Credit: ZHANG Qi et al.
The team led by Professor DU Jiangfeng and Professor WANG Ya from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Key Laboratory of Microscale Magnetic Resonance of the University of Science and Technology of China put forward an innovative spin-to-charge conversion method to achieve high-fidelity readout of qubits, stepping closer towards fault-tolerant quantum computing.
Quantum supremacy over classical computers has been fully exhibited in some specific problems, yet the next milestone, fault-tolerant quantum computing, still requires the accumulated logic gate error and the spin readout fidelity to exceed the fault-tolerant threshold. DU’s team has resolved the first requirement in the nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center system [Nat. Commun. 6, 8748 (2015)] previously and this work targeted at high-fidelity readout of qubits.
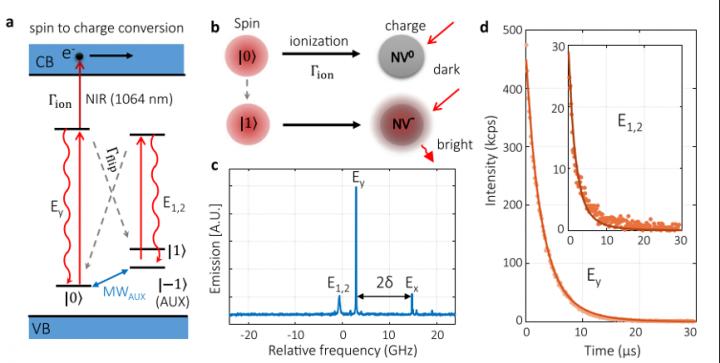
Qubit state, such as spin state, is fragile: a common readout approach may cause the flip between the 0 and 1 states for even a few photons resulting in a reading error. The readout fidelity of traditional resonance fluorescence method is strictly limited by such property. Since the spin state is difficult to measure, researchers blazed a trail to replace it with an easy-to-readout and measurable property: the charge state.
They first compared the optical readout lifetime of the charge state and spin state, finding that charge state is more stable than the spin state by five orders of magnitude. Experiment results showed that the average non-demolition charge readout fidelity reached 99.96%.
Then the team adopted near-infrared (NIR) light (1064 nm) to induce the ionization of the excited spin state, transforming the spin state 0 and 1 to the “electrically neutral” and “negatively charged” charge states respectively. This process converted the spin readout to the charge readout.
The results indicated that the error of traditional resonance fluorescence method reached 20.1%, while the error of this new method can be suppressed to 4.6%.
The article was published in Nature Communications.
This new method is compatible with tradition methods, provisioning a spin readout fidelity exceeding the fault-tolerant threshold in real applications. Thanks to the less damage of NIR light to biological tissues and other samples, this method will also effectively improve the detection efficiency of quantum sensors.
###
Media Contact
Jane FAN Qiong
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




