Credit: Tatsuya Usui, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology
Researchers in Japan have replicated cancer cells from diseased bladder tissue in dogs, minimizing the use of costly stem cell products. The synthesized tumor cells allow scientists to diagnose cancer and optimize treatment without putting the patient through tiresome rigors of chemotherapy trial and error.
The research team led by Senior Assistant Professor Tatsuya Usui from the Laboratory of Veterinary Pharmacology at the Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology published their findings in the journal Scientific Reports on June 10th, 2020.
Organoids are a niche within the booming field of 3D bioprinting, which includes a growing stable of chemical and biological processes that generate living tissue for use in research and medical procedures. Presently, clinically viable 3D bioprinting is limited to simple structures like a small patch of skin, fat, or cartilage. Ultimately the medical community hopes to generate viable replacement organs, eliminating the need for transplant donors.
Professor Usui’s team set out to create a type of organoids without the use of cell-stimulating supplements and Matrigel, a costly product derived from stem cells harvested from genetically engineered rodents. The scarcity of 3D bioprinting products makes them a poor choice for research on a scale that would yield timely cancer diagnoses and new treatments.
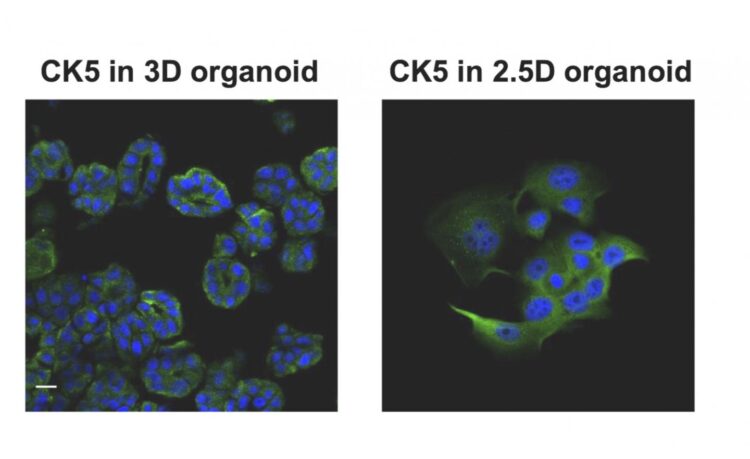
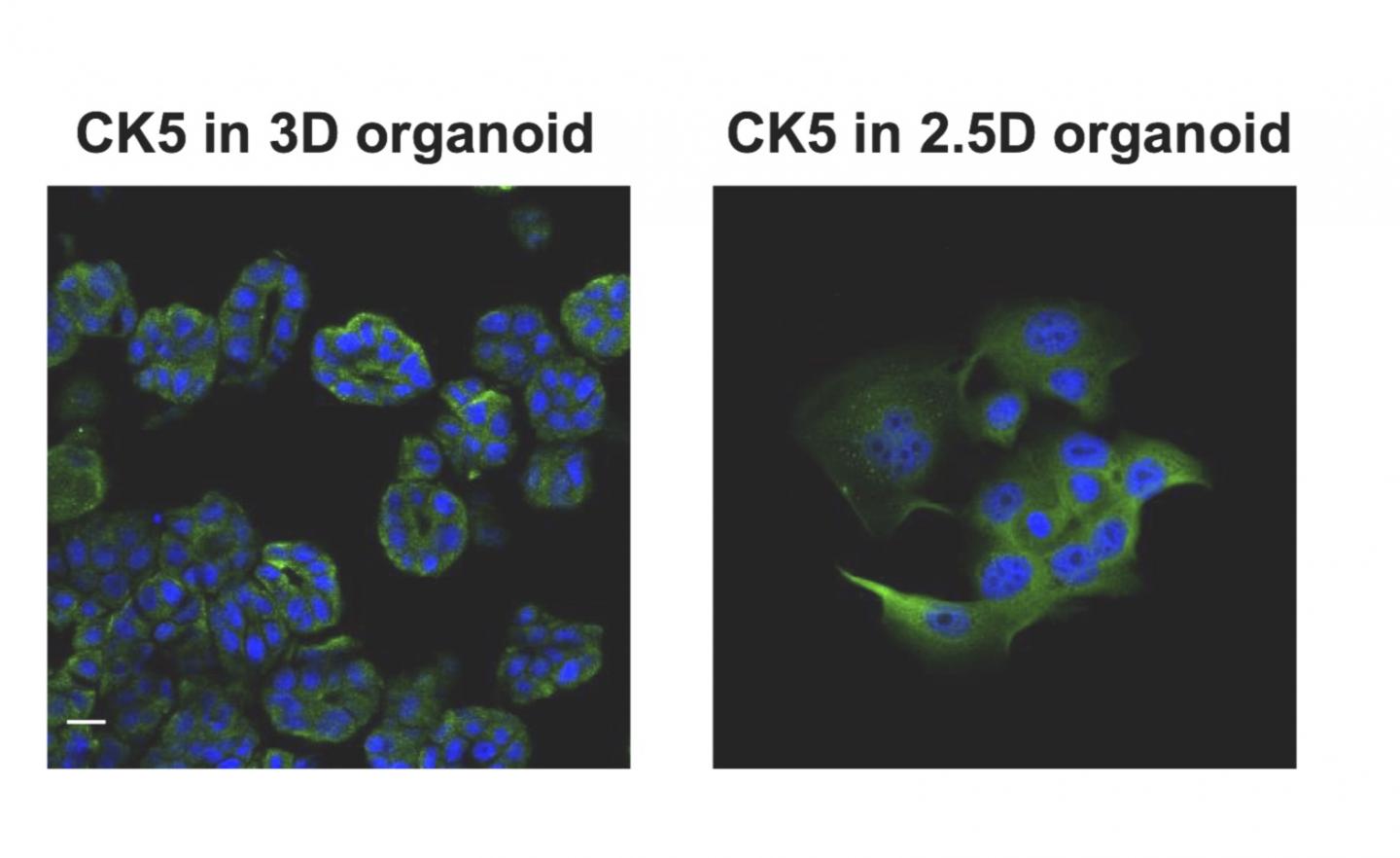
To study this new cell culture approach, the researchers focused on bladder cancer in dogs, a disease which occurs at a rate similar to humans. They captured diseased cells voided in the dogs’ urine and replicated them using a new process that generates bodies mimicing key characteristics of the original tumor cells closely enough that they can effectively be used to diagnose disease and identify possible treatments. The team created the organoids by culturing the captured diseased cells in a protein-rich medium.
“Interestingly, we were able to grow organoid cells using techniques just shy of the traditional, complete 3D bioprinting process – a sort of 2.5D process – while producing most of the 3D organoid features. This means that we could potentially produce cheaper biomaterials for testing and research without jeopardizing much for the accuracy.” Professor Usui said.
