Credit: Shunsuke Fukami (Tohoku University)
Researchers at Tohoku University have, for the first time, successfully demonstrated the basic operation of spintronics-based artificial intelligence.
Artificial intelligence, which emulates the information processing function of the brain that can quickly execute complex and complicated tasks such as image recognition and weather prediction, has attracted growing attention and has already been partly put to practical use.
The currently-used artificial intelligence works on the conventional framework of semiconductor-based integrated circuit technology. However, this lacks the compactness and low-power feature of the human brain. To overcome this challenge, the implementation of a single solid-state device that plays the role of a synapse is highly promising.
The Tohoku University research group of Professor Hideo Ohno, Professor Shigeo Sato, Professor Yoshihiko Horio, Associate Professor Shunsuke Fukami and Assistant Professor Hisanao Akima developed an artificial neural network in which their recently-developed spintronic devices, comprising micro-scale magnetic material, are employed (Fig. 1). The used spintronic device is capable of memorizing arbitral values between 0 and 1 in an analogue manner unlike the conventional magnetic devices, and thus perform the learning function, which is served by synapses in the brain.
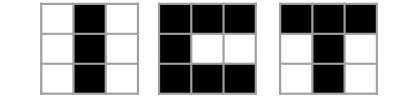
Using the developed network (Fig. 2), the researchers examined an associative memory operation, which is not readily executed by conventional computers. Through the multiple trials, they confirmed that the spintronic devices have a learning ability with which the developed artificial neural network can successfully associate memorized patterns (Fig. 3) from their input noisy versions just like the human brain can.
The proof-of-concept demonstration in this research is expected to open new horizons in artificial intelligence technology – one which is of a compact size, and which simultaneously achieves fast-processing capabilities and ultralow-power consumption. These features should enable the artificial intelligence to be used in a broad range of societal applications such as image/voice recognition, wearable terminals, sensor networks and nursing-care robots.
###
Media Contact
Shunsuke Fukami
[email protected]
@TohokuUniPR
http://www.tohoku.ac.jp/en/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag





