Credit: (c) Julián Valero
Together with colleagues from the USA, scientists from the University of Bonn and the research institute Caesar in Bonn have used nanostructures to construct a tiny machine that constitutes a rotatory motor and can move in a specific direction. The researchers used circular structures from DNA. The results will now be presented in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
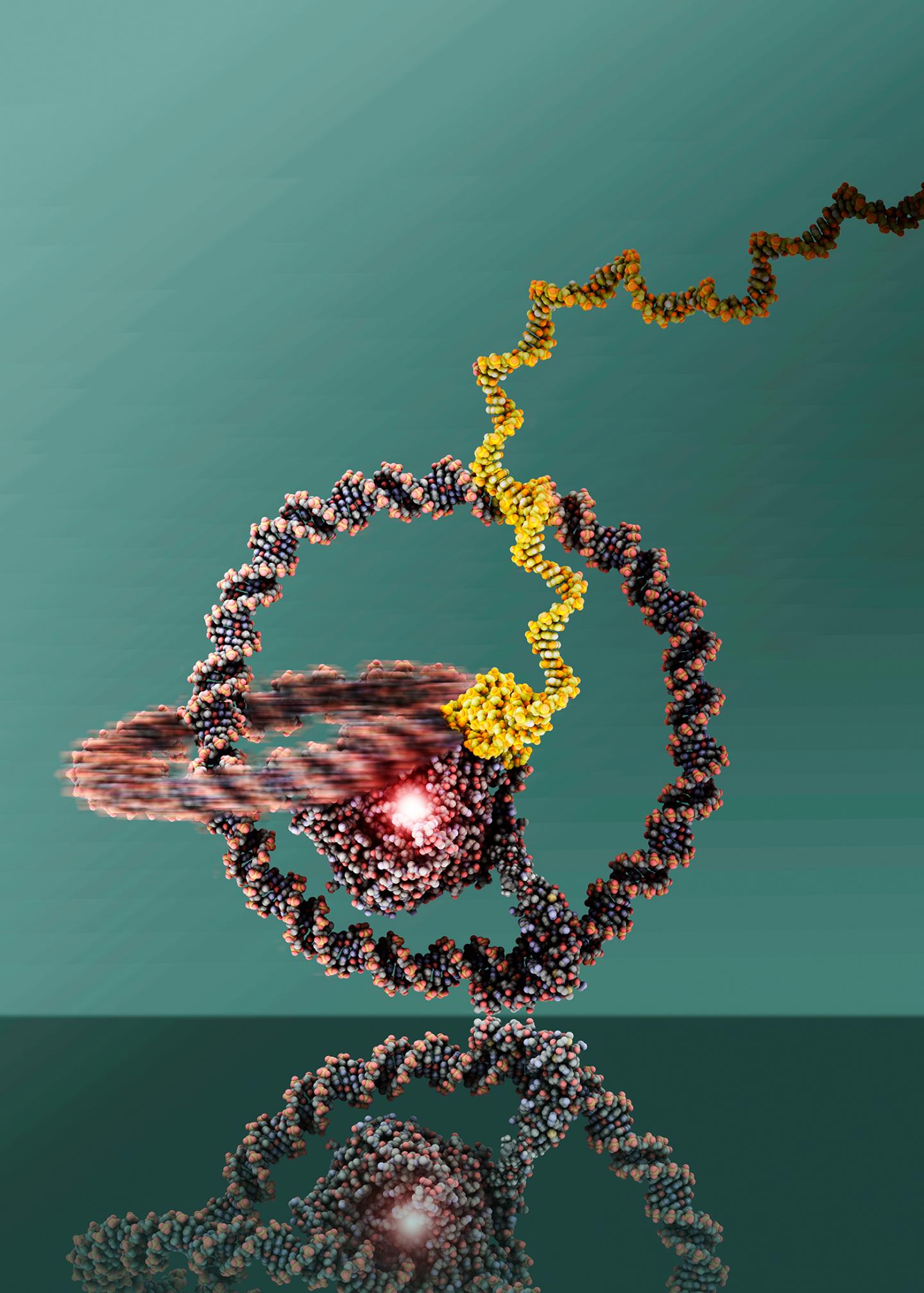
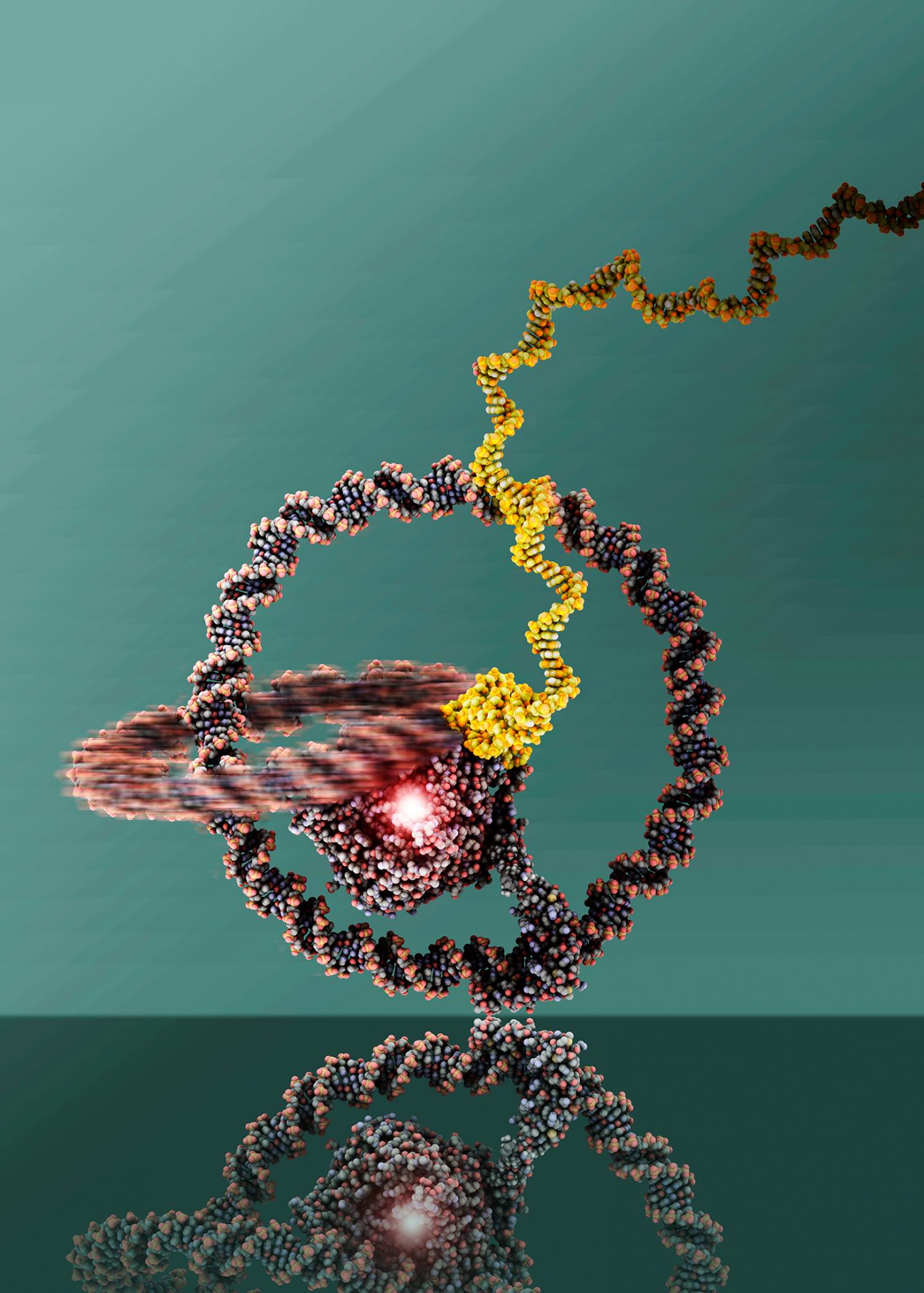
Nanomachines include structures of complex proteins and nucleic acids that are powered with chemical energy and can perform directed movements. The principle is known from nature: Bacteria, for example, propel themselves forward using a flagellum. The team of the University of Bonn, the research institute Caesar in Bonn and the University of Michigan (USA) used structures made of DNA nanorings. The two rings are linked like a chain. "One ring fulfills the function of a wheel, the other drives it like an engine with the help of chemical energy", explains Prof. Dr. Michael Famulok from the Life & Medical Sciences (LIMES) Institute of the University of Bonn.
