Deeper understanding of the climate-water-energy nexus will significantly contribute towards planning and managing transnational power grids.
Credit: SUTD
A study on big droughts in the Greater Mekong region revealed findings that can help reduce the carbon footprint of power systems while providing insights into better designed and more sustainable power plants.
The study, titled ‘The Greater Mekong’s climate-water-energy nexus: how ENSO-triggered regional droughts affect power supply and CO2 emissions’, was published by researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and the University of California, Santa Barbara, in the journal Earth’s Future.
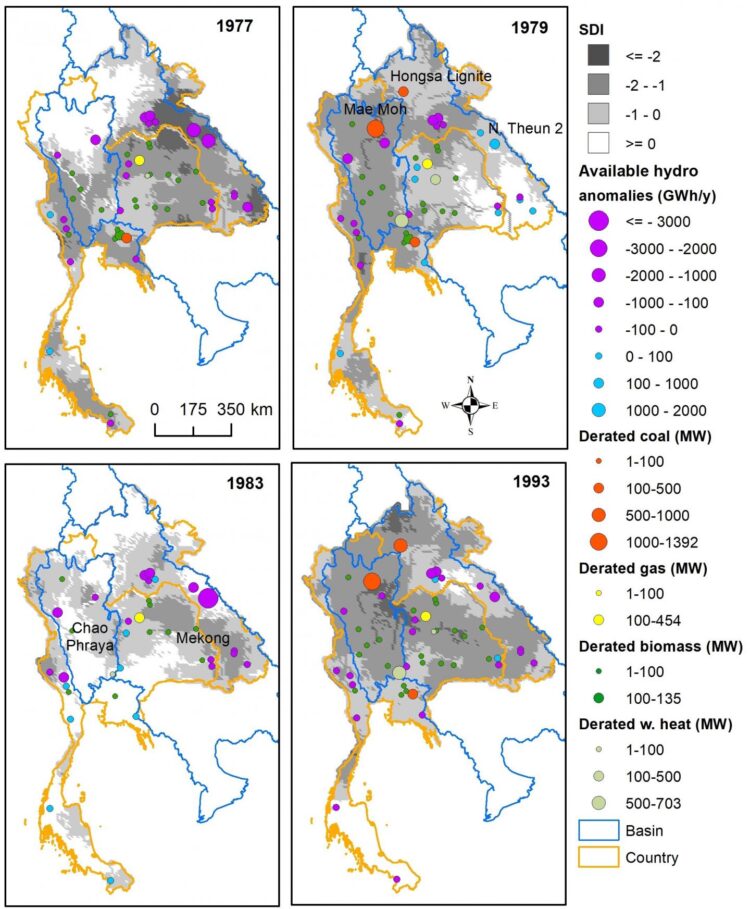
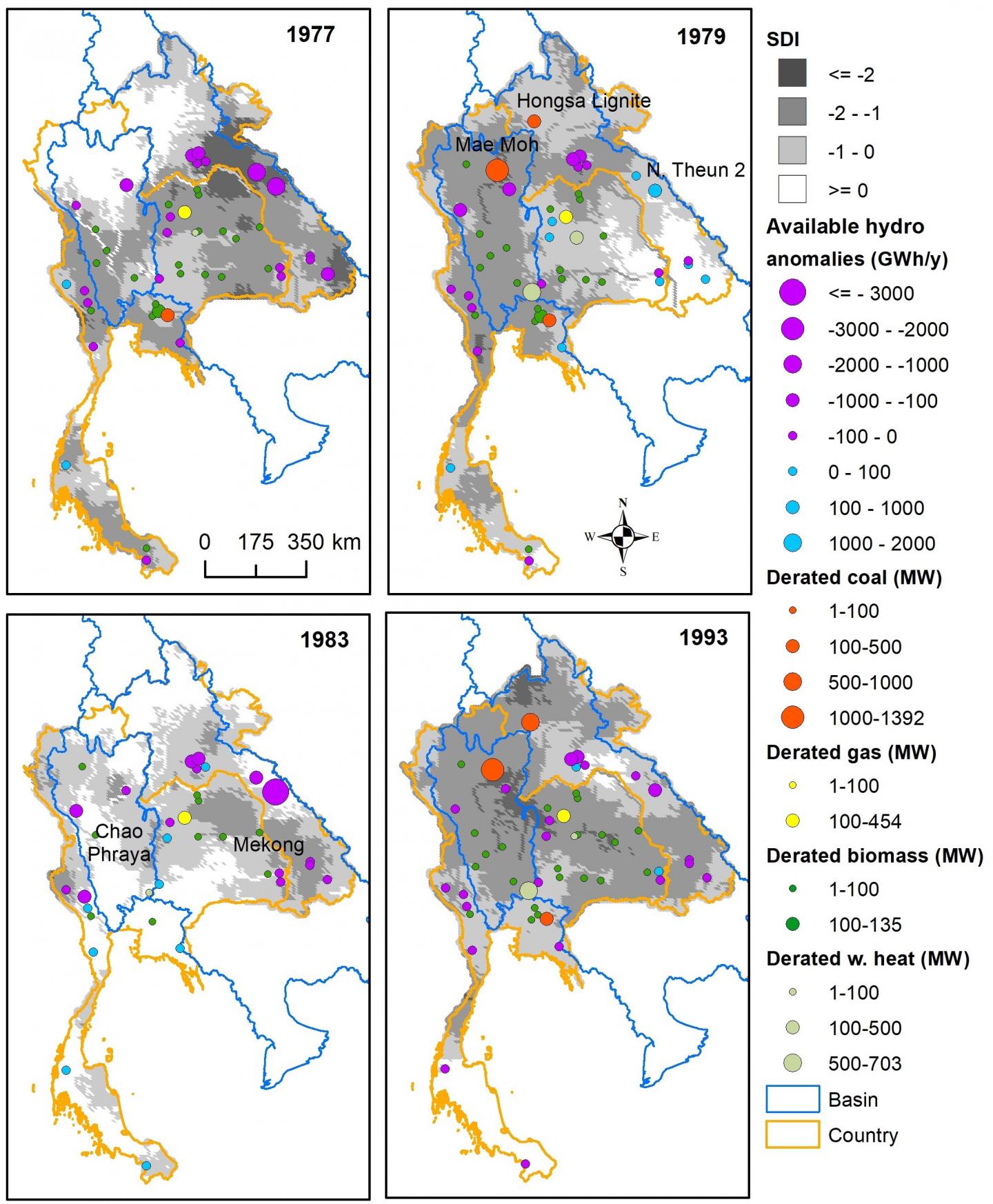
Known as an important means to support economic growth in Southeast Asia, the hydropower resources of the Mekong River Basin have been largely exploited by the riparian countries. The researchers found that during prolonged droughts hydropower production reduces drastically, forcing power systems to compensate with fossil fuels — gas and coal — thus increasing power production costs and carbon footprint. As such, the vulnerability of hydropower dams to inter-annual changes in water availability hinders their ability to keep to the promise of offering clean energy.
Based on the 2016 energy demand, the researchers estimated that prolonged droughts reduce hydropower production in the Thai-Laotian grid (refer to image) by about 4,000 GWh/year, increasing carbon dioxide emissions by 2.5 million metric tonnes, and increasing costs by US$120 million in one year.
At the same time, power supply was surprisingly found not to be at risk during droughts. This finding suggested that some big coal plants may have a capacity larger than necessary, thus contributing adversely to the environment.
The researchers also found that these phenomena — droughts and shifts in energy generation mix — are largely caused by El Nino events. This happens when trade winds weaken, the equatorial Pacific Ocean’s surface is warmer than usual and less moisture is delivered to Southeast Asia from the Pacific. The bad news is that anthropogenic climate change may exacerbate El Nino events: if that happens, we will face a drier summer monsoon, with less water available for power systems.
So, what can we do to make power supply more sustainable?
“The answer may lie in mathematical models,” explained principal investigator Associate Professor Stefano Galelli from SUTD.
“Our study builds on a new generation of high-resolution water-energy models that explain how each individual power plant reacts to external conditions, such as droughts or increased electricity demand. We can use these models to coordinate water-energy operations across countries, or to prepare contingency plans at the onset of a big drought,” he added.
###
Media Contact
Jessica Sasayiah
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.