Credit: ESO
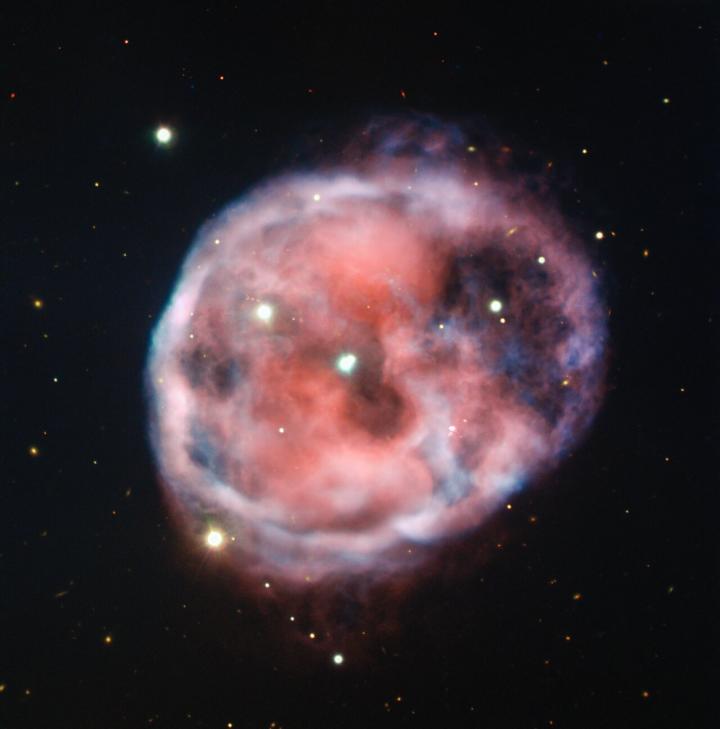
This ethereal remnant of a long dead star, nestled in the belly of The Whale, bears an uneasy resemblance to a skull floating through space. Captured in astounding detail by ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), the eerie Skull Nebula is showcased in this new image in beautiful bloodshot colours. This planetary nebula is the first known to be associated with a pair of closely bound stars orbited by a third outer star.
Also known as NGC 246 , the Skull Nebula lies about 1600 light-years away from Earth in the southern constellation of Cetus (The Whale). It formed when a Sun-like star expelled its outer layers in its old age, leaving behind its naked core — a white dwarf — one of two stars that can be seen at the very centre of NGC 246.
Even though this nebula has been known for centuries, only in 2014 did astronomers discover, using ESO’s VLT, that the white dwarf and its companion are concealing a third star situated at the heart of the Skull Nebula. This star, which is not visible in this image, is a dim red dwarf that sits close to the white dwarf at about 500 times the distance between Earth and the Sun. The red and white dwarf stars orbit each other as a pair, and the outer star orbits the two dwarfs at a distance of around 1900 times the Earth-Sun separation. Collectively, these three stars establish NGC 246 as the first known planetary nebula with a hierarchical triple stellar system at its centre.
Taken by the FORS 2 instrument on ESO’s VLT in the Chilean Atacama Desert, this new image of the Skull Nebula intentionally captures light emitted in some narrow ranges of wavelengths — those associated with hydrogen and oxygen gas. Observations of light emitted by particular elements help reveal a wealth of information about an object’s chemical and structural compositions. This new image of the Skull Nebula highlights where NGC 246 is rich or poor in hydrogen (shown in red) and oxygen (depicted in light blue).
This image was selected as part of the ESO Cosmic Gems programme, an outreach initiative to produce images of interesting, intriguing or visually attractive objects using ESO telescopes, for the purposes of education and public outreach. The programme makes use of telescope time that cannot be used for science observations. All data collected may also be suitable for scientific purposes, and are made available to astronomers through ESO’s science archive.
More information
ESO is the foremost intergovernmental astronomy organisation in Europe and the world’s most productive ground-based astronomical observatory by far. It has 16 Member States: Austria, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom, along with the host state of Chile and with Australia as a Strategic Partner. ESO carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities enabling astronomers to make important scientific discoveries. ESO also plays a leading role in promoting and organising cooperation in astronomical research. ESO operates three unique world-class observing sites in Chile: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope and its world-leading Very Large Telescope Interferometer as well as two survey telescopes, VISTA working in the infrared and the visible-light VLT Survey Telescope. Also at Paranal ESO will host and operate the Cherenkov Telescope Array South, the world’s largest and most sensitive gamma-ray observatory. ESO is also a major partner in two facilities on Chajnantor, APEX and ALMA, the largest astronomical project in existence. And on Cerro Armazones, close to Paranal, ESO is building the 39-metre Extremely Large Telescope, the ELT, which will become “the world’s biggest eye on the sky”.
###
Links
* ESO Cosmic Gems programme – https:/
* Photos of the VLT – http://www.
* For scientists: got a story? Pitch your research – http://eso.
Contacts
Bárbara Ferreira
ESO Public Information Officer
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6670
Email: [email protected]
Media Contact
Bárbara Ferreira
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