The tiny vehicle measures only about 30 nanometers (millionths of a millimeter). The "fuel" is provided by the protein "T7 RNA polymerase". Coupled to the ring that serves as an engine, this enzyme synthesizes an RNA strand based on the DNA sequence and uses the chemical energy released during this process for the rotational movement of the DNA ring. "As the rotation progresses, the RNA strand grows like a thread from the RNA polymerase", reports lead author Dr. Julián Valero from Famulok's team. The researchers are using this ever-expanding RNA thread, which basically protrudes from the engine as a waste product, to keep the tiny vehicle on its course by using markings on a DNA-nanotube track.
Length of the test drive is 240 nanometers
Attached to this thread, the unicycle machine covered about 240 nanometers on its test drive. "That was a first go", says Famulok. "The track can be extended as desired." In the next step the researchers are not only aiming at expanding the length of the route, but also plan more complex challenges on the test track. At built-in junctions, the nanomachine should decide which way to go. "We can use our methods to predetermine which turn the machine should take", says Valero with a view towards the future.
Of course, the scientists cannot watch the tiny vehicle at work with the naked eye. By using an atomic force microscope that scanned the surface structure of the nanomachine, the scientists were able to visualize the interlocked DNA rings. In addition, the team used fluorescent markers to show that the "wheel" of the machine was actually turning. Fluorescent "waymarkers" along the nanotube path lit up as soon as the nano-unicycle passed them. Based thereupon, the speed of the vehicle could also be calculated: One turn of the wheel took about ten minutes. That's not very fast, but nevertheless a big step for the researchers. "Moving the nanomachine in the desired direction is not trivial", says Famulok.
The components of the machine assemble by self-organisation
Of course, unlike macroscopic machines, the nanomachine was not assembled with a welding torch or wrench. The construction is based on the principle of self-organization. As in living cells, the desired structures arise spontaneously when the corresponding components are made available. "It works like an imaginary puzzle", explains Famulok. Each puzzle piece is designed to interact with very specific partners. If you bring together exactly these partners in a single vessel, each particle will find its partner and the desired structure is automatically created.
By now, scientists worldwide have developed numerous nanomachines and nanoengines. But the method developed by Famulok's team is a completely novel principle. "This is a big step: It is not easy to reliably design and realize such a thing on a nanometer scale", says the scientist. His team wants to develop even more complex nanoengine systems soon. "This is basic research", says Famulok. "It is not possible to see exactly where it will lead." With some imagination, possible applications could for instance include molecular computers that perform logical operations based on molecular movements. Additionally, tiny machines could transport drugs through the bloodstream precisely to where they are required. "But these are still visions of the future", says Famulok.
###
Publication: Julián Valero, Nibedita Pal, Soma Dhakal, Nils G. Walter and Michael Famulok: A bio-hybrid DNA rotor-stator nanoengine that moves along predefined tracks, Nature Nanotechnology, DOI: 10.1038/s41565-018-0109-z
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Michael Famulok
Life & Medical Sciences (LIMES)-Institute
University of Bonn
Tel. +49-0-228-731787
E-mail: [email protected]
Media Contact
Prof. Dr. Michael Famulok
[email protected]
49-228-731-787
@unibonn
http://www.uni-bonn.de
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0109-z