Scientists studied fluid mechanics to simulate and build a squidlike robot that’s fast, quiet and hard to see.
Credit: Qiang Zhu
WASHINGTON, D.C., October 1, 2019 — Inspired by the unique and efficient swimming strategy of cephalopods, scientists developed an aquatic robot that mimics their form of propulsion.
These high-speed, squidlike robots are made of smart materials, which make them hard to detect — an advantage that has potential military reconnaissance and scientific applications — while maintaining a low environmental footprint.
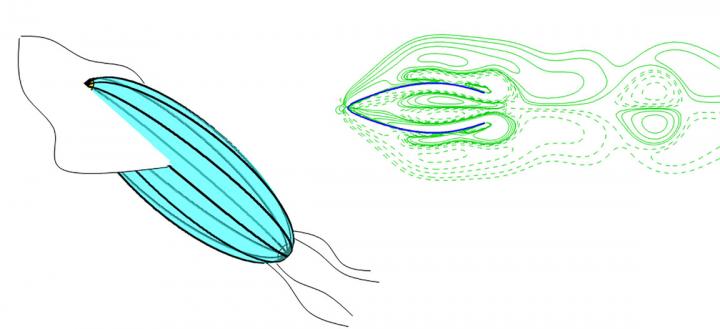
Physicists Xiaobo Bi and Qiang Zhu used numerical simulations to illustrate the physical mechanisms and fluid mechanics of a squid’s swimming method, which uses intermittent bursts through pulsed jet propulsion. By using this form of locomotion, the new device can achieve impressive speeds, just like its animal inspiration. Bi and Zhu discuss their work in this week’s Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing.
When swimming, these squidlike machines suck water into a pressure chamber and then eject it. The soft-bodied device could be used as a platform for environmental monitoring by simultaneously using this feature to test water samples as it swims.
“In addition to the 2D and 3D numerical simulations presented in this article, we are working with an interdisciplinary team to build a prototype of the mechanical device, to perform both straight-line swimming and maneuvers,” Zhu said. “This project will combine fluid dynamics, control, smart materials and robotic design.”
The device could be used as either a stand-alone swimmer or as a propeller of an underwater vehicle.
The researchers have not yet been able to maintain speeds that can last for more than a few cycles due to turbulence and instabilities, but they are working on ways to overcome this. Zhu hopes this research will provide a starting point for more sophisticated modeling and experimental studies to develop robots like their creation.
###
The article, “Fluid-structure investigation of a squid-inspired swimmer,” is authored by Xiaobo Bi and Qiang Zhu. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on Oct. 1, 2019 (DOI: 10.1063/1.5119243). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex or multiphase fluids. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




