Astrophysicists at the Universities of Göttingen and Auckland simulate microscopic clusters from the Big Bang
Credit: Jens Niemeyer, University of Göttingen
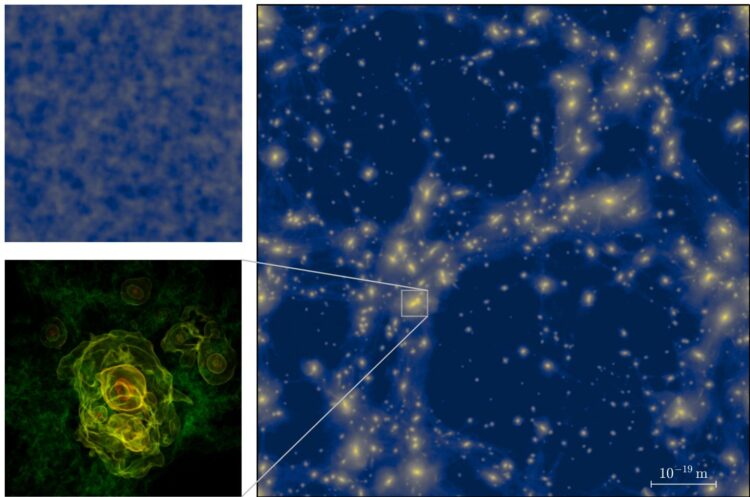
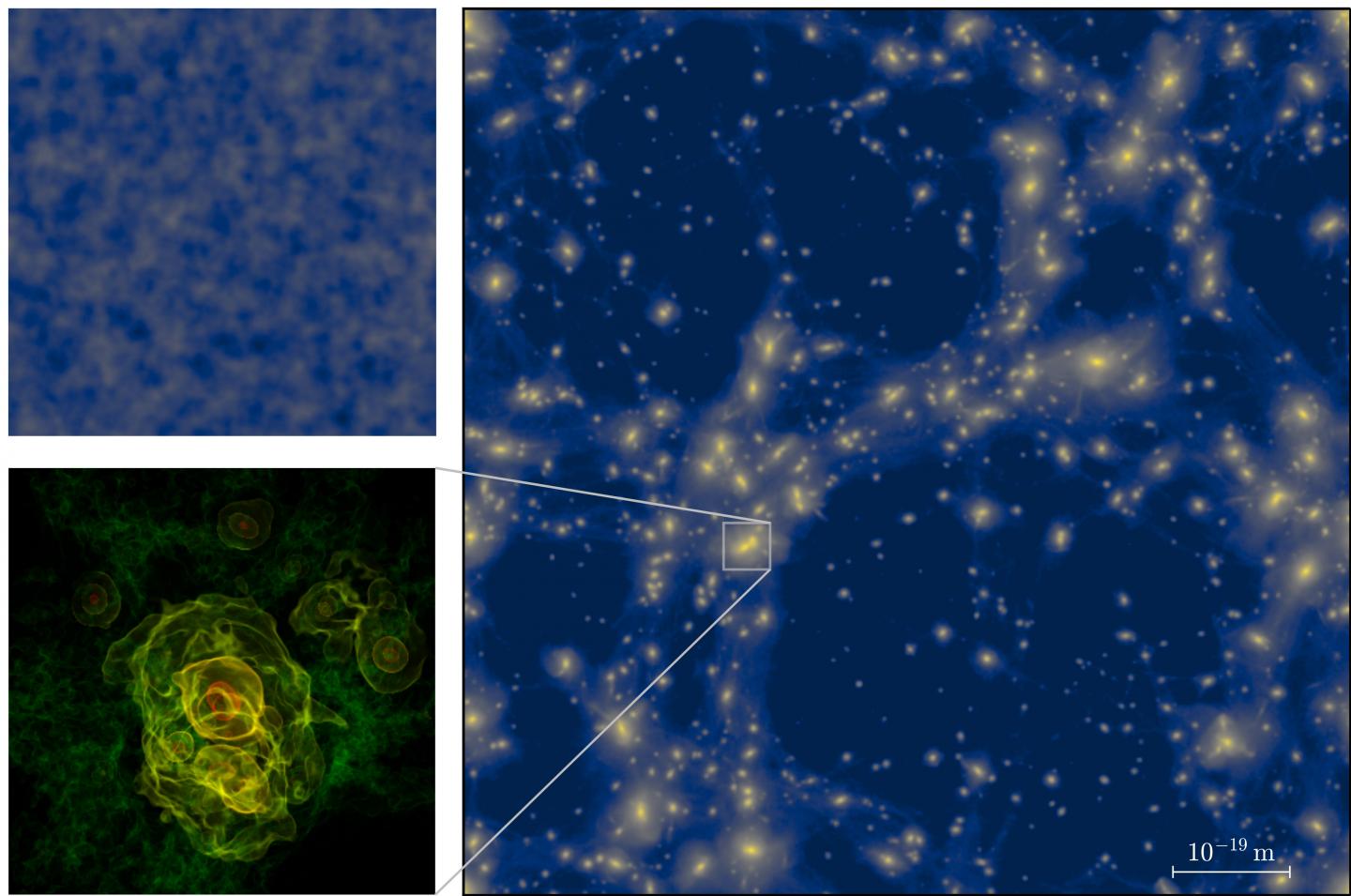
The very first moments of the Universe can be reconstructed mathematically even though they cannot be observed directly. Physicists from the Universities of Göttingen and Auckland (New Zealand) have greatly improved the ability of complex computer simulations to describe this early epoch. They discovered that a complex network of structures can form in the first trillionth of a second after the Big Bang. The behaviour of these objects mimics the distribution of galaxies in today’s Universe. In contrast to today, however, these primordial structures are microscopically small. Typical clumps have masses of only a few grams and fit into volumes much smaller than present-day elementary particles. The results of the study have been published in the journal Physical Review D.
The researchers were able to observe the development of regions of higher density that are held together by their own gravity. “The physical space represented by our simulation would fit into a single proton a million times over,” says Professor Jens Niemeyer, head of the Astrophysical Cosmology Group at the University of Göttingen. “It is probably the largest simulation of the smallest area of the Universe that has been carried out so far.” These simulations make it possible to calculate more precise predictions for the properties of these vestiges from the very beginnings of the Universe.
