew.
Researchers generally run most in situ TEM experiments at room temperature to simplify the experimental setup and minimize the potential for damaging the sensitive instrument, but mesocrystal formation rapid enough to observe occurs at around 80 °C.
“The additional equipment used to heat the samples made the experiments extremely challenging, but we knew the data would be key to understanding how the mesocrystals were forming,” said Zhu.
Once heated, the new hematite nanocrystals make it easy for them to rapidly attach together, which leads, on average, to final mesocrystals of approximately the same size and shape.
Mesocrystals in nature
The chemical key to this rapid, reliable attachment is the oxalate molecules present in the solution. After the first few small crystals form, the oxalate additives help create a chemical gradient at the interface of the liquid and the growing crystal. More chemical components necessary for particle nucleation linger near the crystals, which dramatically increases the likelihood that new particles will form near existing ones.
While this crystal growth pathway was observed in controlled conditions at very small scales, it likely also occurs in natural systems, according to the researchers. Some mineral deposits, including an Australian hematite deposit, contain mesocrystals. Given the natural abundance of oxalate and the PNNL team’s observation that hematite can become mesocrystals at temperatures as low as 40 °C, it seems plausible that this formation route occurs in nature.
Because mesocrystals are found throughout nature, the findings can be applied to understanding nutrient cycling in the environment, among other applications. Moreover, the route to creating near-uniform complex structures requires an understanding of how methods for forming such materials work and how to control them. Thus this work, supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Chemical Sciences, Geosciences, and Biosciences, opens new possibilities to intentionally create mesocrystals or mesocrystal-like materials.
###
The high-resolution imaging and simulations were performed in EMSL, the Environmental and Molecular Sciences Laboratory, a DOE Office of Science User Facility located at PNNL. In addition to Zhu and De Yoreo, this work features contributions from PNNL researchers Maria Sushko, John Loring, Benjamin Legg, Miao Song, Jennifer Soltis, Xiaopeng Huang, and Kevin Rosso.
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory draws on signature capabilities in chemistry, Earth sciences, and data analytics to advance scientific discovery and create solutions to the nation’s toughest challenges in energy resiliency and national security. Founded in 1965, PNNL is operated by Battelle for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit the PNNL’s News Center. Follow us on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, and Instagram.
Media Contact
Karyn Hede
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.