The researchers have developed a novel connection which can help in the design of more efficient multi-agent AI systems.
Credit: SUTD
Game theory is known to be a useful tool in the study of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) Multi-Agent interactions.
One basic component of these ML and AI systems is the exploration-exploitation trade-off, a fundamental dilemma between taking a risk with new actions in the quest for more information about the environment (exploration) and repeatedly selecting actions that result in the current maximum reward or (exploitation).
However, the outcome of the exploration-exploitation process is often unpredictable in practice and the reasons behind its volatile performance have been a long-standing open question in the ML and AI communities.
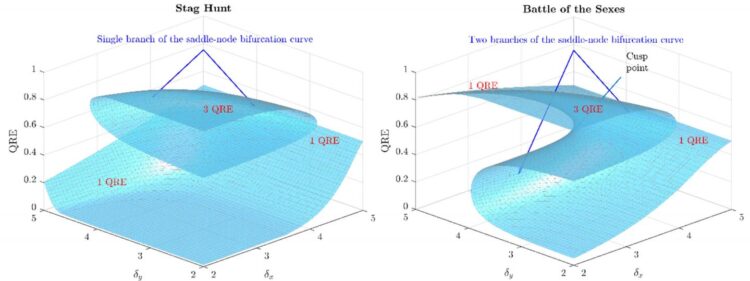
Dr Stefanos Leonardos and Assistant Professor Georgios Piliouras, researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD), applied analytical tools from the theory of dynamical systems in the study of multi-agent systems and established a deep connection between exploration-exploitation and Catastrophe Theory (Figures 1 and 2). The latter is a branch of mathematics that formally explains phase transitions in all kinds of natural systems ranging from the transition from water to ice and disease outbreaks to collapses of financial markets.
This newly established connection provides a tool to predict the consequences and improve the performance of exploration-exploitation techniques in the development of multi-agent AI systems, such as robotic space missions, healthcare management or automated financial investing algorithms.
Their work, titled ‘Exploration-Exploitation in Multi-Agent Learning: Catastrophe Theory Meets Game Theory’, was honored with the Best Paper Award at the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2021.
“In this work, we reasoned about the rich mathematical structure in multi-agent interactions and showed how this underlying geometry shapes the performance of AI systems. We believe our new findings will support the research community in achieving its ambitious goal to push beyond the current AI boundaries,” explained first author Dr Stefanos Leonardos from SUTD.
“We are deeply honored by this recognition and are excited to continue our investigation of phase transitions and their implications to AI systems,” added Assistant Professor Georgios Piliouras from SUTD.
###
Media Contact
Jessica Sasayiah
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/