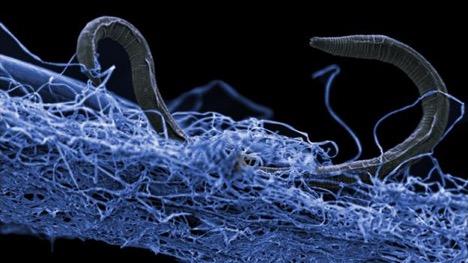
A nematode (eukaryote) in a biofilm of microorganisms. This unidentified nematode (Poikilolaimus sp.) from Kopanang gold mine in South Africa, lives 1.4 km below the surface.
Microorganisms living underneath the surface of the earth have a total carbon mass of 15 to 23 billion tons, hundreds of times more than that of humans, according to findings announced by the Deep Carbon Observatory and coauthored by UT Professor of Microbiology Karen Lloyd.
Carbon is the most prevalent element in living beings because it is part of almost all the molecules that are key for biological processes, including proteins, fats, and even DNA. Ninety percent of the earth’s carbon is in the subsurface.
“Knowing about how carbon is distributed and how living things use it is crucial for understanding not only life cycles but also our environment,” said Lloyd.
The report, which took an international multidisciplinary team 10 years to complete, also sheds light on other aspects of the incredible world of microbial dark matter.
For the research, scientists at hundreds of sites around the world drilled to a depth of 2.5 kilometers into the sea floor. They also took samples from continental mines and boreholes more than 5 kilometers deep into the earth.
In the samples from this deep biosphere, researchers identified members of all three domains of life: bacteria, archaea (microbes with a membrane nucleus), and eukarya (multicellular organisms that contain a nucleus–for example, humans).
“Ten years ago, we knew far less about the physiologies of the bacteria and microbes that dominate the subsurface biosphere,” said Lloyd. “Today we know that, in many places, they invest most of their energy into simply maintaining their existence and little into growth, which is a fascinating way to live.”
The report includes several other striking findings:
- 70 percent of all earth’s bacteria live underground. This realization dramatically expands the visualization of the tree of life, a biological analogy first proposed in Charles Darwin’s On the Origin of Species to explain the relationship between living and extinct organisms.
- The deep biosphere–the zone of life underneath earth’s surface–has a volume of between 2 and 2.3 billion cubic kilometers. This is almost as twice the volume of all oceans.
Since climate change is linked to carbon emissions, understanding how these microorganisms interact with carbon could help scientists produce mitigation strategies against climate change with additional time and research, Lloyd said.
“Some of these underground organisms emit carbon and some others sequester it and turn it into rock, for example. But we don’t know any of that yet. We have a lot to discover,” said Lloyd.
###
CONTACT:
Andrea Schneibel ([email protected], 865-974-3993)
Media Contact
Andrea Y Schneibel
[email protected]
865-974-3993




