Credit: KIRSTY CHALLEN, B.SC., MBCHB, MRES, PH.D., LANCASHIRE TEACHING HOSPITALS, UNITED KINGDOM
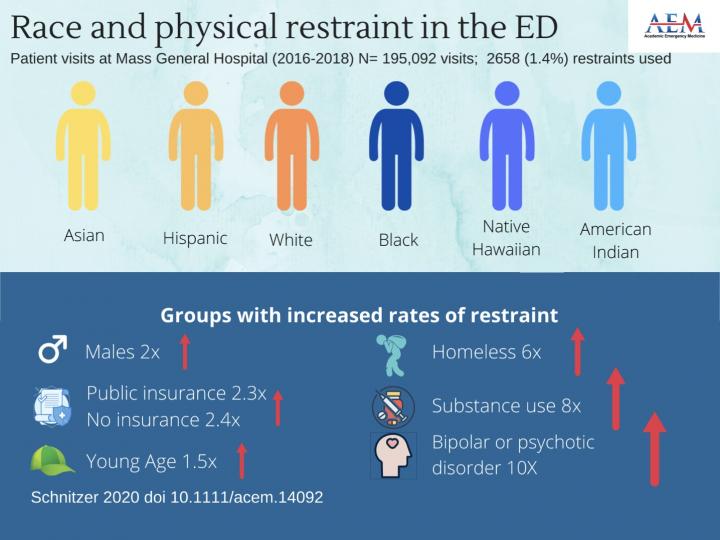
DES PLAINES, IL — A study published in the most recent issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), journal showed an increased risk of restraint use in Black patients compared with white patients in the emergency setting. The risk was not increased in other races or Hispanic/Latino ethnicity.
The lead author of the single-center study is Dr. Kristina Schnitzer MD, a psychiatrist in the Schizophrenia Clinical and Research Program at Massachusetts General Hospital and an instructor at Harvard Medical School. The findings of the study are discussed with two of the authors in episode 43 of AEM Early Access, a FOAMed podcast collaboration between the Academic Emergency Medicine Journal and Brown Emergency Medicine.
The increased risk of restraint was present in Black patients after controlling for other variables, including repeated visits, using a specialized regression technique. Concerning data also showed that 7-8 percent of all patients with psychosis or bipolar disorder, and six percent of all homeless patients were restrained. The study also identifies that there is an increased risk of patients to be restrained who are on public insurance or uninsured.
The study results warrant a careful examination of current practices and potential biases in utilization of restraint in emergency settings.
###
ABOUT ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE
Academic Emergency Medicine, the monthly journal of Society for Academic Emergency Medicine, features the best in peer-reviewed, cutting-edge original research relevant to the practice and investigation of emergency care. The above study is published open access and can be downloaded by following the DOI link: 10.1111/acem.14092. Journalists wishing to interview the authors may contact Stacey Roseen at [email protected].
ABOUT THE SOCIETY FOR ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE
SAEM is a 501(c)(3) not-for-profit organization dedicated to the improvement of care of the acutely ill and injured patient by leading the advancement of academic emergency medicine through education and research, advocacy, and professional development. To learn more, visit saem.org.
Media Contact
Stacey Roseen
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




