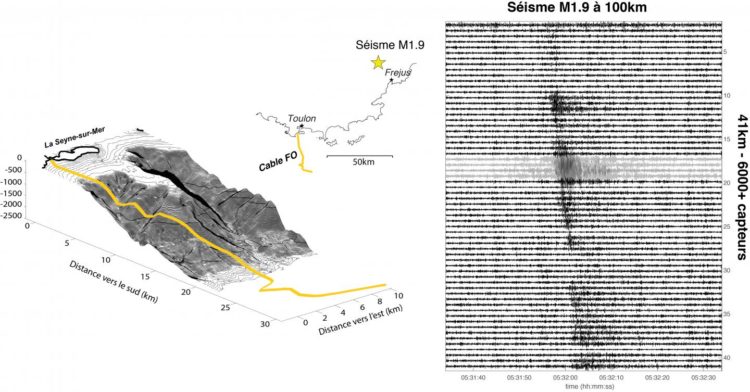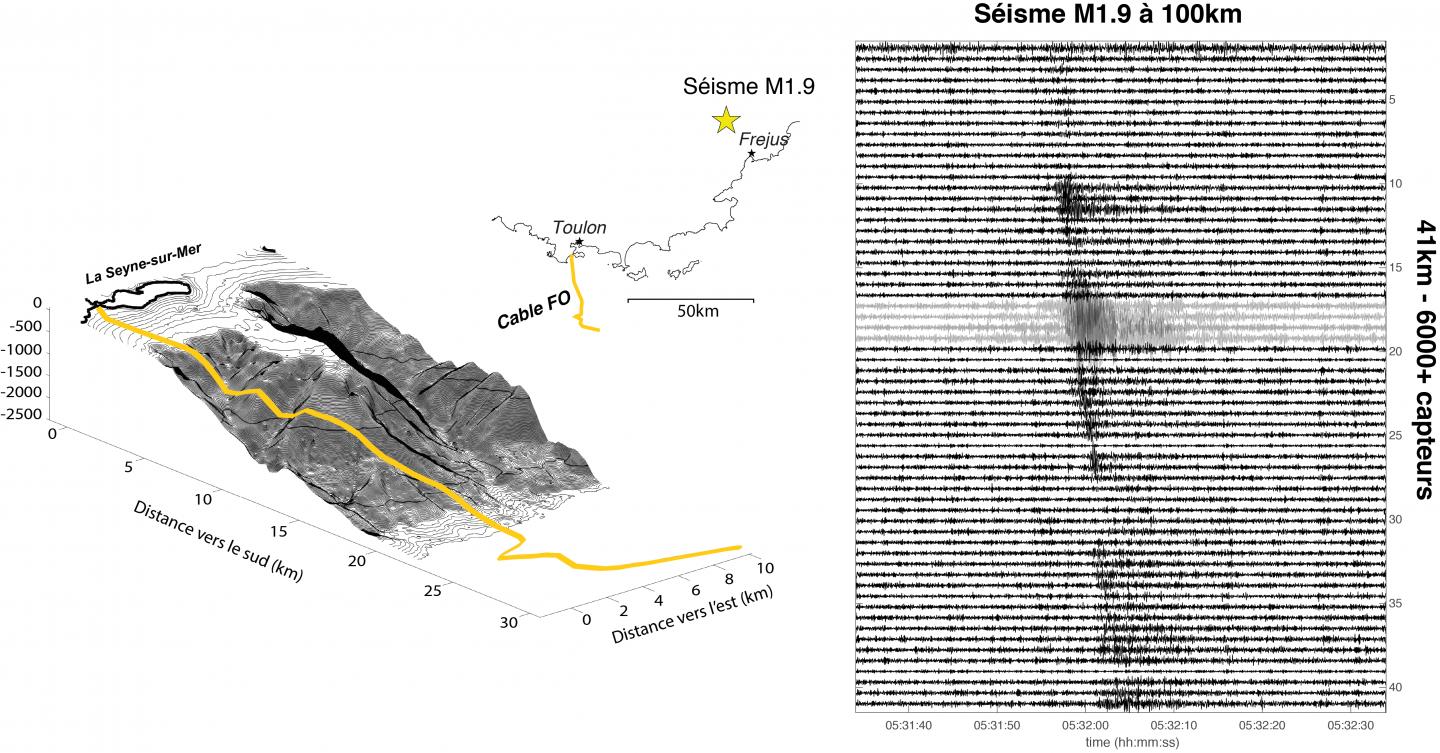
Seismic waves generated by a 1.9 magnitude earthquake located north of Fréjus (Var), recorded along the 41 km-long fibre optic cable deployed on the seafloor off Toulon.