Although the computer-simulated structures would be very short-lived and eventually “vaporise” into standard elementary particles, traces of this extreme early phase may be detectable in future experiments. “The formation of such structures, as well as their movements and interactions, must have generated a background noise of gravitational waves,” says Benedikt Eggemeier, a PhD student in Niemeyer’s group and first author of the study. “With the help of our simulations, we can calculate the strength of this gravitational wave signal, which might be measurable in the future.”
It is also conceivable that tiny black holes could form if these structures undergo runaway collapse. If this happens they could have observable consequences today, or form part of the mysterious dark matter in the Universe. “On the other hand,” says Professor Easther, “If the simulations predict black holes form, and we don’t see them, then we will have found a new way to test models of the infant Universe.”
###
Original publication: Eggemeier B et al, Formation of inflation halos after inflation. Physical Review D (2021). DoI: 10.1103/PhysRevD.103.063525
Contact:
Benedikt Eggemeier
University of Göttingen
Institute for Astrophysics
Friedrich-Hund-Platz 1, 37077 Göttingen
Email: [email protected]
http://www.
Professor Jens Niemeyer
University of Göttingen
Institute for Astrophysics
Friedrich-Hund-Platz 1, 37077 Göttingen
Email: [email protected]
http://www.
Professor Richard Easther
University of Auckland
Department of Physics
38 Princes Street Auckland, New Zealand
Email: [email protected]
https:/
Media Contact
Melissa Sollich
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.