Researchers from the National Graphene Institute at the University of Manchester and the University of Pennsylvania identify ultra-fast gas flows through atomic-scale apertures in 2D membrane and validate a century-old equation of fluid dynamics.
Credit: N Hassani & M N-Amal, Shahid Rajee University
Researchers from the National Graphene Institute at the University of Manchester and the University of Pennsylvania have identified ultra-fast gas flows through the tiniest holes in one-atom-thin membranes, in a study published in Science Advances.
The work – alongside another study from Penn on the creation of such nano-porous membranes – holds promise for numerous application areas, from water and gas purification to monitoring of air quality and energy harvesting.
In the early 20th century, renowned Danish physicist Martin Knudsen formulated theories to describe gas flows. Emerging new systems of narrower pores challenged the Knudsen descriptions of gas flows, but they remained valid and it was unknown at which point of diminishing scale they might fail.
The Manchester team – led by Professor Radha Boya, in collaboration with the University of Pennsylvania team, led by Professor Marija Drndi? – has shown for the first time that Knudsen’s description seems to hold true at the ultimate atomic limit.
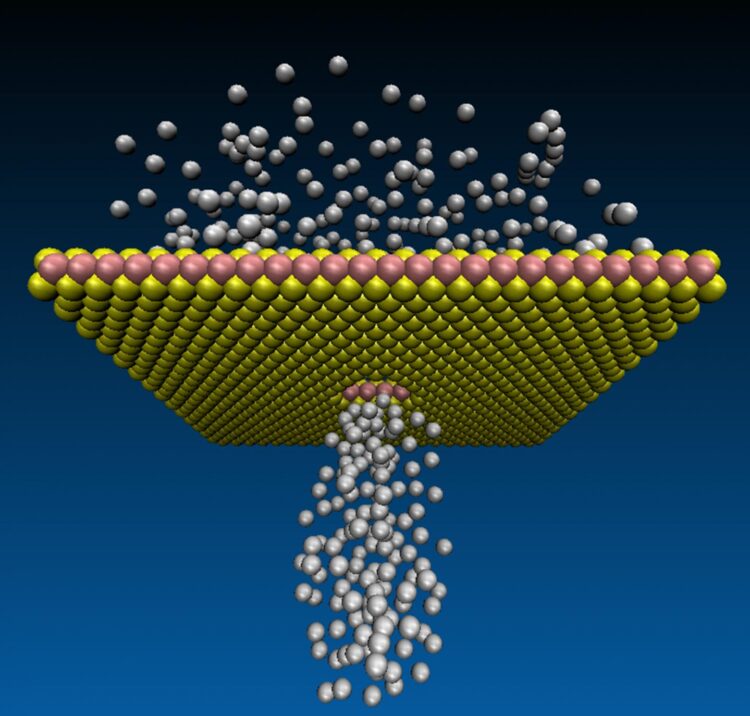
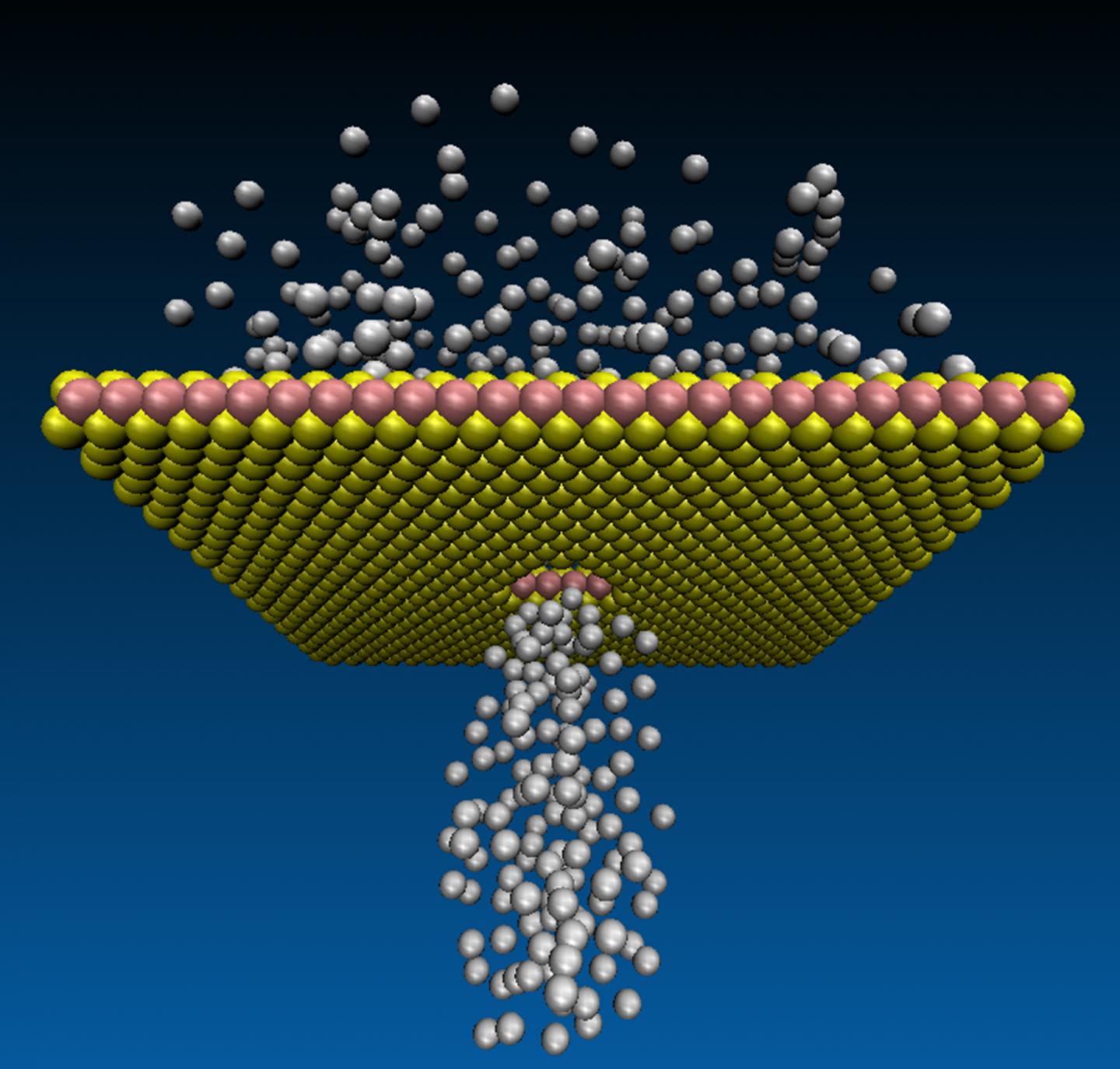
The science of two dimensional (2D)-materials is progressing rapidly and it is now routine for researchers to make one-atom-thin membranes. Professor Drndi?’s group in Pennsylvania developed a method to drill holes, one atom wide, on a monolayer of tungsten disulphide. One important question remained, though: to check if the atomic-scale holes were through and conducting, without actually seeing them manually, one by one. The only way previously to confirm if the holes were present and of the intended size, was to inspect them in a high resolution electron microscope.
Professor Boya’s team developed a technique to measure gas flows through atomic holes, and in turn use the flow as a tool to quantify the hole density. She said: “Although it is beyond doubt that seeing is believing, the science has been pretty much limited by being able to only seeing the atomic pores in a fancy microscope. Here we have devices through which we can not only measure gas flows, but also use the flows as a guide to estimate how many atomic holes were there in the membrane to start with.”
