A paper was published by Kazan Federal University in the Journal of Structural Biology
Credit: Kazan Federal University
Project leader, Head of Structural Biology Lab Konstantin Usachev explains, “One of the main factors favoring a microorganism’s survival in extreme conditions is preserving ribosomes – a macromolecular complex comprising RNA and proteins. For this purpose, a cell synthesizes special proteins which may stop translating ribosomes until the stress is over. One of such proteins is hibernation promoting factor (HPF) which transfers ribosomes to the ‘hibernation state’.”
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most dangerous bacteria for humans, a pathogen causing many nosocomial infections. The danger is both in the staph’s virulence and antibiotic resistance. There are currently no specific anti-staphylococcus antibiotics. That’s why it’s so important to seek new targets for antibiotic therapy in the bacteria.
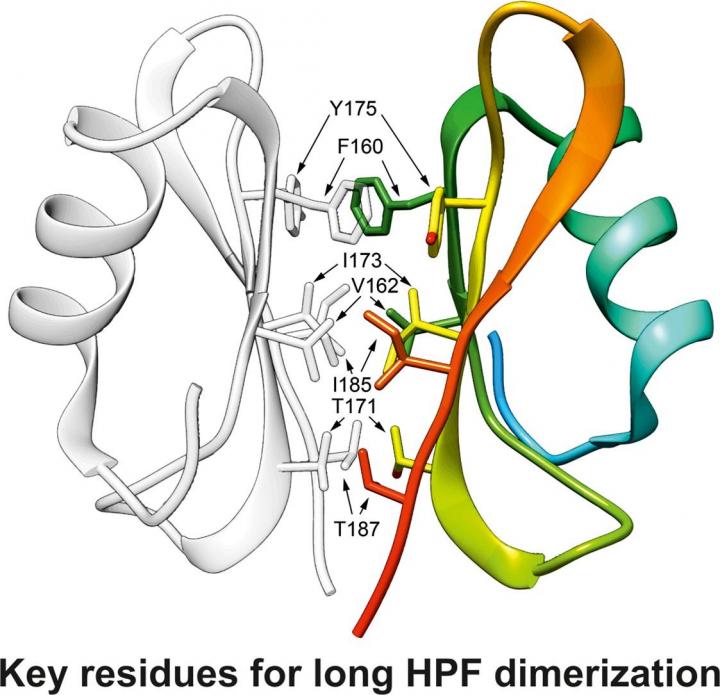
“Using high-resolution (1,6 Å) X-ray structure analysis, we solved the structure of the domain of HPF from Staphylococcus aureus, which regulates the dimerization of ribosomes and keeps in their ‘hibernation state’. Based on the obtained information, we found the key amino acid residues which provide for the functioning of the protein and used genetic engineering to produce mutated forms of this protein by single amino acid residues substitutions. After that, the mutated forms were analyzed for their capabilities of ribosome hibernation, and we found five residues essential for the functioning of the protein. Our results open the way to exploring new compounds that could bond with this protein areas and decrease the vitality of Staphylococcus aureus under stress,” adds Dr. Usachev.
This was the first protein structure solved by X-ray analysis implemented with the new XtaLab Synergy S diffractometer; it was installed at the Structural Biology Lab this past May.
“Our new diffractometer has a sensitive detector, which allows analyzing the structure of large biomolecules in a monocrystal form, such as proteins and nucleic acids,” concludes Dr. Usachev.
###
The Structural Biology Lab currently cooperates with the Chemoinformatics and Molecular Modelling Lab in searching the databases for new compounds which can bind with the Staph stress proteins.
Media Contact
Yury Nurmeev
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




