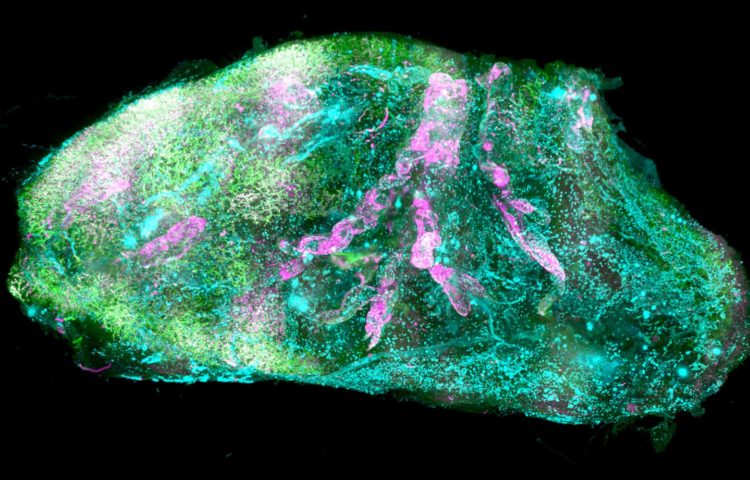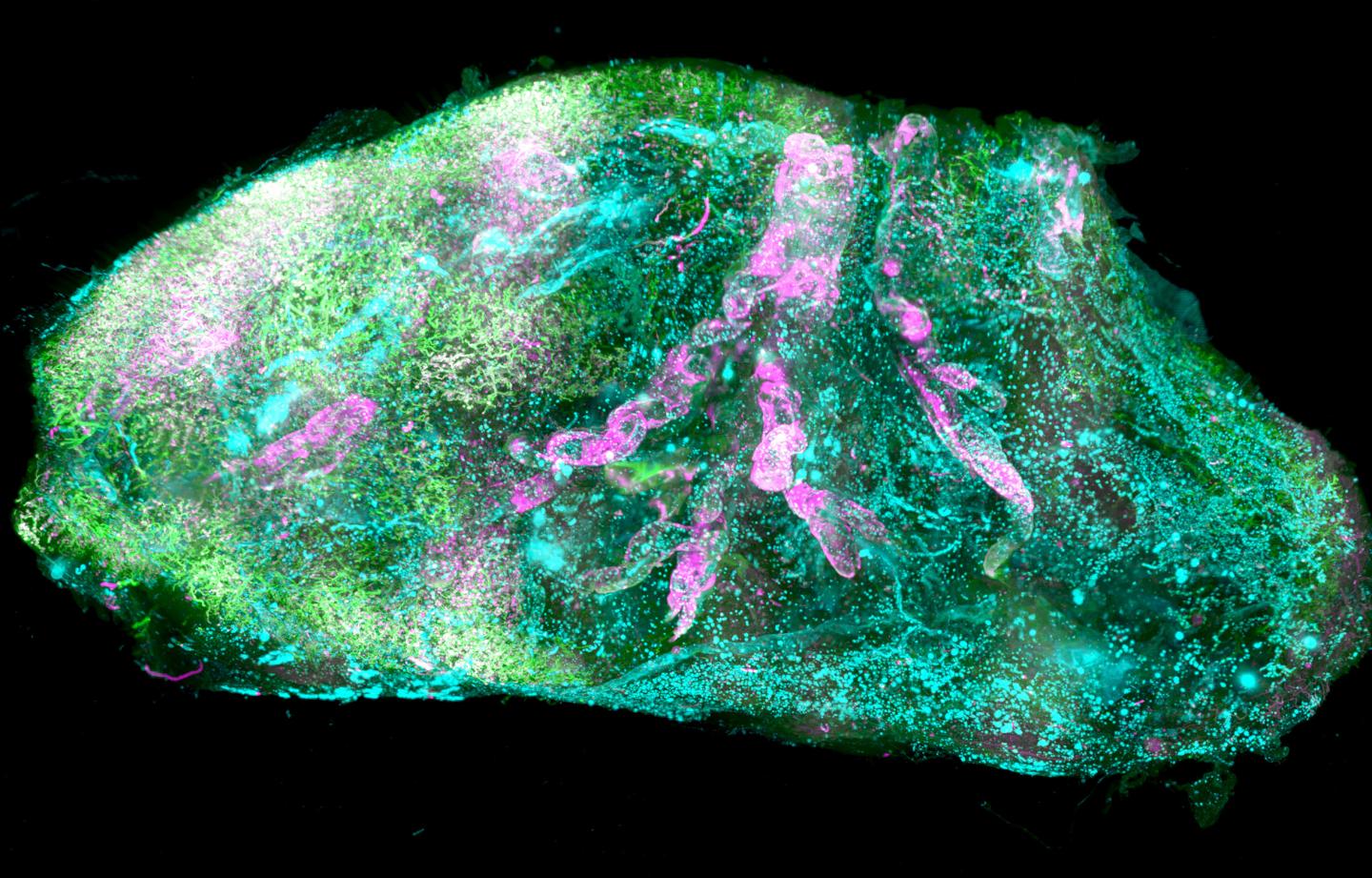
Credit: ©Helmholtz Zentrum München / Ertürk lab
For the first time, researchers managed to make intact human organs transparent. Using microscopic imaging they could revealed underlying complex structures of the see-through organs at the cellular level. Resulting organ maps can serve as templates for 3D-bioprinting technologies. In the future, this could lead to the creation of on demand artificial organs for many patients in need. The findings published in Cell joined forces from Helmholtz Zentrum München, Ludwig Maximilians University Munich (LMU), and Technical University of Munich (TUM).
