Researchers develop highly accurate numerical method for electromagnetic noise that considers both conduction phenomena within conductors and radiation phenomena outside conductors that form electric circuits
Credit: Osaka University
Osaka, Japan – Most of the devices used in our daily lives are operated and controlled by electricity. From the standpoint of safety and the tight supply and demand of electricity, circuit design that satisfies low electromagnetic noise and power saving is becoming increasingly important.
In an electric circuit, electric signals transmit inside the conductor, and electromagnetic fields radiate outside the conductor. Furthermore, the electromagnetic field propagates through the air and is converted into signals for itself and other circuits, which leads to electromagnetic noise. Now, a research team at Osaka University has formulated a numerical method to visualize how signals propagate and radiate depending on the conductor’s shape, allowing us to anticipate the causes of electromagnetic noise in the circuit designing stage.
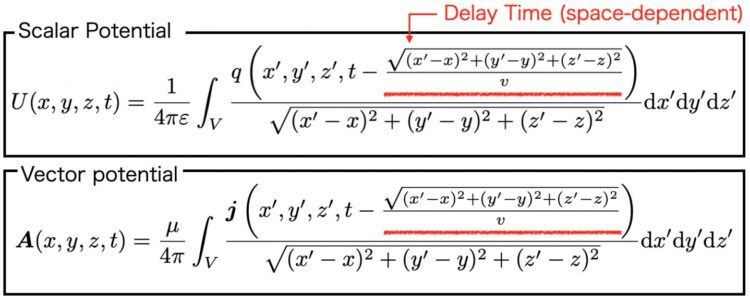
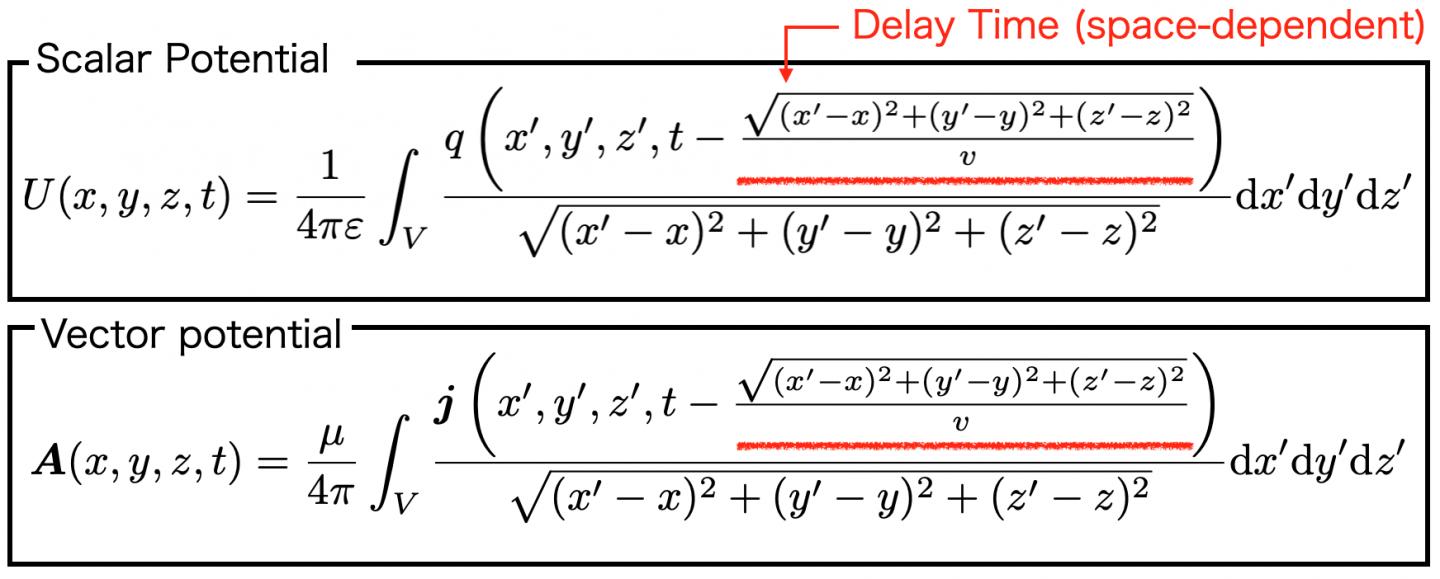
“It is necessary to simultaneously calculate electrical signals and external radiation phenomena to treat electromagnetic noise. To this end, we aimed to precisely solve the delay integral equations of the scalar potential (potential) U and the vector potential A derived from Maxwell’s equations, as shown in Fig. 1,” says lead author Souma Jinno.
In the conventional method, as shown in Fig. 2, the delay time is approximated by a constant that does not depend on space, but this numerical calculation is not stable. This research has achieved numerical stability through a numerical calculation (discretization) method that more strictly considers the delay time. The team also developed an algorithm that simultaneously calculates Ohm’s law and the equation of continuity and the circuit element of the boundary (lumped parameter circuit).
“We will show the effect of radiation on the conducted signal by applying our method to the circuit shown in Fig. 3 and comparing it with a calculation result that ignores radiation, shown as a red and blue line, respectively. By comparing the two results, we can see that the calculation with radiation is immediately damped and converges to zero, while the calculation without radiation continues to oscillate without damping. Since the conductor’s resistance component is assumed to be zero, there is no loss due to conduction. From the above results, the conduction signal current attenuates due to external radiation. The attenuation indicates that a single conductor is not suitable for conducting a signal because of the extensive external radiation. Usually, electrical circuits use two conductors, which can conduct with less radiation,” explains Souma Jinno.
“In order to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), society is moving toward electrification. However, rapid electrification has potential problems such as tight supply and demand for electricity and invisible environmental pollution caused by electromagnetic noise. Using the electromagnetic circuit simulator developed in this research, we aim to realize a ‘sustainable electrified society’ by further reducing noise and power consumption of electric circuits by correctly handling and consuming electric power,” says corresponding author Masayuki Abe.
###
The article, “Time-domain formulation of a multi-layer plane circuit coupled with lumped-parameter circuits using Maxwell equations,” was published in Scientific Reports at DOI: https:/
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan’s most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https:/
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.