Scientists have for the first time shown that it is possible to detect the propagation of seismic waves on the seafloor using submarine telecommunications cables. According to their observations, this existing infrastructure could be used to detect earthquakes, as well as swell and underwater noise. The results are published in the journal Nature Communications on December 18, 2019, by researchers from the CNRS, OCA, IRD and Université Côte d’Azur working together in the Géoazur laboratory, in collaboration with the company Fébus Optics and the Centre de Physique des Particules de Marseille (CNRS/Aix-Marseille Université) (1).
The ocean floor is criss-crossed by 1.2 million kilometres of telecommunications cables (three times the distance from the Earth to the Moon). Made up of optical fibres, they facilitate much of our communication by telephone, SMS and e-mail. And they could soon take on a new role, that of detecting acoustic and seismic waves.
Here, the scientists used a 41 km-long cable deployed off the coast of Toulon in southern France to retrieve data from the sensors of the MEUST-NUMerEnv (2) underwater observatory at a depth of 2500 m. The method they developed takes advantage of small impurities in the optical fibres, which send part of the light they carry back to the transmitter. By stretching or contracting the fibre, the passage of a seismic or acoustic wave alters the distance between these impurities, and thus the backscattered signal, by a tiny amount (3). Yet, they needed to prove that these differences were detectable since, in submarine cables, the optical fibres are surrounded by several insulating layers.
By injecting pulses of light into an optical fibre and analysing the backscattered signal, the team converted the 41 km of optical fibre into more than 6000 seismic sensors. A magnitude 1.9 earthquake that occurred during the trial was detected at each of the measuring points with a sensitivity close to that of a coastal seismic station, even though it was located over 100 km from the cable (Figure 1).
But that’s not all: the measuring points are also sensitive to waves that travel through the ocean, such as those produced by swell. The authors recorded the impact of waves on the seafloor near the coast, as well as their effect on the abyssal plain, where they generate ‘seismic background noise’. The sensors made it possible to observe for the first time how these very small vibrations, which constantly interact with the Earth’s interior, are produced, enabling geophysicists to probe its structure.
The researchers believe that a telecom cable, rather like a string of microphones, could in the same way detect underwater noise produced by ships and cetaceans.
Faced with the logistic and financial challenge of deploying instrumentation on the seafloor, telecom cables could provide a way of improving our understanding of this terra incognita covering two thirds of the Earth’s surface, and address a wide range of scientific and societal issues, such as earthquakes, coastal erosion, interaction between life, the oceans and the solid Earth, etc.
A certain number of cables currently in operation will be phased out by telecommunications operators over the coming years. Thanks to this research, they could soon take on a second life.
###
Notes
(1) These conclusions have been independently confirmed by another team, whose article is published in the same edition (Teleseisms and microseisms on an ocean-bottom distributed acoustic sensing array, E Williams, MR Fernandez-Ruiz, R Magalhaes, R Vanthillo, Z Zhan, M Gonzàlez-Herràez, H.F. Martins).
(2) The MEUST-NUMerEnv underwater observatory, managed by the CNRS, is made up of a neutrino telescope and sensors dedicated to Earth and environmental sciences.
(3) Around one nanometre (one billionth of a metre, which is about a thousandth of the diameter of a hair).
Media Contact
Veronique Etienne
[email protected]
33-144-965-137
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.