Scientists have for the first time obtained stem cells from livestock that grow under chemically defined conditions, paving the way for manufacturing cell cultured meat and breeding enhanced livestock.
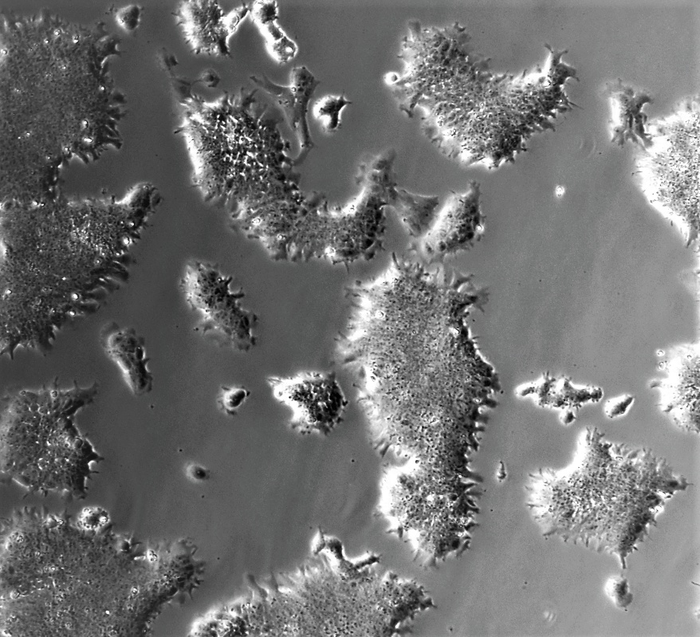
Credit: University of Nottingham, Professor Ramiro Alberio
Scientists have for the first time obtained stem cells from livestock that grow under chemically defined conditions, paving the way for manufacturing cell cultured meat and breeding enhanced livestock.
Researchers from the University of Nottingham’s School of Biosciences, together with colleagues at the Universities of Cambridge, Exeter Tokyo and Meiji (Japan) have developed stem cell lines from pigs, sheep and cattle embryos grown without the need for serum, feeder cells or antibiotics. The research “Pluripotent stem cells related to embryonic disc exhibit common self-renewal requirements in diverse livestock species” has been published today in the journal Development and was funded by BBSRC, EU (ERC), MRC and Wellcome Trust.
The chemically defined conditions are growth medium suitable for the in vitro cell culture of animal cells in which all of the chemical components are known. Standard cell culture media commonly consist of a basal medium supplemented with animal serum (such as fetal bovine serum, FBS) as a source of nutrients and other ill-defined factors.
The technical disadvantages to using serum include its undefined nature, batch-to-batch variability in composition, and the risk of contamination so this new chemically defined approach provides greater consistency and safety, making it an ideal solution for manufacturing new lab grown food products.
Professor Ramiro Alberio led the research and explains: “The ability to derive and maintain livestock stem cells under chemically defined conditions paves the way for the development of novel food products, such as cultured meat . The cell lines we developed are a step change from previous models as they have the unique ability to permanently grow to make muscle and fat.”
These novel cell lines can differentiate into multiple cell types, they can be genetically manipulated using Crispr/Cas9 gene editing tool and can be used as donors for nuclear transfer. This technology offers new opportunities for expanding research into gene editing animals to improve their productivity, and adaptation to to climate change and modifications of diets to reduce the environmental impact of livestock production.
Professor Alberio adds: “Gene editing in this way makes modifications that could happen naturally over a long time but in a selective a rapid manner to customize specific traits. This can accelerate the pace of genetic selection of livestock and cultured meat to improve productivity and creation of healthier foods. With a growing population to feed in a changing climate finding reliable and sustainable food is vital. This research offers potential solutions that the food industry could use at scale.”
Professor Austin Smith, Director of the University of Exeter’s Living Systems Institute, one of the world’s leading experts in stem cell research said: “It is very exciting that starting from a fundamental question about early development in different animals we have discovered a technique that may revolutionise future production of meat”.
Journal
Development
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Pluripotent stem cells related to embryonic disc exhibit common self-renewal requirements in diverse livestock species
Article Publication Date
7-Dec-2021




