In cancer therapy, the effectiveness of an approach is determined by its ability to preserve the non-cancerous cells. Simply put, the higher the collateral damage, the greater are the side-effects of a therapy. An ideal situation is where only the cancer cells can be targeted and destroyed. In this regard, photothermal therapy–an approach in which cancer cells infused with gold nanoparticles can be heated up and destroyed using near-infrared (NIR) light that is strongly absorbed by the gold nanoparticles–has emerged as a promising strategy due to its minimally invasive nature.
“Because NIR light is able to penetrate biological tissues, it can illuminate the gold nanoparticles within the body and turn them into nano-sized cell heating agents,” explains Prof. Masayoshi Tanaka from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Japan, who researches nanomaterials for biomedical applications.
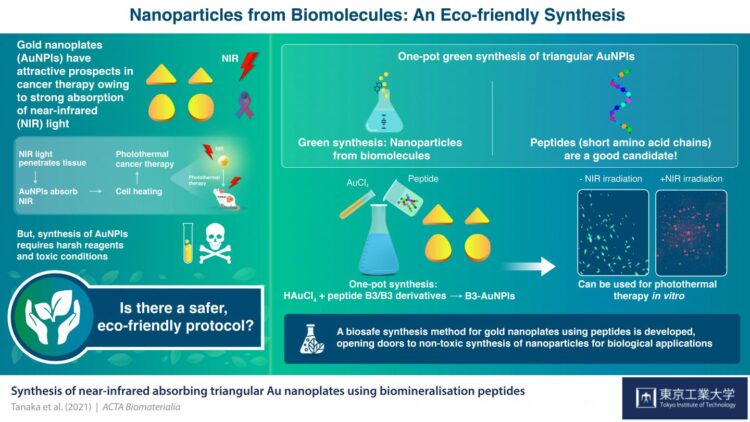
In particular, gold nanoplates (AuNPls) are extremely attractive as photothermal therapeutic agents owing to their efficient absorption of NIR light. However, synthesizing these nanoparticles requires harsh reagents and highly toxic conditions, making the process hazardous. In a new study, Prof. Tanaka and his collaborators from UK (University of Leeds) and Korea (Chung-Ang University) have now addressed this issue by developing a safer and more eco-friendly protocol for AuNPl synthesis, the results of which are published in ACTA Biomaterialia.
The team took the hint from a process called “biomineralization” that uses biomolecules to generate metal nanoparticles with tunable structures. “Peptides, or short chains of amino acids, are particularly attractive candidates for this purpose because of their relatively small size and stability. However, their use for producing Au nanoparticles with optimized structures for efficient NIR absorption has not yet been reported,” says Prof. Tanaka.
Motivated, the team began by identifying peptides suitable for the mineralization of AuNPls and, after picking out over 100 peptides, decided to examine the potential of a peptide named B3 for synthesizing AuNPls with controllable structure that can serve as photothermal conversion agents.
In a process called “one pot synthesis”, the team mixed a gold salt, HAuCl4, along with B3 peptide and its derivatives at various concentrations in a buffer solution (an aqueous solution resistant to changes in pH) at neutral pH and synthesized triangular and circular-shaped AuNPls with different levels of NIR absorption based on the peptide concentration.
The team then tested the effect of the AuNPls on cultured cancer cells under irradiated conditions and found them to exhibit the desired therapeutic effects. Furthermore, on characterizing the peptide using B3 derivatives, they found that an amino acid called histidine governed the structure of the AuNPls.
“These findings provide not only an easy and green synthetic method for AuNPls but also insight into the regulation of peptide-based nanoparticle synthesis,” comments Prof. Tanaka excitedly. “This could open doors to new techniques for non-toxic synthesis of nanoparticle therapeutic agents.”
Indeed, we might have struck gold with gold nanoparticles!
###
Media Contact
Kazuhide Hasegawa
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.