Potential for the development of tailor-made fermented milks to help reduce hypertension, according to the Journal of Dairy Science
Credit: Journal of Dairy Science
Philadelphia, March 19, 2021 – In recent years, fermented dairy foods have been gaining attention for their health benefits, and a new review published in the Journal of Dairy Science indicates these foods could help reduce conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure). A team of investigators from the Center for Food Research and Development in Sonora, Mexico, and the National Technological Institute of Mexico in Veracruz reports on numerous studies of fermented milks as antihypertensive treatments and in relation to gut microbiota modulation. They also examine the potential mechanistic pathways of gut modulation through antihypertensive fermented milks.
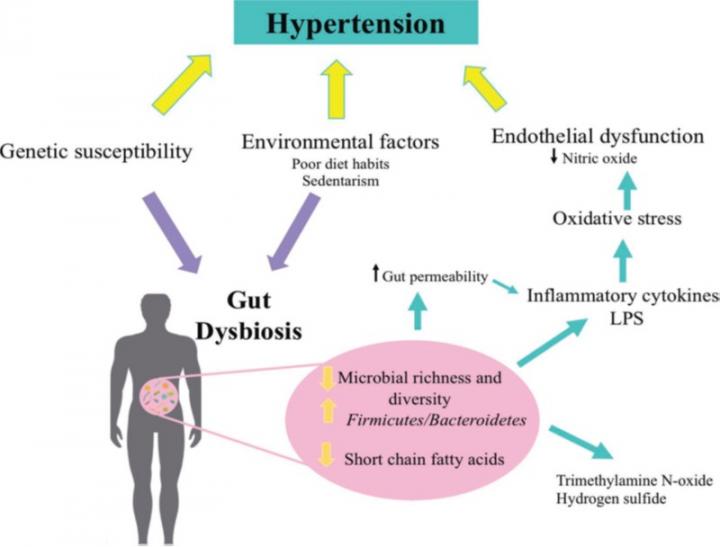
In addition to the impact of genetics and the environment, there is growing evidence that gut microbiota may also have an effect on the development of hypertension. In this sense, gut dysbiosis (a marked decrease in richness and diversity of the gut microbiota) has been linked to different metabolic diseases, including hypertension.
“Several studies have indicated that fermented milks may positively affect gut microbiota or provide antihypertensive effects,” explained investigator Belinda Vallejo-Córdoba, PhD, of the Center for Food Research and Development. “However, few studies have shown a link between the antihypertensive effect of fermented milks and induced microbial balance (or eubiosis). Remarkably, the antihypertensive effect has been attributed mainly to ACEI peptides, and few studies have attributed this effect to gut modulation.”
“New evidence suggests that antihypertensive fermented milks, including probiotics, bioactive peptides, and exopolysaccharides obtained from milk fermented with specific lactic acid bacteria, may modulate gut microbiota. Therefore, there is potential for the development of tailor-made fermented milks with gut microbiota modulation and blood pressure-lowering effects,” added Vallejo-Córdoba.
The authors say that future studies are needed to help understand the antihypertensive effects of fermented milks.
Hypertension is a risk factor for developing cardiovascular disease and is one of the leading causes of death globally. Gut microbiota have been found to influence intestinal development, barrier integrity and function, body metabolism, the immune system and the central nervous system. A microbial imbalance affects metabolism, which may lead to metabolic diseases like hypertension, obesity, and type 2 diabetes.
###
Media Contact
Eileen Leahy
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




