Researchers have discovered the surprising propulsion system that enables these regenerative cells to migrate through surrounding tissue to repair damage.
Credit: Hong-pyo Lee
Our bodies often dispatch stem cells to mend or replace biological damage, but how these repair agents make their way through dense tissue to arrive at the scene had been a mystery. “How stem cells squeeze through tissue openings a hundred to a thousand times smaller than themselves had been a perplexing question,” says Ovijit Chaudhuri, professor of mechanical engineering.
In an article published in the Jan. 8 edition of Science Advances, Chaudhuri and colleagues reveal that stem cells use their nucleus – a large, stiff organelle within the cell – as a means of propulsion.
Their discovery was surprising because scientists had thought cells would have particular difficulty forcing this big, stiff lump through tiny pores in surrounding tissue. Instead, they found that bone-marrow derived stem cells use the physical force generated by the nucleus to help bore through biological obstacles to reach fractures and help initiate healing. “Our finding presents a completely new understanding of how cells utilize the nucleus to generate mechanical force,” says Hong-Pyo Lee, the study’s first author, who recently graduated as a PhD student in mechanical engineering.
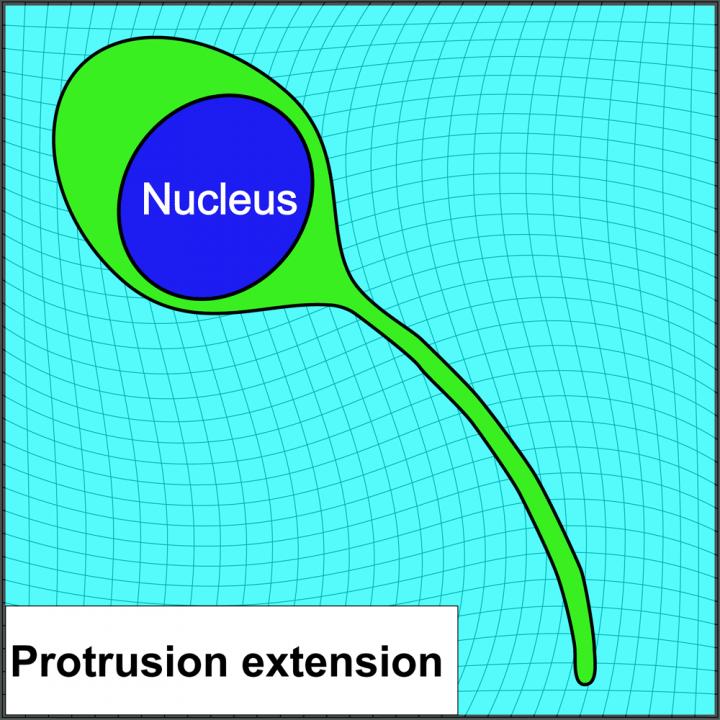
To arrive at this finding, the researchers extracted stem cells from bone marrow and used hydrogels to mimic the tissues that compose their biological environments. The researchers found that stem cells propel their nucleus into a needle-like protrusion that penetrates the physical barriers inside the body. The nucleus moves into the protrusion and, through a complex biochemical mechanism, inflates the protrusion like a balloon, creating an opening in the tissue wide enough for the entire stem cell to migrate through. The piston-like behavior of the nucleus, Chaudhuri says, is reminiscent of the action of a mechanical piston within the internal combustion engine of a car.
Their insight could help guide the design of biomaterial implants that would use stem cells for regenerative medicine. Chaudhuri notes that other stem cells, immune cells and cancer cells also migrate through surrounding tissue, suggesting fruitful areas for future research into whether these cells use the same propulsion system, knowledge that might be turned to therapeutic advantage.
“This is a beautiful example of how the principles of mechanical engineering can help us understand cellular behavior that affects health,” he says.
###
Ovijit Chaudhuri is an associate professor of mechanical engineering, member of Stanford Bio-X and faculty fellow of Stanford ChEM-H. Hong-Pyo Lee is co-founder of MEDIC Life Sciences. Other authors include Julie Chang and Kolade Adebowale of Stanford University, and Professor Vivek Shenoy and Dr. Farid Alisafaei of the University of Pennsylvania.
The work was funded by a CAREER award from the National Science Foundation to Chaudhuri.
Media Contact
Tom Abate
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




