Credit: by Tian Dong, Jiujiu Liang, Philip Camayd-Muñoz, Yueyang Liu, Haoning Tang, Shota Kita, Peipei Chen, Xiaojun Wu, Weiguo Chu, Eric Mazur, and Yang Li
A refractive index of zero induces a wave vector with zero amplitude and undefined direction. Therefore, light propagating inside a zero-index medium does not accumulate any spatial phase advance, resulting in perfect spatial coherence. Such coherence brings several potential applications, including arbitrarily shaped waveguides, phase-mismatch-free nonlinear propagation, large-area single-mode lasers, and extended super radiance. A promising platform to achieve these applications is an integrated Dirac-cone material that features an impedance-matched zero index. However, although this platform eliminates ohmic losses via its purely dielectric structure, it still entails out-of-plane radiation loss (about 1 dB/μm), restricting the applications to a small scale.
In 2018, Professor Shanhui Fan’s research group at Stanford University designed a low-loss Dirac-cone zero-index material based on symmetry-protected bound states in the continuum (BICs). However, this Dirac cone is consisted of high-order modes, thus it is challenging to homogenize the photonic crystal slab as a bulk zero-index medium.
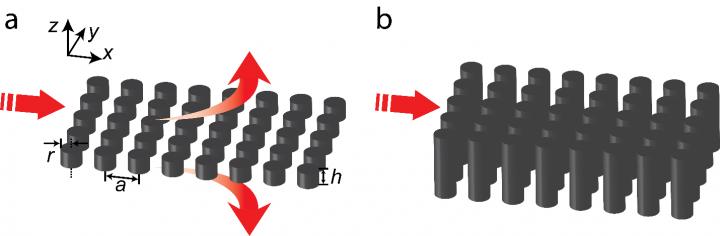
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Yang Li from the Department of Precision Instrument at Tsinghua University, China, Professor Eric Mazur from the John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences at Harvard University, the US, Professor Weiguo Chu from Nanofabrication Laboratory at the National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, China, and co-workers achieved a zero-index design based on a purely dielectric photonic crystal slab (PhC slab). This design supports an accidental Dirac-cone degeneracy of an electric monopole mode and a magnetic dipole mode at the centre of the Brillouin zone. Such low-order mode-based design can be better treated as a homogeneous zero-index medium.
Their design consists of a square array of silicon pillars embedded in silicon dioxide background matrix, featuring an easy fabrication using standard planar processes. To reduce the radiation loss, they model the top and bottom interfaces of a zero-index PhC slab as two partially reflective mirrors to form a Fabry-Pérot (FP) cavity. Then, they adjust the thickness of this FP cavity to induce destructive interference of upward (downward) radiations in the far field. Inside each pillar, there are axially propagating mode(s) with dipole symmetry showing a round-trip phase of an integer multiple of 2π, therefore becoming resonance-trapped modes. The monopole mode does not radiate in the out-of-plane direction because of its intrinsic mode symmetry.
“Our design exhibits an in-plane propagation loss as low as 0.15 dB/mm at the zero-index wavelength. Furthermore, the refractive index is near zero (|neff|
For applications, Yueyang Liu predict: “our on-chip BIC Dirac-cone zero-index PhC slabs provide an infinite coherence length with low propagation loss. This opens the door to applications of large-area zero-index materials in linear and nonlinear optics as well as lasers. For examples, electromagnetic energy tunnelling through a zero-index waveguide with an arbitrary shape, nonlinear light generation without phase mismatch over a long interaction length, and lasing over a large area in a single mode.”
“This work can also serve as an on-chip lab to explore fundamental quantum optics such as efficient generation of entangled photon pairs and collective emission of many emitters. Particularly, because the spatial distribution of Ez in each silicon pillar oscillates between a monopole mode and a dipole mode as time elapses, all the quantum emitters within the pillars will experience the same spatial phase in the monopole half cycle. This significantly alleviates the challenge of precise positioning of quantum emitters in a photonic cavity.” Yueyang Liu added.
###
Media Contact
Yang Li
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




