Credit: Dr. Alejandro Manjavacas
A new scientific paper published, in part, by a University of New Mexico physicist is shedding light on a strange force impacting particles at the smallest level of the material world.
The discovery, published in Physical Review Letters, was made by an international team of researchers lead by UNM Assistant Professor Alejandro Manjavacas in the Department of Physics & Astronomy. Collaborators on the project include Francisco Rodríguez-Fortuño (King's College London, U.K.), F. Javier García de Abajo (The Institute of Photonic Sciences, Spain) and Anatoly Zayats (King's College London, U.K.).
The findings relate to an area of theoretical nanophotonics and quantum theory known as the Casimir Effect, a measurable force that exists between objects inside a vacuum caused by the fluctuations of electromagnetic waves. When studied using classical physics, the vacuum would not produce any force on the objects. However, when looked at using quantum field theory, the vacuum is filled with photons, creating a small but potentially significant force on the objects.
"These studies are important because we are developing nanotechnologies where we're getting into distances and sizes that are so small that these types of forces can dominate everything else," said Manjavacas. "We know these Casimir forces exist, so, what we're trying to do is figure out the overall impact they have very small particles."
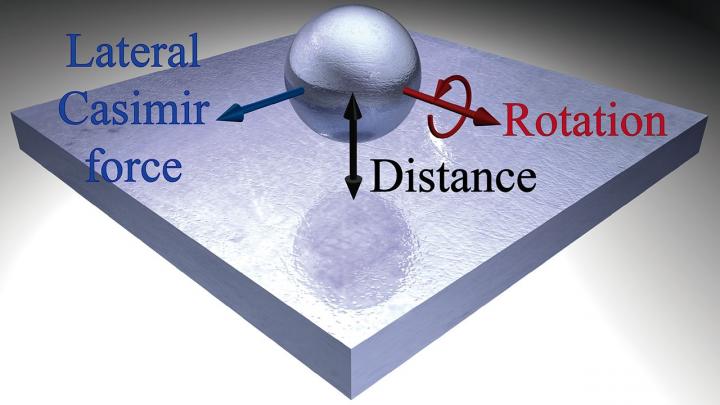
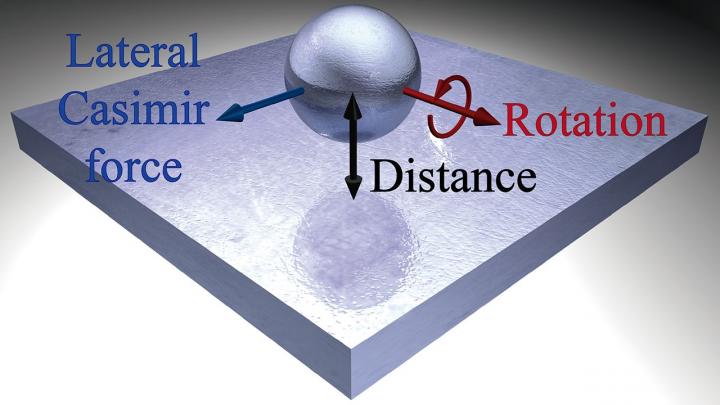
Manjavacas' research expands on the Casimir effect by developing an analytical expression for the lateral Casimir force experienced by nanoparticles rotating near a flat surface.
Imagine a tiny sphere (nanoparticle) rotating over a surface. While the sphere slows down due to photons colliding with it, that rotation also causes the sphere to move in a lateral direction. In our physical world, friction between the sphere and the surface would be needed to achieve lateral movement. However, the nano-world does not follow the same set of rules, eliminating the need for contact between the sphere and the surface for movement to occur.
"The nanoparticle experiences a lateral force as if it were in contact with the surface, even though is actually separated from it," said Manjavacas. "It's a strange reaction but one that may prove to have significant impact for engineers."
While the discovery may seem somewhat obscure, it is also extremely useful for researchers working in the always evolving nanotechnology industry. As part of their work, Manjavacas says they've also learned the direction of the force can be controlled by changing the distance between the particle and surface, an understanding that may help nanotech engineers develop better nanoscale objects for healthcare, computing or a variety of other areas.
For Manjavacas, the project and this latest publication are just another step forward in his research into these Casimir forces, which he has been studying throughout his scientific career. After receiving his Ph.D. from Complutense University of Madrid (UCM) in 2013, Manjavacas worked as a postdoctoral research fellow at Rice University before coming to UNM in 2015.
Currently, Manjavacas heads UNM's Theoretical Nanophotonics research group, collaborating with scientists around the world and locally in New Mexico. In fact, Manjavacas credits Los Alamos National Laboratory Researcher Diego Dalvit, a leading expert on Casimir forces, for helping much of his work progress.
"If I had to name the person who knows the most about Casimir forces, I'd say it was him," said Manjavacas. "He published a book that's considered one of the big references on the topic. So, having him nearby and being able to collaborate with other UNM faculty is a big advantage for our research."
###
Media Contact
Aaron Hilf
[email protected]
505-377-1727
http://www.unm.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag