High-speed motor protein developed by gene fusion promotes growth and seed yield of Camelina sativa
Credit: Motoki Tominaga
In JST Strategic Basic Research Programs, a group of Zhongrui Duan (Researcher, Waseda University) and Motoki Tominaga (Associate professor, Waseda University) et al. succeeded in promoting plant growth and increasing seed yield by heterologous expression of protein from Arabidopsis (artificially modified high-speed motor protein(1) ) in Camelina sativa, which is expected as a useful plant for biodiesel.
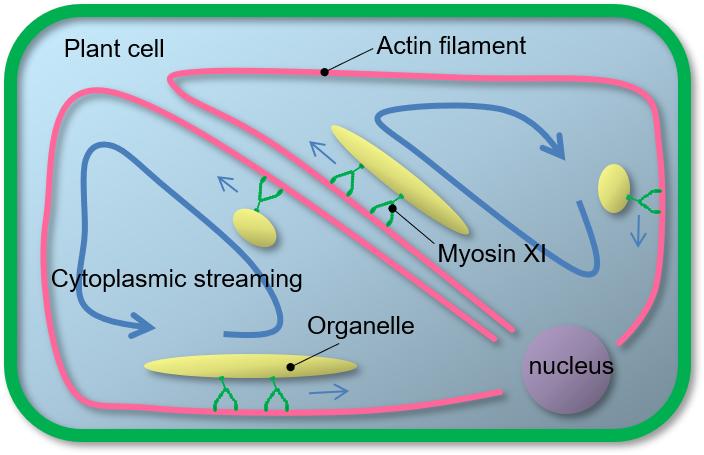
Cytoplasmic streaming is seen in any plant cells from algae to higher plants as a phenomenon of active cytoplasmic movement with organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. It is known that cytoplasmic streaming is generated by the sliding of motor protein myosin XI(2), which is binding to organelles, along the cytoskeleton constituting actin filaments. Previously, the research group has achieved the growth promotion and increasing size of the model plant Arabidopsis by the development of high-speed-type myosin. This technology has been expected to apply to other plant species than Arabidopsis.
In this study, the research group showed that the increase of seed yield and the growth promotion of stems and leaves in Camelina could be achieved by heterologous expression of high-speed-type myosin XI gene derived from Arabidopsis in Camelina.
Considering the increase of seed yield in Camelina enabled by the expression of high-speed-type myosin XI, it is expected to increase the productivity of biodiesel per area unit. In the future, it is aimed to increase the productivity and quality of camelina oil by co-expressing the genes related to fat synthesis and modification of fatty acid composition with high-speed-type myosin XI. Moreover, as the group showed that the promotion of plant growth by the high-speed-type myosin XI is also effective in other plant species than the model plant Arabidopsis, application development, such as the reduction of CO2 and biomass, is also expected by increasing the production of plant resources, such as corn, rice, sugar cane, and jatropha.
###
(1) Motor protein
The protein which converts chemical energy via ATP hydrolysis into physical movement. Myosin moving on actin filaments and kinesin or dynein moving on the microtubules is representative examples.
(2) Myosin
A type of motor protein. There are approximately 80 classes of myosin discovered in animals and plants. In plants, there are two classes of plant-specific myosin: myosin VIII (class 8) and myosin XI (class 11). Cytoplasmic streaming is known to occur by the movement of myosin XI.
Media Contact
Motoki Tominaga
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




