Credit: Marine Life Science & Technology
Announcing a new publication for Marine Life Science & Technology journal. In this research article the authors Hungchia Huang, Jinpeng Yang, Shixiang Huang, Bowei Gu, Ying Wang, Lei Wang and Nianzhi Jiao from Xiamen University, Xiamen, China and Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China consider the spatial distribution of planktonic ciliates in the western Pacific Ocea: along a transect from Shenzhen (China) to Pohnpei (Micronesia).
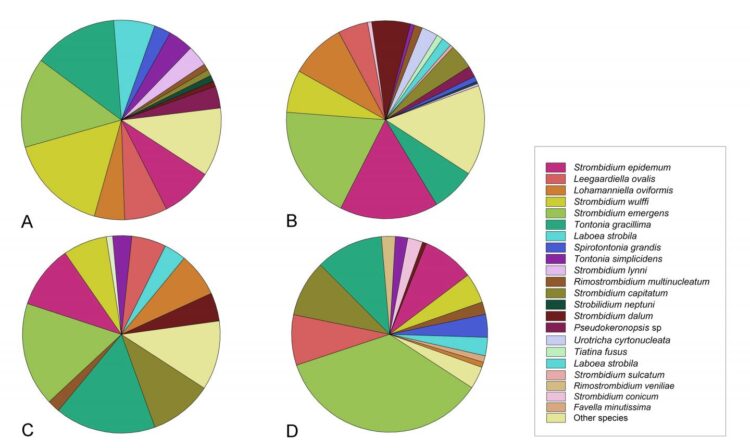
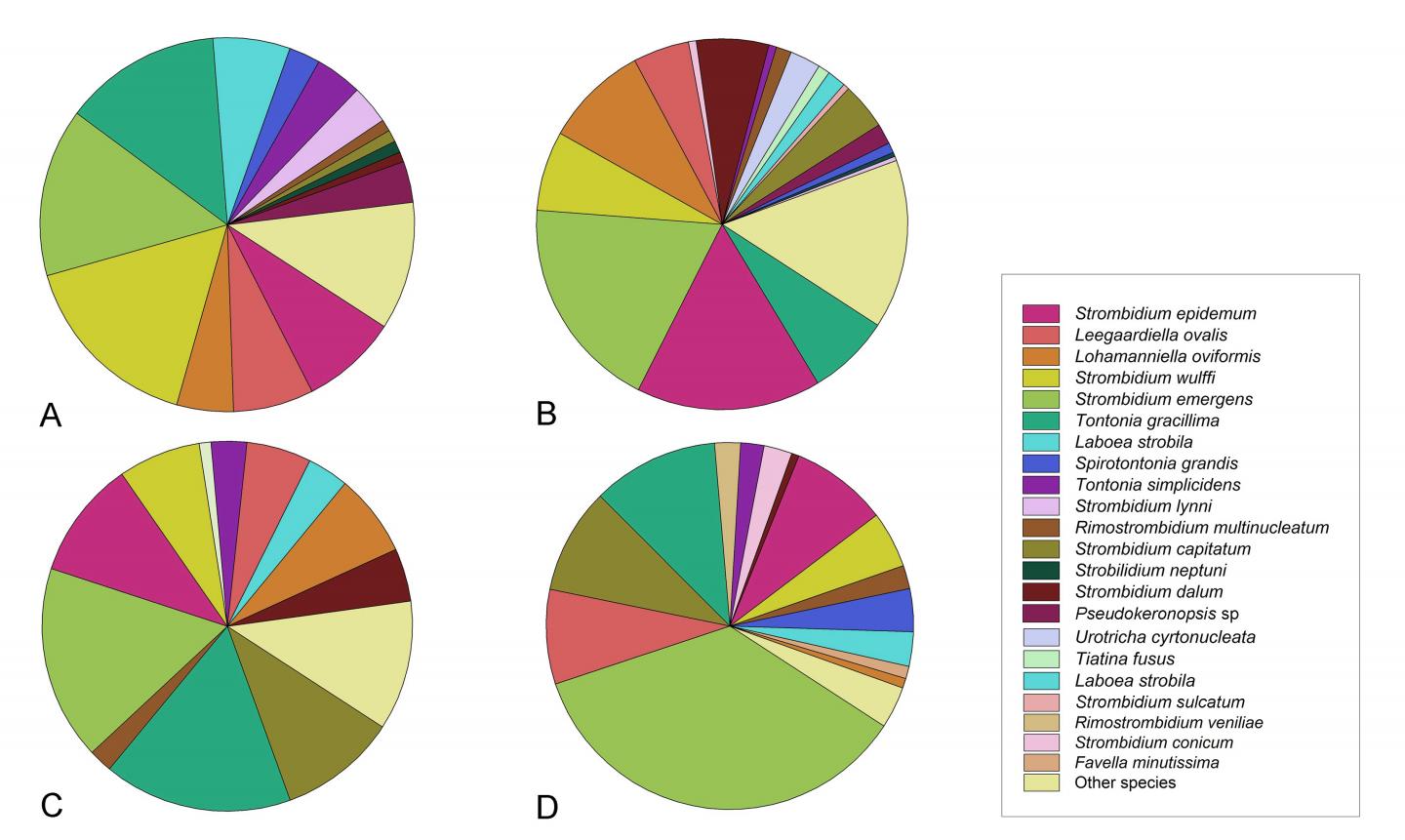
Planktonic ciliates have been recognized as major consumers of nano- and picoplankton in pelagic ecosystems, playing pivotal roles in the transfer of matter and energy in the microbial loop. However, due to the difficulties in identification, the species composition of ciliate assemblages, especially for the small, fragile, and naked species that usually dominate the ciliate communities in the oceanic waters, remains largely unknown.
The authors sampled 22 stations along the transect from Shenzhen (China) to Pohnpei (Micronesia) for the enumeration of picoplankton and nanoflagellates. In addition, pigment analysis of major phytoplankton groups along with the measurements of environmental variables including temperature, salinity, and nutrients were also carried out. Ciliates were identified at species level using quantitative protargol stain to reveal the species composition and their distribution patterns from offshore to open ocean. Ciliate abundance was positively correlated with phosphate, silicate, and pico-sized pigmented eukaryotes (PPEs), whereas the biomass was closely related with PPEs, heterotrophic nanoflagellates, and chlorophytes. The ciliate communities were separated into four groups showing a nearshore to open ocean trend.
The authors identified the combination of silicate and pigmented nanoflagellates as the major factor driving the ciliate community composition. This close relationship between silicate and ciliate abundance and community structure needs further validation based on more data collected from oceanic waters. The study demonstrates the necessity of using techniques that can reveal the community composition at higher taxonomic resolutions in future studies on ciliates.
