Credit: Eun Young Kwon
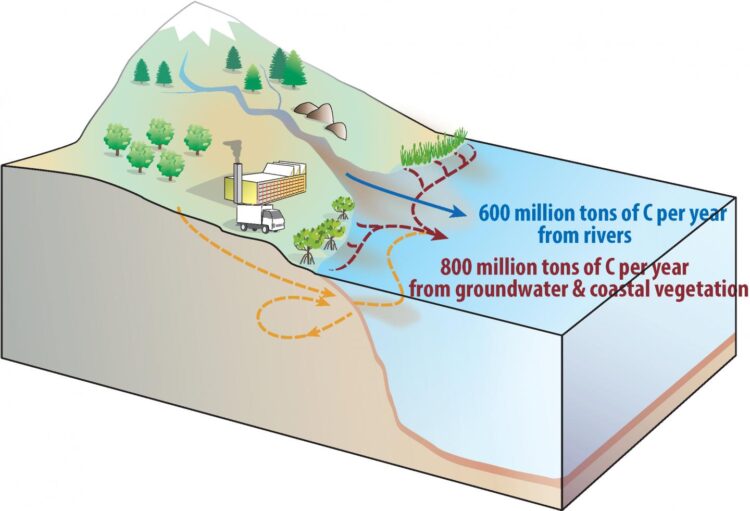
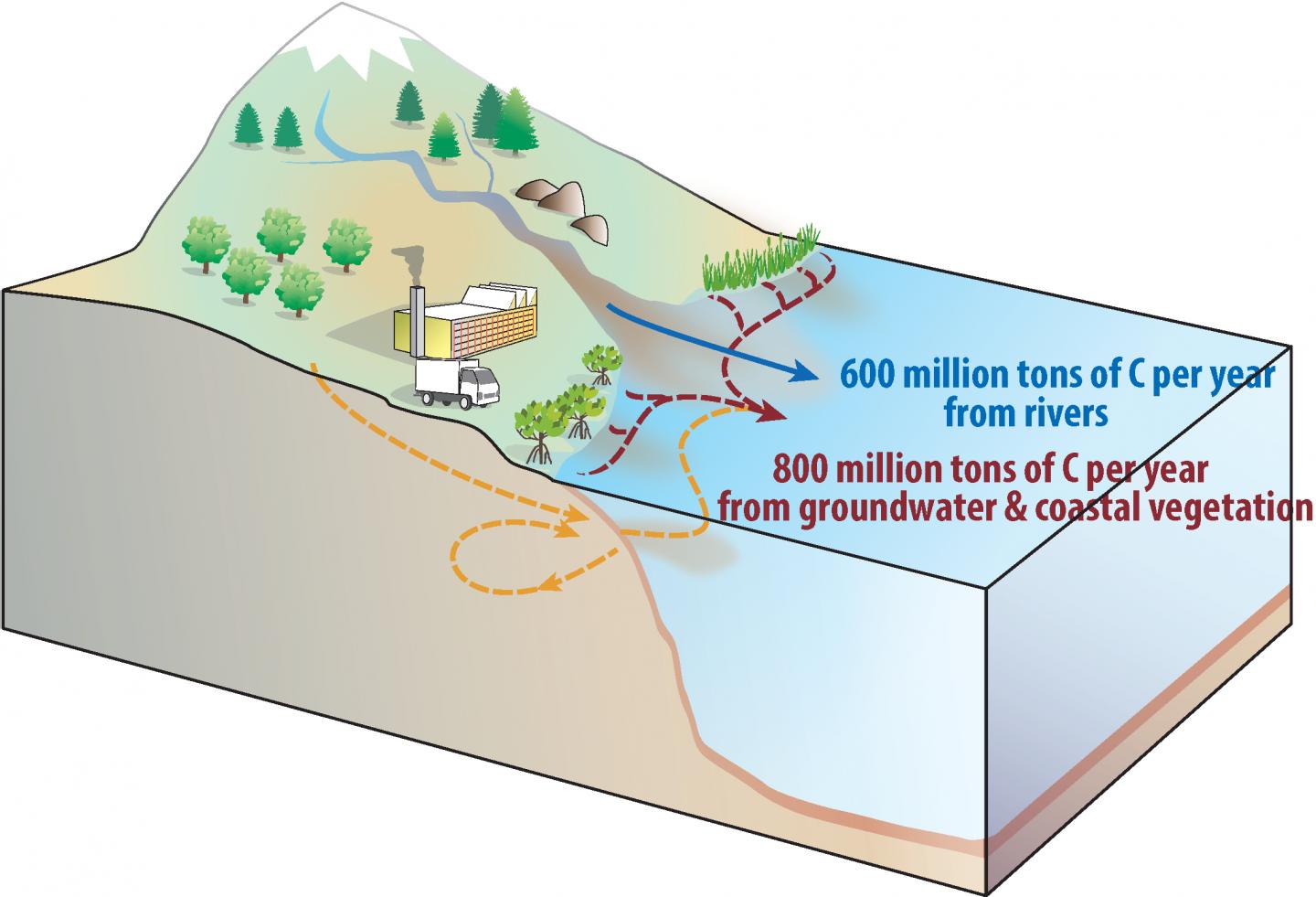
Every year 600-900 million tons of carbon flow through rivers to the ocean either as particles or in dissolved form. Researchers have known for a long time that this does not represent the total amount of carbon that gets transported from the land to the ocean. But the remaining contributors mostly from coastal ecosystems, such as carbon-rich mangrove forests, and from groundwater discharge into the ocean have been notoriously difficult to measure.
A new study published in the journal Global Biogeochemical Cycles and spearheaded by Dr. Eun Young Kwon, project leader at the IBS Center for Climate Physics South Korea provides new estimates of this elusive component of the global carbon cycle. The study makes use of the existence of two stable carbon isotopes, 12C and 13C, with the latter being slightly heavier, because it has one more neutron in its nucleus. The concentration ratio between these two carbon isotopes (referred to as ?13C) provides a means to track carbon through the different components of the carbon cycle, including the atmosphere, oceans, river systems and the biosphere. Knowing the typical ?13C value of land biosphere and for coastal vegetation, one can now track how this quantity gets diluted in the oceans. “The carbon isotope values act like an invisible dye that tells us something about the source where it came from and how much got released initially” says Dr. Kwon, lead author of the study.
By using oceanic observations of ?13C and estimates of the ocean currents, Dr. Kwon and her international team were able to calculate how much carbon would have to come from the land to explain the ocean data. The calculations are a bit more complicated because carbon can also get deposited in the deep ocean as sediment or outgas to the atmosphere. Furthermore, fossil fuel burning also changes the ?13C of atmospheric and eventually oceanic carbon.
After accounting for these effects, the authors were up for a surprise: they found much higher numbers for the land to ocean carbon transfer of 900-1900 million tons per year (see Figure). Most of non-riverine carbon inputs of about 300-1300 million tons of carbon per year occur mostly along the coastlines of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. “This is consistent with the idea that groundwater discharge and coastal ecosystems, the so-called blue carbon, play a fundamental role in the global carbon cycle” says Dr. Kwon.
One of the remaining open questions is which oceanic processes are responsible for carrying the dissolved carbon from the coastal zones to the open ocean, where part of it outgases back to the atmosphere. “This question will be addressed in future with a series of new earth system model simulations that we just conducted on our supercomputer Aleph”, says Axel Timmermann, co-author of the study and Director of the IBS Center for Climate Physics.
###
Media Contact
William I. Suh
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.