Credit: ©URV
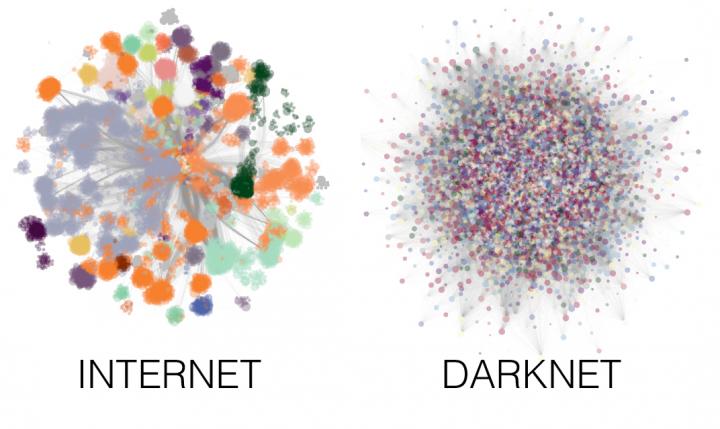
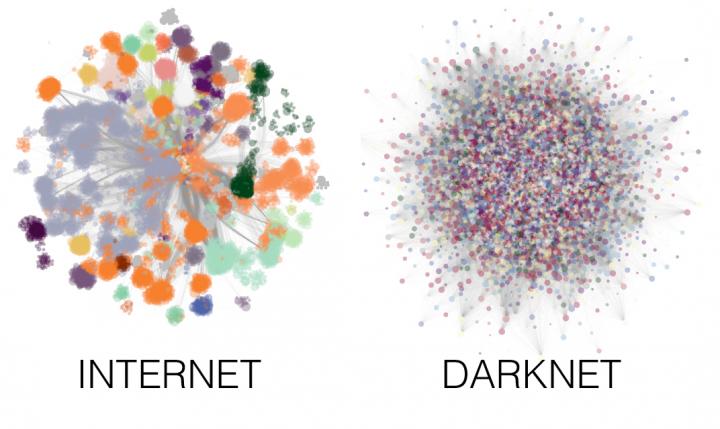
The Darknet is a part of the internet that people can access and use anonymously. This privacy and the ability to work away from prying eyes means that the network is frequently used for anonymous exchanges of sensitive information and for illegal activities such as drug trafficking, sharing child pornography or exchanging protected intellectual property free of charge.
Cyberattacks are frequently launched against this network but usually with little success. Now, the researchers Manlio De Domenico and Alex Arenas from the URV's Department of Computer Engineering and Mathematics have manged to determine why the Darknet is so difficult to attack. In an article published in Physical Review E, the Darknet is practically impenetrable because of its unique topology, which is significantly different from the rest of the internet.
To demonstrate this, the researchers have used data published by the Internet Research Lab of the University of California (Los Angeles) and network analysis to quantify the resilience of the Darknet. They have described its topology and have developed a model that shows how information is transmitted using the "onion router", a technique that encrypts messages in multiple layers.
This has allowed them to simulate how the Darknet would respond to three types of attack: attacks on a specific node, attacks that cause certain nodes to fail randomly, and attacks that unleash a wave of errors that are propagated across the network.
The study's results show that to cause significant disruption an attack on the Darknet's various nodes needs to be four times stronger than an attack against the internet's nodes. Furthermore, the Darknet is able to easily counter the waves of attacks through its different nodes by simply adding more network capacity. The authors attribute this resilience to a more decentralised topology that emerges spontaneously from the Darknet's onion router protocol. In comparison, the internet's structure is much more heterogeneous.
###
Manlio De Domenico and Alex Arenas. "Modeling Structure and Resilience of the Dark Network". Physical Review, 2017. E. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.95.022313
Media Contact
Alex Arenas
[email protected]
34-977-559-687
@universitatURV
http://www.urv.cat
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag