Credit: Marine Life Science & Technology
Announcing a new publication for Marine Life Science & Technology journal. In this review article the authors Caiwen Li, Meng Li and Qian Huang from Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, China consider the impact of the parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium on aquaculture of marine crustaceans in China.
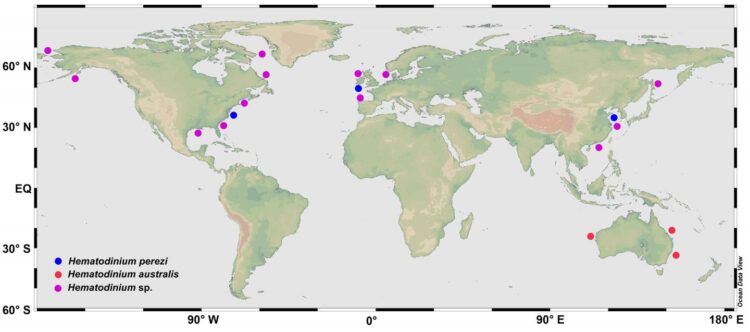
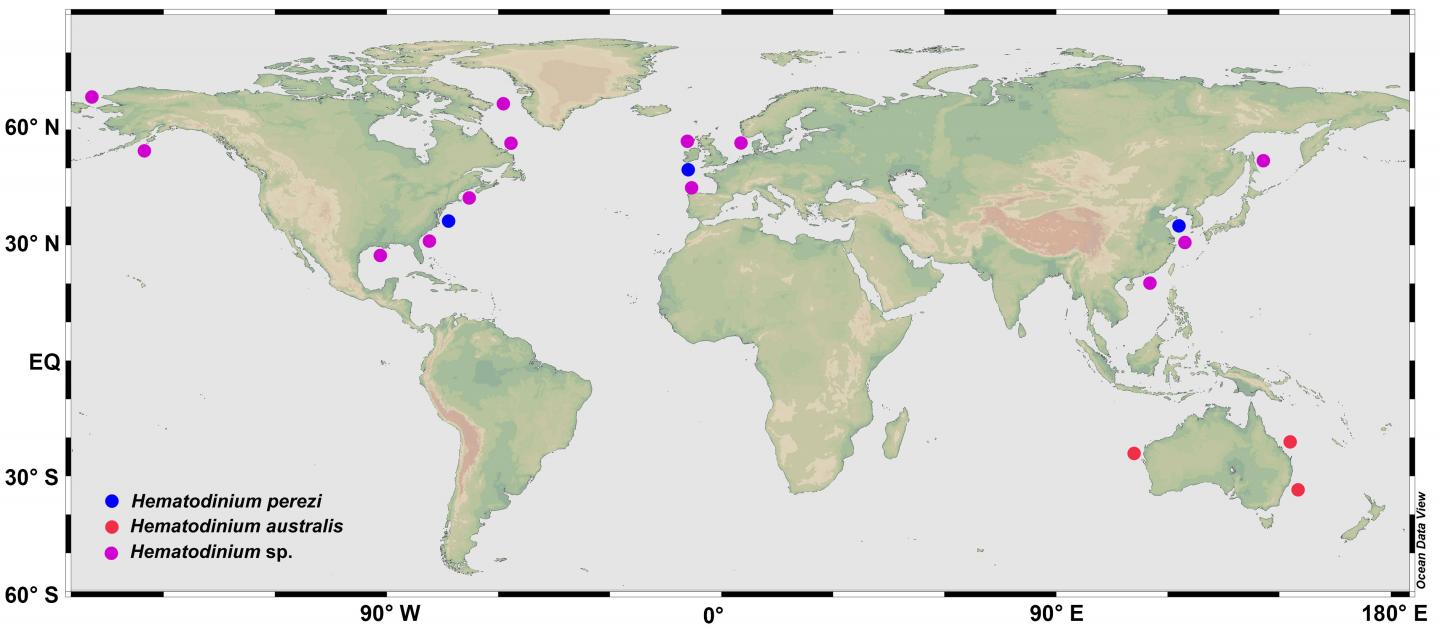
Hematodinium is a type of parasitic dinoflagellate that infects marine crustaceans globally. The parasite lives mainly in the hemolymph or hemocoels of affected hosts, and results in mortalities due to malfunction or loss of functions of major organs.
In recent years, the parasite has developed into an emerging epidemic pathogen not only affecting wild populations of economically valuable marine crustaceans in western countries but also the sustainable yield of aquaculture of major crabs in China. Epidemics of the parasitic disease have expanded recently in the coastal waters of China causing frequent outbreaks in aquaculture of major crab species, especially Portunus trituberculatus and Scylla paramamosain. The pathogen also infected two species of co-cultured shrimps and multiple cohabitating wild crabs, suggesting it is a significant threat to the sustainable culture of commercially valuable marine crustaceans. The polyculture system that is widely used along the coast of China may facilitate the spread and transmission of the pathogen.
To provide a better understanding of the biological and ecological characteristics of the parasitic dinoflagellate and highlight important directions for future research, the authors of this article review the current knowledge on the taxonomy, life cycle, pathogenesis, transmission and epidemiology of Hematodinium spp. proposing ecological countermeasures for the prevention and control of this emerging infectious disease.
###
Article reference: Caiwen Li, Meng Li and Qian Huang, The parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium infects marine crustaceans, Marine Life Science & Technology, 2020, ISSN 2662-1746, https:/
Keywords: Parasitic dinoflagellate, Diversity, Life cycle, Pathogenesis, Outbreak mechanism, Ecological control
Marine Life Science & Technology (MLST) provides a platform that introduces new discoveries and theories associated with marine organisms, bioresources, and biotechnology. The journal is intended for marine scientists, biological oceanographers, conservation biologists, marine technologists, policy makers and legislators. Accordingly, we publish original research papers across a broad range of marine life sciences and technologies with an emphasis on synergistic interactions of multiple disciplines. Both theoretical and practical papers are welcome, including laboratory and field experimental studies relevant to marine life science and technology. Focused reviews, viewpoints, comments, and short communications are also accepted. As the journal’s aim is to foster multidisciplinary approaches to marine sciences, authors are encouraged to emphasise the relevance of their work in relation across the journals key-disciplines.
For more information, please visit https:/
Editorial Board: https:/
MLST is available on SpringerLink (https:/
Submissions to MLST may be made using ScholarOne ManuscriptsTM (https:/
Abstracted and indexed in:
Astrophysics Data System (ADS)
CNKI
Dimensions
EBSCO Discovery Service
Google Scholar
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China
Meta
Naver
OCLC WorldCat Discovery Service
ProQuest-ExLibris Primo
ProQuest-ExLibris Summon
TD Net Discovery Service
ISSN 2662-1746
Media Contact
Morgan Lyons
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.