Scientists have developed a method involving terahertz radiation to monitor temperature changes when laser light is focused on tiny gold particles in water
Credit: Roberto Morandotti
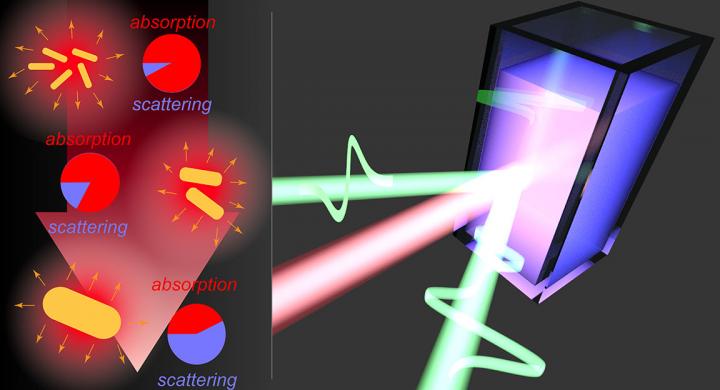
WASHINGTON, D.C., December 17, 2019 — An emerging technology involving tiny particles that absorb light and turn it into localized heat sources shows great promise in several fields, including medicine. For example, photothermal therapy, a new type of cancer treatment, involves aiming infrared laser light onto nanoparticles near the treatment site.
Localized heating in these systems must be carefully controlled since living tissue is delicate. Serious burns and tissue damage can result if unwanted heating occurs in the wrong place. The ability to monitor temperature increases is crucial in developing this technology. Several approaches have been tried, but all of them have drawbacks of various kinds, including the need to insert probes or inject additional materials.
In this week’s issue of APL Photonics, from AIP Publishing, scientists report the development of a new method to measure temperatures in these systems using a form of light known as terahertz radiation. The study involved suspensions of gold nanorods of various sizes in water in small cuvettes, which were illuminated by a laser focused on a small spot within the cuvette.
The tiny gold rods absorbed the laser light and converted it to heat that spread through the water by convection. “We are able to map out the temperature distribution by scanning the cuvette with terahertz radiation, producing a thermal image,” co-author Junliang Dong said.
The study also looked at the way the temperature varied over time. “Using a mathematical model, we are able to calculate the efficiency by which the gold nanorod suspensions converted infrared light to heat,” said co-author Holger Breitenborn.
The smallest gold particles, which had a diameter of 10 nanometers, converted laser light to heat with the highest efficiency, approximately 90%. This value is similar to previous reports for these gold particles, indicating the measurements using terahertz radiation were accurate.
Although the smaller gold rods had the highest light-to-heat conversion efficiency, the largest rods — those with a diameter of 50 nanometers — displayed the largest molar heating rate. This quantity has been recently introduced to help evaluate the use of nanoparticles in biomedical settings.
“By combining measurements of temperature transients in time and thermal images in space at terahertz frequencies, we have developed a noncontact and noninvasive technique for characterizing these nanoparticles,” co-author Roberto Morandotti said. This work offers an appealing alternative to invasive methods and holds promise for biomedical applications.
###
The article, “Quantifying the photothermal conversion efficiency of plasmonic nanoparticles by means of terahertz radiation,” is authored by H. Breitenborn, J. Dong, R. Piccoli, A. Bruhacs, L.V. Besteiro, A. Skripka, Z. Wang, A.O. Govorov, L. Razzari, F. Vetrone, R. Naccache and R. Morandotti. The article will appear in the journal APL Photonics on Dec. 17, 2019 (DOI: 10.1063/1.5128524). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Photonics is the dedicated home for open access multidisciplinary research from and for the photonics community. The journal publishes fundamental and applied results that significantly advance the knowledge in photonics across physics, chemistry, biology and materials science. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
301-209-3090
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




