Credit: Ming Chang
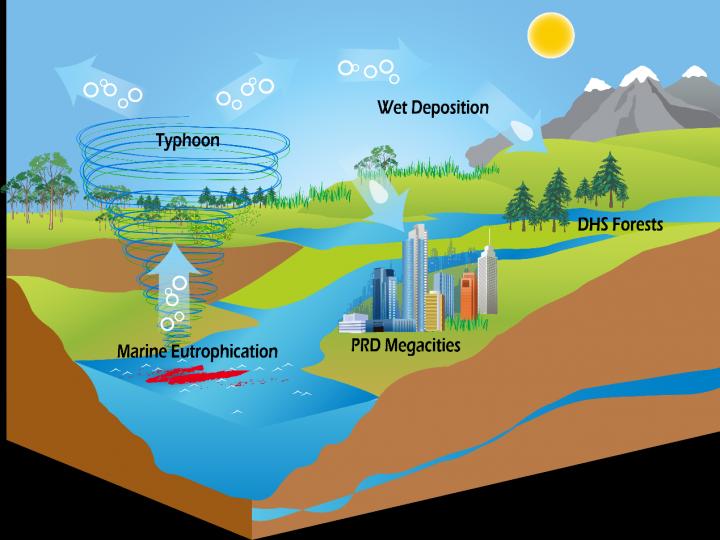
Atmospheric nitrogen deposition has a significant impact on both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, and alterations in its level will significantly affect the productivity and stability of an ecosystem. In recent years, with the reduction of anthropogenic inorganic nitrogen emissions, interest in organic nitrogen (ON) has increased because it represents a large fraction of total nitrogen. Given this large amount of ON deposition, researchers are interested in identifying its sources. However?scientists find large gaps between ON deposition and emission?and therefore suspect that there are missing sources of ON.
In a paper recently published in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, Dr. Ming Chang from the Institute for Environmental and Climate Research, Jinan University, and his coauthors, try to address this concern based on their recently completed preliminary work on the deposition-emission relationship.
“We classified observed flux data of dissolved ON in terms of the attributes of the wet deposition event itself, such as the season, precipitation, air mass backward trajectory, and effect of typhoons. The reverse trajectories of each air mass responsible for high ON flux precipitation events were tracked and superimposed with chlorophyll-a concentration maps in the ocean,” says Dr. Chang.
According to this study, approximately one third of the total wet deposition of ON was found to be derived from a confluence of three factors: rain in the wet season, air masses from the ocean, and rainfall over 50 mm. It was also found that the co-occurrence of intense events, such as a typhoons and eutrophic surface sea waters, might be an important source of dissolved ON in wet deposition.
“However, further quantitative and targeted research is needed to confirm the validity of these possibilities,” adds Dr. Chang.
###
Media Contact
Ms. Zheng Lin
[email protected]
86-108-299-5053
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




