Columbia engineers use a membrane-based technique and a closed-loop system to recover ammonia as a valuable fertilizer product while simultaneously removing it as a pollutant from waste streams
Credit: Ngai Yin Yip and Chanhee Boo/Columbia Engineering
New York, NY–May 6, 2019–Ammonia is a key component of fertilizer and vital in supporting plant growth and ultimately providing food for populations around the world. It is also a major pollutant that, after it is used in the food chain, enters municipal wastewater treatment plants where it is often not adequately removed. It is then released into the environment where it pollutes aquatic settings and damages ecosystems, triggering destructive algal blooms, dead zones, and fish kills.
Ammonia capture is now a critical challenge for the 21st century, especially as city populations are expected to increase dramatically, with a projected urban growth of 2.5 billion people by 2050. At the same time, providing improved sanitation to the 2.3 billion people who are currently unserved globally will entail the installation of new toilets, wastewater facilities, and sanitation infrastructure, putting even more stress on the environment.
To date, most ammonia capture is done through an extremely energy-intensive technique, the Haber-Bosch process, which is used by industry across the globe to produce fertilizer and accounts for 1-2% of the world’s annual energy consumption. A Columbia Engineering team, led by Ngai Yin Yip, assistant professor of earth and environmental engineering, reports today that they have recovered ammonia through a new method that uses a very low level of energy, approximately a fifth of the energy used by the Haber-Bosch process. In addition, because the technique recycles ammonia in a closed loop, the ammonia can be recaptured for reuse in fertilizer, household cleaners, and other industrial products. The findings are published today by ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
The management of nitrogen, an essential nutrient for life, has been recognized by the National Academy of Engineering as one of the Grand Challenges of the 21st century. Yip’s group, which focuses on advancing sustainable production of both energy and water, wanted to invent a better, more ecological way to produce nitrogen, of which ammonia is a bioavailable form.
“It was clear that we needed a paradigm shift to transition to a circular economy model, where nitrogen is recovered and recycled, instead of the current unsustainable linear approach of costly production, utilization, and then discarding pollutants to the environment,” Yip says.
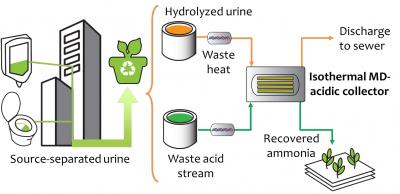
Yip’s team has expertise in membrane distillation, a technique that drives the permeation of volatile species, in this case, ammonia, from a feed stream to a collector stream, while the non-volatile species remain in the feed stream. The volatile species are driven across the membrane by a difference in vapor pressure, which is dependent on temperature and concentration. The researchers developed a technique, which they call “isothermal membrane distillation with acidic collector,” or IMD-AC, that uses low-temperature heat, and applied it to selectively separate and capture ammonia from the ammonia-rich waste stream of urine (simulated for this project).
“Because our process is driven by moderate temperatures as low as 20-60 degrees Celsius, the energy can be supplied by cheap or even free waste heat from, for instance, cooling tower water, bath water, or solar thermal collectors,” Yip says.
Next steps for the team include exploring ways to recover phosphorus, another key ingredient of fertilizer, sustainably and cheaply from urine.
“Now that we’ve demonstrated the sustainable recovery of nitrogen from urine,” Yip adds, “we think that the growing population and sanitation trends present ideal opportunities for the introduction of decentralized urine diversion facilities for nutrient recovery, without costly retrofits or overhauls of the existing system, shifting wastewater management to a more sustainable and efficient paradigm.”
###
About the Study
The study is titled “Novel Isothermal Membrane Distillation with Acidic Collector for Selective and Energy-Efficient Recovery of Ammonia from Urine.”
Authors are: Stephanie N. McCartney, Natalie Williams, Chanhee Boo, Xi Chen, and Ngai Yin Yip, (Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering, Columbia University; Yip is also a member of the Columbia Water Center).
The study was supported by the National Science Foundation INFEWS Award (#1903705).
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.
LINKS:
Paper: https:/
DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00643
http://engineering.
https:/
https:/
http://www.
Columbia Engineering
Columbia Engineering, based in New York City, is one of the top engineering schools in the U.S. and one of the oldest in the nation. Also known as The Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science, the School expands knowledge and advances technology through the pioneering research of its more than 220 faculty, while educating undergraduate and graduate students in a collaborative environment to become leaders informed by a firm foundation in engineering. The School’s faculty are at the center of the University’s cross-disciplinary research, contributing to the Data Science Institute, Earth Institute, Zuckerman Mind Brain Behavior Institute, Precision Medicine Initiative, and the Columbia Nano Initiative. Guided by its strategic vision, “Columbia Engineering for Humanity,” the School aims to translate ideas into innovations that foster a sustainable, healthy, secure, connected, and creative humanity.
Media Contact
Holly Evarts
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




