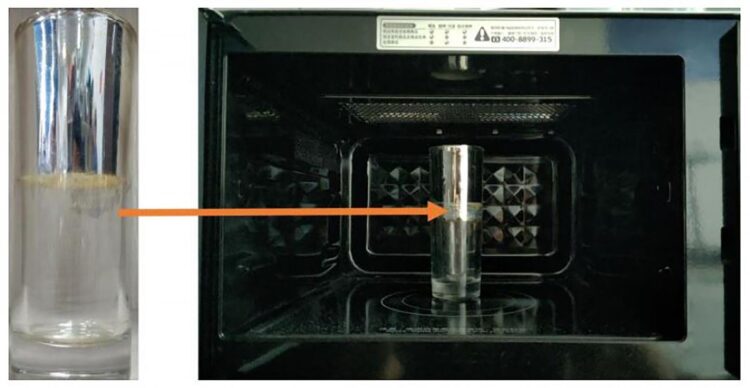
Why microwaving liquids is different from other heating techniques, and how this issue can be resolved

Credit: Baoqing Zeng
WASHINGTON, August 4, 2020 — Tea drinkers have been saying it for years. Water heated in a microwave just isn’t the same.
Typically, when a liquid is being warmed, the heating source — a stove, for example — heats the container from below. By a process called convection, as the liquid toward the bottom of the container warms up, it becomes less dense and moves to the top, allowing a cooler section of the liquid to contact the source. This ultimately results in a uniform temperature throughout the glass.
Inside a microwave, however, the electric field acting as the heating source exists everywhere. Because the entire glass itself is also warming up, the convection process does not occur, and the liquid at the top of the container ends up being much hotter than the liquid at the bottom.
A team of researchers from the University of Electronic Science & Technology of China studied this nonuniform heating behavior and presents a solution to this common problem in the journal AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing.
By designing a silver plating to go along the rim of a glass, the group was able to shield the effects of the microwave at the surface of the liquid. The silver acts as a guide for the waves, reducing the electric field at the top and effectively blocking the heating. This creates a convection process similar to traditional approaches, resulting in a more uniform temperature.
Placing silver in the microwave may seem like a dangerous idea, but similar metal structures with finely tuned geometry to avoid ignition have already been safely used for microwave steam pots and rice cookers.
“After carefully designing the metal structure at the appropriate size, the metal edge, which is prone to ignition, is located at weak field strength, where it can completely avoid ignition, so it is still safe,” said Baoqing Zeng, one of the authors on the paper and professor of electronic science and engineering at UESTC.
Solids don’t undergo convection, so getting your leftovers to warm up uniformly is a completely different challenge.
“For solids, there is no simple way to design a bowl or plate in order to achieve a much better heating result,” Zeng said. “We can change the field distribution, but the change is very small, so the improvement is limited.”
The group is considering other ways to improve nonuniformity in solid foods, but the methods are currently too expensive for practical use. For now, they’re focusing their efforts on working with a microwave manufacturer to commercialize their microwave accessories for liquids.
A future in which tea can be microwaved without ridicule may not be too far away.
###
The article, “Multiphysics analysis for unusual heat convection in microwave heating liquid,” is authored by Peiyang Zhao, Weiwei Gan, Chuanqi Feng, Zongxing Qu, Jianlong Liu, Zhe Wu, Yubin Gong and Baoqing Zeng. The article will appear in AIP Advances on Aug. 4, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0013295). After that date, it can be accessed at http://aip.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
AIP Advances is an open access journal publishing in all areas of physical sciences–applied, theoretical, and experimental. The inclusive scope of AIP Advances makes it an essential outlet for scientists across the physical sciences. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.