The Rising Role of Exosomal RNA in Head and Neck Cancers: A New Frontier in Precision Medicine
Recent advancements in our understanding of cancer biology highlight the potential of exosomal RNA (exRNA) as a revolutionary tool in the diagnosis and treatment of head and neck cancers (HNCs). Researchers from the prestigious SRM Institute of Science and Technology, led by the esteemed Dr. KN Aruljothi, have published a groundbreaking study in the journal ExRNA that explores the pivotal functions of exRNA in HNCs. This study illuminates how these small, molecular messengers, secreted by tumor cells, could redefine the landscape of cancer diagnostics and therapeutic strategies.
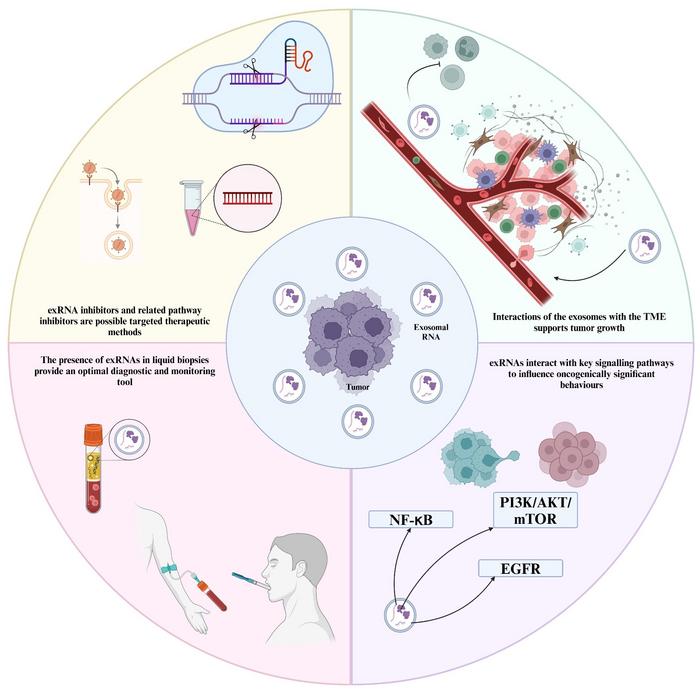
Exosomal RNA serves as a potent biomarker, capturing the complexities of tumor behavior and enabling a non-invasive approach to cancer management. Unlike traditional methods that rely on invasive biopsies, the detection and analysis of exRNA from non-invasive sources such as saliva and blood open new avenues for early diagnosis. This innovative method significantly reduces patient discomfort and risks associated with surgical biopsies, allowing for timely intervention and better clinical outcomes.
The mechanisms through which exRNAs drive tumor progression are intricate and multifaceted. Exosomes, the extracellular vesicles that carry exRNA, facilitate communication between cells in the tumor microenvironment, leading to critical alterations in cellular behavior. Within the realm of HNCs, exosomal miRNAs, mRNAs, and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play crucial roles in modulating key signaling pathways. Notably, these pathways include NF-κB, EGFR, and PI3K/AKT/mTOR, which are intimately linked to tumor survival, proliferation, and metastasis.
The study emphasizes that exRNAs are not merely byproducts of tumor activity; rather, they actively engage in orchestrating cancer progression. For instance, specific miRNAs such as miR-21 and miR-486 have been implicated in promoting not just tumor cell proliferation but also mechanisms that allow cancer cells to evade the host’s immune system. This significant insight alters our fundamental understanding of how tumors manage to thrive despite therapeutic interventions.
Furthermore, the impact of lncRNAs like HOTAIR and MALAT1 cannot be overlooked. These RNA species are crucial mediators of cancer cell invasion and motility, facilitating the spread of cancer within the head and neck regions. As they contribute to the transformation of benign cells into malignant entities, their potential as therapeutic targets becomes increasingly apparent. Therapies that can manipulate the activity or expression of these exosomal RNAs could pave the way for innovative treatment modalities.
A particularly exciting aspect of the study is the exploration of the clinical applications of exRNA analysis in liquid biopsies. The non-invasive collection of saliva and blood presents a formidable opportunity to implement real-time cancer diagnostics effectively. By analyzing the exRNA profile of patients, clinicians could assess cancer status, monitor response to therapy, and detect recurrence earlier than ever before. This paradigm shift towards precision medicine positions exRNAs as not only diagnostic markers but also as substantiated therapeutic targets.
The complexities of the exRNA landscape encompass various classes of RNA. For instance, circular RNAs (circRNAs) and PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) serve specialized roles in fortifying cancer cells against immune detection while also influencing their resilience against chemotherapy. This adaptation of tumor cells to therapeutic stress poses significant challenges in the effective treatment of HNCs. Nevertheless, a thorough understanding of these RNA classes offers novel opportunities to devise strategies that restore sensitivity to existing treatments.
Another focal point of the research highlights the regulatory influence of exRNAs on major oncogenic pathways. For instance, the NF-κB pathway remains a critical player in inflammation and tumor survival, wherein exRNAs significantly tilt the balance in favor of tumor growth. Considering the intricate web of interactions among the PI3K/AKT/mTOR, EGFR, and TP53 pathways, the research illustrates how exRNAs serve as vital conduits for integrating signals that can either promote or impede cancer progression.
The collaborative nature of exRNA signaling emphasizes that a singular approach may not suffice in addressing the complexities of HNCs. Future therapeutic strategies could benefit from a multimodal approach utilizing both exRNA-based diagnostics and engineered therapies aimed at restoring tumor suppressor pathways or inhibiting oncogenic signals triggered by exRNAs. The promise of engineered exosomes for targeted RNA delivery is yet another frontier that could potentially revolutionize cancer therapy.
The study concludes with a bright outlook for the integration of exRNA profiling into clinical practice, despite existing challenges such as standardizing exosome isolation techniques and pinpointing specific RNA biomarkers. Future research must prioritize these areas, alongside validating the therapeutic efficacy of targeting exRNAs in diverse patient populations. As we uncover the underlying mechanisms that drive exRNA-mediated tumor biology, we inch closer to transforming head and neck cancer management.
Ultimately, the evidence presented by Dr. Aruljothi and his team showcases exosomal RNAs as dynamic players in cancer pathogenesis and highlights their potential to revolutionize diagnostics and treatment. The journey towards harnessing these molecular messengers in the battle against head and neck cancers is just beginning, but the prospects for precision oncology have never seemed more promising. By marrying exRNA-based strategies with existing treatment modalities, clinicians can aspire to offer improved therapeutic outcomes and hope to patients navigating the challenging landscape of HNCs.
As science continues to unravel the complexities of cancer biology, exRNAs stand out as a beacon of hope—a transformative element in the quest for more effective, less invasive cancer care.
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: RNA cargo in motion: the exosomal connection to head and neck cancers
News Publication Date: 27-Mar-2025
Web References: DOI
References: None available
Image Credits: Department of Genetic Engineering, School of Bioengineering, SRM Kattankulathur, Chennai- 603203
Keywords: MicroRNA, exosomal RNA, head and neck cancers, cancer diagnostics, precision medicine, exosomes, cancer biology.
Tags: advancements in cancer biologybiomarkers for cancer diagnosiscancer management innovationsexosomal RNA in head and neck cancersexosomal RNA therapeutic strategiesnon-invasive cancer detection methodsprecision medicine in oncologyrole of exosomes in cancer progressionsaliva and blood as diagnostic toolsSRM Institute of Science and Technology researchtumor behavior analysistumor microenvironment communication