Credit: Zhao, L., Huokko, T., Wilson, S. et al.
Biological membranes play important roles in shaping the cell, sensing the external environment, molecule transport, and generating energy for life. One of the most significant biological membranes are the thylakoid membranes produced in plants, algae and cyanobacteria, which carry out the light reactions of photosynthesis.
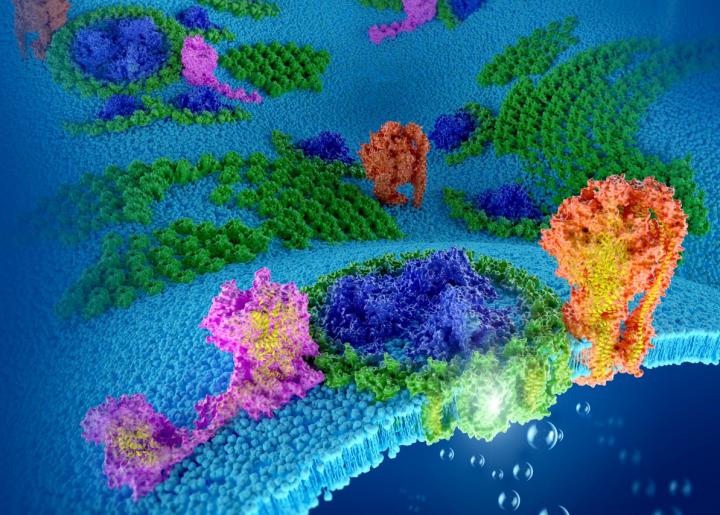
Researchers at the University of Liverpool have uncovered the molecular architecture and organisational landscape of thylakoid membranes from a model cyanobacterium in unprecedented detail. The study, which is published in Nature Plants, could help researchers find new and improved artificial photosynthetic technologies for energy production.
Professor Luning Liu, who led the study, explained: “Cyanobacteria perform plant-like photosynthesis. Hence, thylakoid membranes from laboratory-grown cyanobacteria are the ideal model system for studying and tuning plant photosynthesis.”
The researchers used state-of-the-art atomic force microscopy (AFM) to probe the structures and organisation of photosynthetic proteins within the thylakoid membranes. The results reveal how thylakoid membranes modulate the abundance of different photosynthetic proteins and form structurally variable complexes to adapt to the changing environments.
Dr Longsheng Zhao, the first author of this paper, said: “We observed that different protein complexes have their specific locations in the thylakoid membranes. We also visualised that distinct photosynthetic complexes can be close to each other, indicating that these photosynthetic complexes can form ‘supercomplex’ structures to facilitate electron transport between these protein complexes.”
Professor Luning Liu, added: “The development of structural biology approaches has greatly improved our understanding of individual photosynthetic complexes. However, these techniques have limitations for studying membrane multi-protein assembly and interactions in their native membrane environment. Our research has proved the power and potential of AFM in exploring complex, dynamic membrane structures and transient protein assembly.”
The researchers hope their ongoing work could help find solutions to modulate the photosynthetic efficiency of crop plants to boost plant growth and productivity.
###
The project was done in collaboration with the University’s Centre for Cell Imaging and researchers from Queen Mary University of London, Shandong University (China), Ocean University of China and Henan University (China). The research at the Liu lab was funded by the BBSRC and the Royal Society.
Media Contact
Nicola Frost
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.





