Credit: Rebecca Gentek
Mast cells are immune system cells that play a role in inflammatory processes in the body. They provide an initial line of defence against certain pathogens and play a vital role in allergic reactions. Until now, research on these cells has shown that they are produced in bone marrow, as are most cells found in blood.
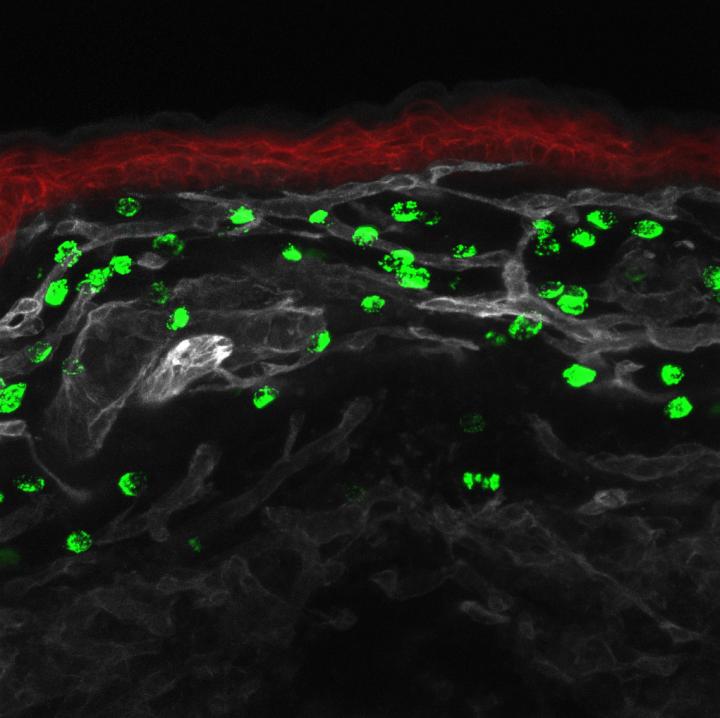
In this study, scientists from CNRS, INSERM and AMU identified other mast cells generated in the embryonic stage of life. Called "primitive mast cells", these cells are produced in the yolk sac, an extra-embryonic organ known to supply nutrients to the embryo and generate certain blood cells. In mice, these primitive mast cells are generated after the 8th day of embryonic development. They then migrate to what will be the dermis and remain there until birth, gradually disappearing as the embryo begins to produce the other "definitive" mast cells.
Given that an embryo is already protected by the physical and immune barriers of its mother, researchers concur that primitive mast cells do not serve an immune-related purpose. The next step for researchers is to understand why the body produces two successive waves of mast cells with what appears to be same genetic origin but different functions. The study is also an opportunity for the scientific community to approach the subject from a different angle.
###
Media Contact
Juliette Dunglas
[email protected]
33-014-496-4634
http://www.cnrs.fr
Original Source
http://www2.cnrs.fr/en/3126.htm http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.025