J Thiruraman, the co-first author of the study, said: “Being able to reach that atomic scale experimentally, and to have the imaging of that structure with precision so you can be more confident it’s a pore of that size and shape, was a challenge.”
Professor Drndi? added: “There’s a lot of device physics between finding something in a lab and creating a usable membrane. That came with the advancement of the technology as well as our own methodology, and what is novel here is to integrate this into a device that you can actually take out, transport across the ocean if you wish [to Manchester], and measure.”
Dr Ashok Keerthi, another lead author from the Manchester team, said: “Manual inspection of the formation of atomic holes over large areas on a membrane is painstaking and probably impractical. Here we use a simple principle, the amount of the gas the membrane lets through is a measure of how holey it is.”
The gas flows achieved are several orders of magnitude larger than previously observed flows in angstrom-scale pores in literature. A one-to-one correlation of atomic aperture densities by transmission electron microscopy imaging (measured locally) and from gas flows (measured on a large scale) was combined by this study and published by the team. S Dar, a co-author from Manchester added: “Surprisingly there is no/minimal energy barrier to the flow through such tiny holes.”
Professor Boya added: “We now have a robust method for confirming the formation of atomic apertures over large areas using gas flows, which is an essential step for pursuing their prospective applications in various domains including molecular separation, sensing and monitoring of gases at ultra-low concentrations.”
###
This work was conducted through an international collaboration and, includes experimental teams from Manchester and Philadelphia, and as well as theoretical groups from Shahid Rajee University, Iran and the University of Antwerp, Belgium.
Media Contact
Erica Brockmeier
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.