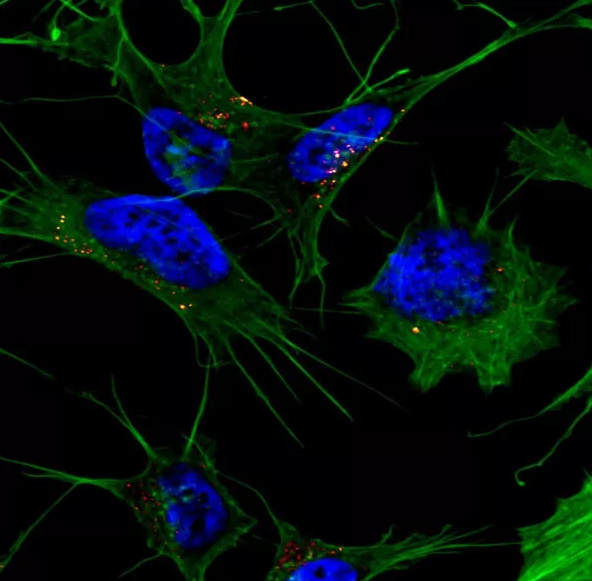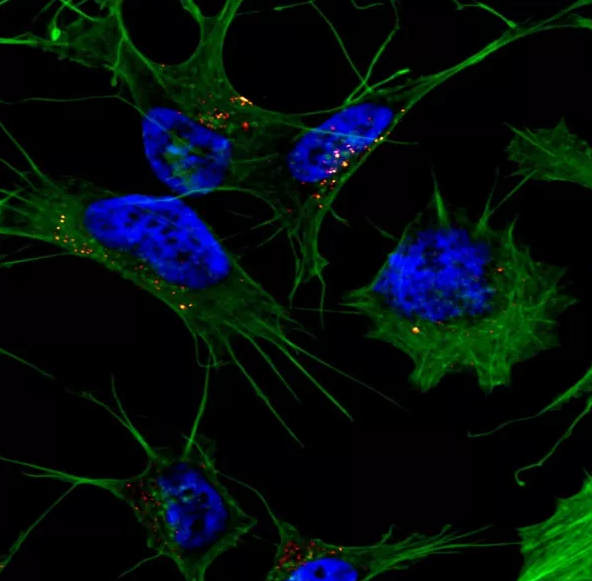
Researchers have known that the peptide amyloid beta plays a role in causing Alzheimer’s disease, but they are still working to determine how it becomes toxic.
Jan Bieschke, a biomedical engineer at Washington University in St. Louis, and collaborators in Germany have found that amyloid beta must change its internal structure into a long, flat structure called a beta sheet to be absorbed into the cell and become toxic. Results of the research were published Sept. 9 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Bieschke, assistant professor of biomedical engineering in the School of Engineering & Applied Science, and his collaborators found that the amyloid beta protein structure that was able penetrate the cell had a specific type of beta sheet in which its peptides stacked onto each other, similar to a layer cake.
“Somewhere on this aggregation pathway, this type of structural element is formed for the amyloid beta to get into the cell,” Bieschke said. “There is a two-step process: amyloid beta can bind to the membrane and form aggregates while on the surface of the cell, then it gets taken up into the cell.”
Alzheimer’s researchers have had a long-standing debate on whether amyloid beta is toxic before entering the nerve cell or after entering the cell. Amyloid beta can interfere with the mitochondria, or the cell’s energy powerhouse. This causes the cell to stop breathing and leads to eventual cell death. Studies of patients with late-stage Alzheimer’s disease reveal the death of many nerve cells in the brain.
With this knowledge, Bieschke and his collaborators can investigate what happens next to amyloid beta once inside the cell and how it interacts with the mitochondria.
“We will determine if we can see and measure the interaction with the mitochondria membrane, and if these structures are interacting with mitochondria the same way as with the outer cell membrane,” he said. “Another question we will ask is: Can we manipulate the uptake or formation of these structures so they cannot enter the cell? This may be a therapeutic strategy to help future patients with Alzheimer’s.”
Story Source:
The above post is reprinted from materials provided by Washington University in St. Louis.
The post The Shape-Shifting Protein Behind Alzheimer’s Disease appeared first on Scienmag.