Researchers from Osaka University fabricated ultrathin, flexible, transparent sensors with cross-aligned silver nanowire microelectrodes fabricated using print technique that are scalable and require minimal raw materials
Credit: Osaka University
Osaka, Japan – Transparent electronics–such as head-up displays that allow pilots to read flight data while keeping their eyes ahead of them–improve safety and allow users to access data while in transit. For healthcare applications, the electronics need to not only be cheap and straightforward to fabricate, but also sufficiently flexible to conform to skin. Silver nanowire networks meet these criteria. However, current methods of development create random nanowire alignment that’s insufficient for advanced applications.
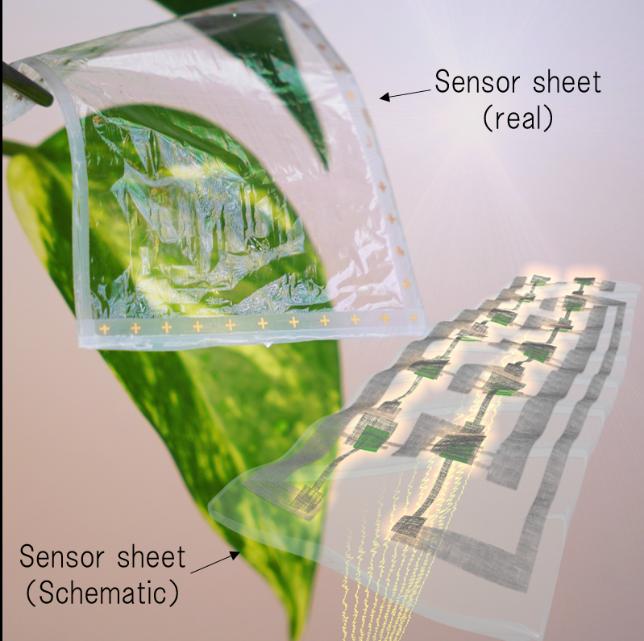
In an upcoming study in Advanced Intelligent Systems, researchers from Osaka University have used high-resolution printing to fabricate centimeter-scale cross-aligned silver nanowire arrays, with reproducible feature sizes from 20 to 250 micrometers. As a proof-of-concept for functionality, they used their arrays to detect electrophysiological signals from plants.
The researchers first created a patterned polymer surface to define the subsequent nanowire feature size. Using a glass rod to sweep silver nanowires across the pattern led to either parallel or cross-aligned nanowire networks, depending on the direction of the sweep. Nanowire cross-alignment, alignment within the pattern, and electro-optical properties were impressive.
“The sheet resistance of patterns less than 100 micrometers ranged from 25 to 170 ohms per square, and the visible light transmittance at 550 nanometers was 96% to 99%,” says Teppei Araki, co-senior author. “These values are well-suited for transparent electronics.”
The researchers showed off the utility of their technology by monitoring the electric potential of Brazilian waterweed leaves. Because the nanowire arrays are transparent, the researchers were able to keep the leaf under visual observation while acquiring data over long periods of time. A 2- to 3-micrometer-thick device conformed to the surface of a leaf without causing damage.
“Our microelectrodes-based organic field-effect transistors exhibited excellent multi-fuctionality,” says Tsuyoshi Sekitani, co-senior author. “For example, transparency of 90%, the on-off ratio was ~106, and the leakage current remained stable upon bending at a radius of 8 millimeters.”
Transparent electronics is an emerging technology. It must be simple and inexpensive to mass-produce for biomedicine, civil engineering, agriculture, and other applications that require underlying visual observation. The advance described here is an important step in that direction. The Osaka University researchers plan on making further technical improvements, such as incorporating graphene onto the nanowire’s surface. This will improve the uniformity of the microelectrodes’ sheet resistance. Ultimately, the researchers’ technology will help minimize the raw material input of electronics, and exceed the functionality of conventional non-transparent electronics.
###
The article, “Printable transparent microelectrodes toward mechanically and visually imperceptible electronics,” was published in Advanced Intelligent Systems at DOI: https:/
The related articles are below:
https:/
https:/
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




