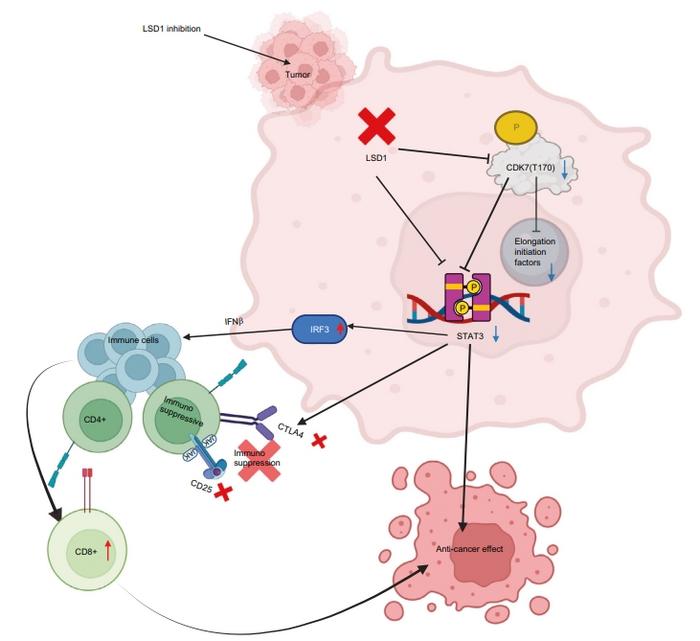
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) remains a formidable challenge within oncology, owing to its high prevalence and often late-stage diagnosis. Despite significant advances in cancer biology, the molecular events that propel preneoplastic lesions toward invasive OSCC have remained elusive, particularly regarding the epigenetic alterations that may serve as early triggers in tumorigenesis. A groundbreaking study published in the International Journal of Oral Science on April 17, 2025, now illuminates the critical role of lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) in dictating the fate of OSCC initiation and progression. This research, conducted collaboratively by teams led by Manish Bais at Boston University and colleagues at the University of Florida, unveils precise molecular mechanisms linking LSD1 activity to oncogenic and immunosuppressive pathways that promote tumor development.
Immune evasion remains a hallmark of cancer progression, and the revelation that LSD1 inhibition diminishes CTLA4-mediated immunosuppression marks a significant milestone in the modulation of tumor-immune dynamics. The restoration of CD8+ T cell infiltration and effector functions upon LSD1 blockade suggests that epigenetic regulators critically modulate the immunological landscape of early OSCC lesions. By relieving the immune checkpoint constraints and invigorating anti-tumor immunity, LSD1 inhibitors present an appealing complementary approach to existing immunotherapies, potentially overcoming resistance mechanisms inherent in OSCC.
Furthermore, the study challenges the conventional paradigm that treats OSCC predominantly at invasive stages. The ability to intercept tumorigenesis at its preneoplastic inception by modulating epigenetic readers and writers portends a paradigm shift in oral oncology. Early therapeutic intervention leveraging LSD1 inhibitors could drastically reduce OSCC incidence and improve long-term survival, circumventing the morbidity associated with advanced disease and exhaustive treatments.
This investigation also propels the field of cancer epigenetics forward, emphasizing the nuanced roles of demethylases such as LSD1 in tumor progression outside of classical genetic mutations. Integrating epigenetic modulation with immune reactivation offers a multipronged strategy to disrupt the complex crosstalk between cancer cells and their microenvironment. The potential to combine LSD1 inhibitors with immune checkpoint blockade or other targeted agents opens exciting avenues for combination therapies aimed at durable tumor suppression.
Given the compelling evidence in both murine and feline models, future clinical trials in humans are poised to validate LSD1 inhibition as a cornerstone in early OSCC management. The ongoing development of potent, selective LSD1 inhibitors with favorable pharmacokinetic profiles will be critical to translating these findings into effective therapies. Moreover, identifying reliable biomarkers to stratify patients most likely to benefit from such interventions will optimize clinical outcomes.
Dr. Manish Bais and his team underscored the importance of this discovery by emphasizing how targeting the epigenetic machinery is not merely about halting tumor cell proliferation but also about restoring the intricate balance of immune surveillance that cancer subverts. The dual action of stopping tumor progression and reawakening effective anti-tumor immunity represents a sophisticated therapeutic advance that harnesses the body’s natural defenses in combating early oral cancer.
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Lysine-specific demethylase 1 controls key OSCC preneoplasia inducer STAT3 through CDK7 phosphorylation during oncogenic progression and immunosuppression
News Publication Date: 17-Apr-2025
Web References: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41368-025-00363-x
References: 10.1038/s41368-025-00363-x
Image Credits: international journal of oral science
Keywords: Oral cancer
Tags: cancer biology advancementschromatin dynamics and cancerearly-stage OSCC biomarkersepigenetics in oral cancerhistone modifications in cancerimmunosuppressive tumor environmentlysine-specific demethylase 1 roleoncogenic pathways in OSCCOSCC progression mechanismspreneoplastic lesions progressiontargeted therapies for oral cancertranscriptional regulation in tumors