Once the team succeeded in creating organoids from the dogs’ diseased cells, they tested their response to three common anti-cancer drugs as well as several antibodies. They later applied a preservative to the study samples, essentially halting the treatment processes to analyze the results. They also reversed the process, generating 3D organoid cells using traditional bioprinting, then planted them into mice. The cells became tumors as anticipated, giving the team further evidence that 2.5D organoids may be an accurate and effective research medium.
“We are confident that our method will make a breakthrough in bladder cancer diagnosis and treatment in both animals and humans, as it efficiently reduces the culture time, handling, gel, and media supplement costs, and therefore it can be an important platform for the development of new bladder cancer therapy,” Usui said.
###
For more information about the Usui laboratory, please visit http://vet-pharmacol.
Original publication:
Establishment of 2.5D organoid culture model using 3D bladder cancer organoid culture
Amira Abugomaa, Mohamed Elbadawy, Megumi Yamanaka, Yuta Goto, Kimika Hayashi, Takashi Mori, Tsuyoshi Uchide, Daigo Azakami, Ryuji Fukushima, Toshinori Yoshida, Makoto Shibutani, Risako Yamashita, Mio Kobayashi,Hideyuki Yamawaki, Yuta
Shinohara, Masahiro Kaneda, Tatsuya Usui*, Kazuaki Sasaki.
Scientific Reports doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66229-w
http://www.
*: corresponding author
About Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT):
TUAT is a distinguished university in Japan dedicated to science and technology. TUAT focuses on agriculture and engineering that form the foundation of industry, and promotes education and research fields that incorporate them. Boasting a history of over 140 years since our founding in 1874, TUAT continues to boldly take on new challenges and steadily promote fields. With high ethics, TUAT fulfills social responsibility in the capacity of transmitting science and technology information towards the construction of a sustainable society where both human beings and nature can thrive in a symbiotic relationship. For more information, please visit http://www.
Contact:
Tatsuya Usui, DVM, PhD.
Senior Assistant Professor
Laboratory of Veterinary Pharmacology, Department of Veterinary Medicine, Faculty of Agriculture, TUAT, Japan
Media Contact
Yutaka Nibu
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.