New small molecules promote the differentiation of brown adipocytes
Credit: Issey Takahashi | ITBM, Nagoya University
The circadian clock controls a variety of biological phenomena that occur during the course of the day, such as sleeping and waking. Perturbation of the circadian clock has been associated with many diseases such as sleep disorders, metabolic syndrome, and cancer. The development of small-molecule compounds to regulate specific components of the circadian clock facilitates the elucidation of the molecular basis of clock function, and provides a platform for the therapeutic treatment of clock-related diseases.
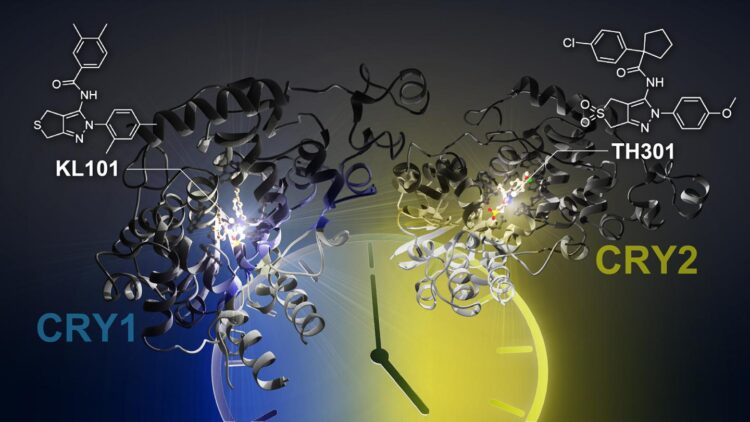
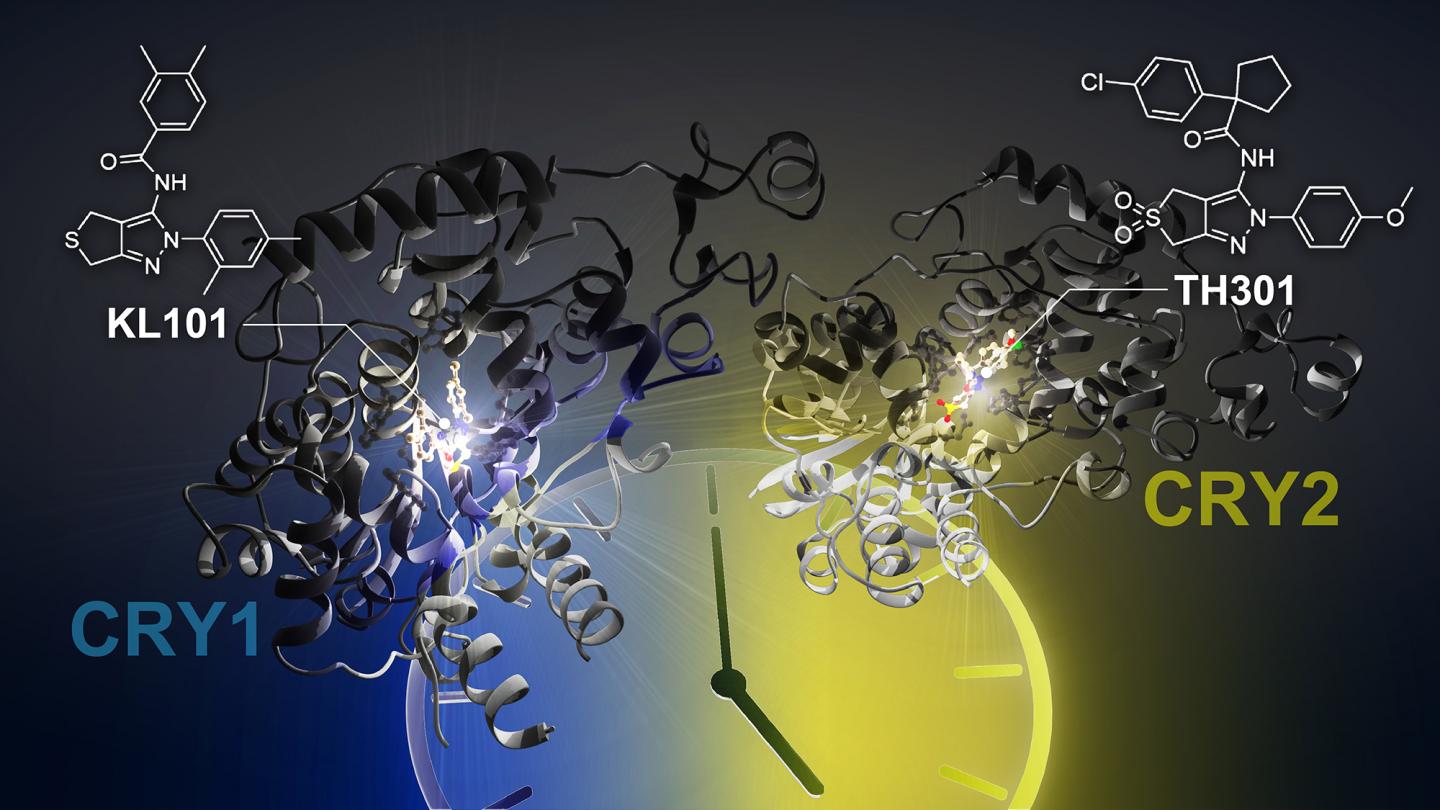
In this study, the research team discovered the small molecules, KL101 and TH301, that lengthen the period of the circadian clock. They found that KL101 and TH301 are the first compounds that selectively target clock components CRY1 and CRY2, respectively. By utilizing X-ray crystallography to determine the structures, they revealed how KL101 and TH301 bind to CRY1 and CRY2.
However, additional experiments were required to determine the mechanism of CRY1 and CRY2 selectivity. It was found that the disordered tail regions of CRY proteins impart compound selectivity. Additionally, in collaboration with Project Associate Professor Megumi Hatori and Postdoctoral Fellow You Lee Son of the Keio University School of Medicine, they found that CRY1 and CRY2 are required for the differentiation of brown adipocytes, and both KL101 and TH301 are expected to provide a promising foundation for the therapeutic treatment of obesity.
###
Media Contact
Dr. Tsuyoshi Hirota
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.