Discovery in laboratory mice suggests possible role for anti-cancer drugs in treating pulmonary fibrosis
Credit: Cedars-Sinai
LOS ANGELES (March 20, 2019) — A protein associated with cancer growth appears to drive the deadly lung disease known as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, according to new research from Cedars-Sinai. The discovery, made in laboratory mice and human tissue samples, may have implications for treating the disease using existing anti-cancer therapies that inhibit the protein PD-L1.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic, progressive lung condition of unknown cause that affects more than 100,000 people in the U.S. It consists of fibrosis–a buildup of fibrous scar tissue–that eventually robs the lungs of the ability to transport oxygen to the bloodstream. Although the disease progresses at variable rates, most patients die within five years after being diagnosed, according to the National Institutes of Health.
“At present, there is no known cure for this devastating condition,” said Paul Noble, MD, professor of Medicine and chair of the Department of Medicine, director of the Women’s Guild Lung Institute and the Vera and Paul Guerin Family Distinguished Chair in Pulmonary Medicine at Cedars-Sinai. “Current FDA- approved drugs only slow the fibrosis in certain individuals or treat some symptoms. This study opens a pathway for developing a treatment for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.”
Noble and Dianhua Jiang, MD, PhD, professor of Medicine at Cedars-Sinai, were co-corresponding authors of the research published in the journal JCI Insight.
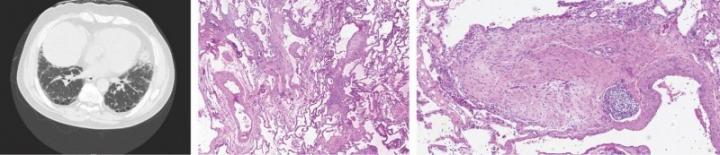
The study focused on cells known as fibroblasts, which produce proteins to help build the extracellular matrix–a meshwork of macromolecules that provides structure and biochemical support for cells in the body’s tissues. In idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, defective fibroblasts invade normal lung tissue and generate excessive deposits of fibrous (scar) tissue that progressively impairs lung function.
In examining lung tissue samples from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients, the study’s investigators found that the invasive fibroblasts secreted high levels of PD-L1, a protein found on normal cells that prevents immune cells from attacking them. By “masquerading” as normal cells, the invasive fibroblasts could evade destruction by the body’s immune system.
In experiments with laboraory mice, the team then demonstrated that introduction of normal fibroblasts did not result in developing pulmonary fibrosis and that the severity of disease could be reduced by using genetic and antibody techniques to inhibit PD-L1.
“Cumulatively, these results identify PD-L1 as a driver of fibroblast invasion in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and support PD-L1 as a potential therapeutic target for the condition,” Jiang said.
Based on the findings, the research team is designing a proposal for a Phase I clinical trial involving the use of a PD-L1-inhibiting drug against this disease. The trial would evaluate the safety of the drug in patients. If found to be safe, the drug could then be tested in later trials to gauge its effectiveness and further test its safety.
Currently, there are several PD-L1-inhibiting drugs approved by the FDA for treating cancer. Some cancer cells thwart attack by the immune system by secreting PD-L1 in a process similar to the one described in the new study. “Our proposal is to use one of these FDA-approved drugs in a clinical trial for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis,” Noble said.
###
Cedars-Sinai is an internationally recognized leader in lung fibrosis research. Noble leads a scientific team that was awarded $12 million last year by the National Institutes of Health to investigate idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic lung allograft dysfunction. The JCI Insight study, published in the March 21 issue, was partially funded by that grant.
Funding: Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases under award number R01 AI052201 and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute under award numbers R01 HL060539, P01 HL108793 and R01 HL122068 of the National Institutes of Health.
Media Contact
Jane Engle
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