###
Article reference: Hungchia Huang, Jinpeng Yang, Shixiang Huang, Bowei Gu, Ying Wang, Lei Wang, Nianzhi Jiao, Spatial distribution of planktonic ciliates in the western Pacific Ocean: along the transect from Shenzhen (China) to Pohnpei (Micronesia), Marine Life Science & Technology, 2020, ISSN 2662-1746, https:/
Keywords: Community structure, Distribution pattern, Diversity, Nanoflagellates, Quantitative protargol stain
Marine Life Science & Technology (MLST) provides a platform that introduces new discoveries and theories associated with marine organisms, bioresources, and biotechnology. The journal is intended for marine scientists, biological oceanographers, conservation biologists, marine technologists, policy makers and legislators. Accordingly, we publish original research papers across a broad range of marine life sciences and technologies with an emphasis on synergistic interactions of multiple disciplines. Both theoretical and practical papers are welcome, including laboratory and field experimental studies relevant to marine life science and technology. Focused reviews, viewpoints, comments, and short communications are also accepted. As the journal’s aim is to foster multidisciplinary approaches to marine sciences, authors are encouraged to emphasise the relevance of their work in relation across the journals key-disciplines.
For more information, please visit https:/
Editorial Board: https:/
MLST is available on SpringerLink (https:/
Submissions to MLST may be made using ScholarOne ManuscriptsTM (https:/
Abstracted and indexed in:
Astrophysics Data System (ADS)
CNKI
Dimensions
EBSCO Discovery Service
Google Scholar
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China
Meta
Naver
OCLC WorldCat Discovery Service
ProQuest-ExLibris Primo
ProQuest-ExLibris Summon
TD Net Discovery Service
ISSN 2662-1746
Media Contact
Morgan Lyons
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.