In biomedical research, seeing is believing. Deciphering the structural complexity of human organs has always been a major challenge due to the lack of technologies to image them at the cellular level. Recent developments in tissue clearing allowed researchers to obtain first cellular views of intact transparent mouse organs in 3D. These methods, however, were not applicable to human organs.
“We had to change our approach completely”
Human organs are particularly stiff due to accumulation of insoluble molecules including collagen in tissues that have grown for years or even decades. Thus, traditional detergents that are used for making mouse organs transparent do not work on human organs, particularly adult ones. “We had to change our approach completely and start from scratch to find new chemicals which can make human organs transparent,” says Shan Zhao, PhD student at Helmholtz Zentrum München and first author of the study. After exhausting trials, the team discovered that a detergent called CHAPS could make small holes throughout the entire stiff human organs. CHAPS allows additional solutions to travel deep into centimeters-thick human organs and convert them into a transparent structure.
After making the human organs transparent, which were obtained post mortem from Prof. Ingo Bechmann’s lab at the University of Leipzig, the team had to tackle additional challenges for both organ imaging and the analysis of the large amount of resulting data. First, they developed a new laser-scanning microscope with a large sample holding capacity called “Ultramicroscope Blaze” in collaboration with Miltenyi Biotec. This microscope enabled imaging of human organs as large as the kidney. Next, together with Prof. Bjoern Menze from TUM, the team developed deep learning algorithms to be able to analyze hundreds of millions of cells in 3D.
The researchers named this new technology SHANEL (Small-micelle-mediated Human orgAN Efficient clearing and Labeling). “SHANEL can develop into a key technology for mapping intact human organs in the near future. This would dramatically accelerate our understanding of organs such as the brain, their development and function in health and disease,” explains Dr. Ali Ertürk, Director of the Institute for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine at Helmholtz Zentrum München and also Principal Investigator at the Institute for Stroke and Dementia Research at the hospital of LMU.
Final goal: 3D-bioprinting of artificial organs
Cellular maps of human organs could be used to engineer large scale human tissues and organs with emerging 3D-bioprinting technologies. Towards this goal, Ertürk and his team are currently working on mapping major human organs, starting with the pancreas, heart and kidney.
“There is a huge shortage of organ donors for hundreds of thousands of people,” says Ertürk. “The waiting time for patients and the transplantation costs are a real burden. Detailed knowledge about the cellular structure of human organs brings us an important step closer to creating functional organs artificially on demand.”
###
Watch the video: https:/
Helmholtz Zentrum München is a research center with a mission to discover personalized medical solutions for the prevention and therapy for environmentally triggered diseases and promote a healthier society in a rapidly changing world. Helmholtz Zentrum München is headquartered in Neuherberg in the north of Munich and has about 2,500 employees. It is a member of the Helmholtz Association, the largest scientific organization in Germany with more than 40,000 employees at 19 research centers.
The Institute for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine at Helmholtz Zentrum München is interested in elucidating the mechanisms leading to neurological diseases and ageing, in particular stroke and dementia. To this end, the Institute develops and implements 3D imaging technologies to be able to generate the highest resolution views of intact organs.
Media Contact
Dr. Ali Ertuerk
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.